AN2739 I
2
S general description
5/26
1 I
2
S general description
1.1 I
2
S protocol
I
2
S (IC-to-IC sound) is an audio data transfer standard using a three-line bus for serial and
synchronous data transmission.
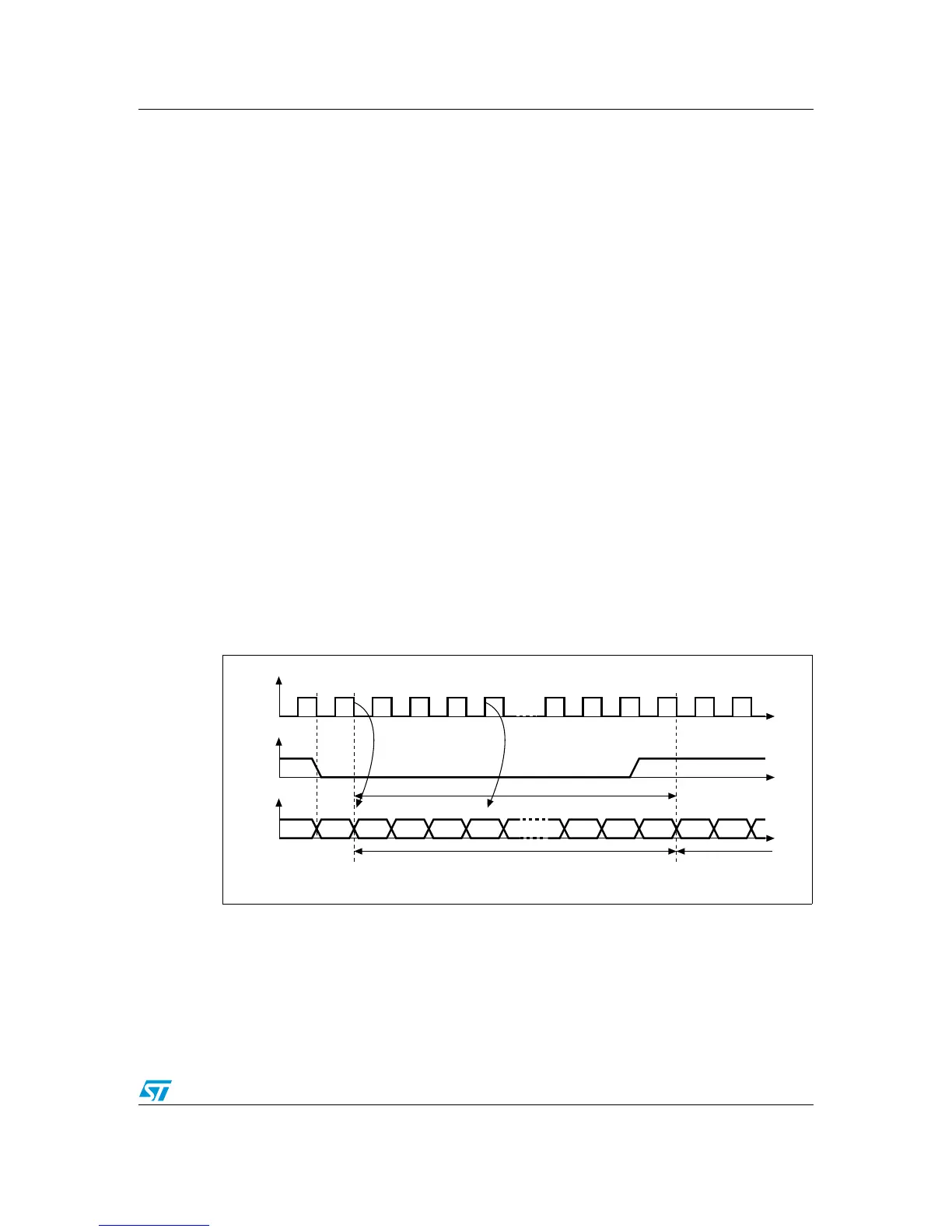
Data are transmitted on the SD line (Serial Data) in Little Endian format (MSB first). Data
length is not limited (usually 16/20/24/32/64 bits). Data are synchronized by the rising or
falling edge of SCK (Serial Clock) for the transmitter, and by the falling edge of SCK for the
receiver. Refer to Figure 1.
Data represent stereo digital sound, so each sample contains two words, the right-channel
sample and the left-channel sample. Instead of using two data channels, multiplexing is
performed by transmitting each word over half a sampling period, which doubles the
sampling rate, and makes it possible to transmit two words per period.
A control signal WS (Word Select) is then used to determine if the word being sent is the
right or left one. This signal also determines the beginning and the end of the data: there is
no need to fix the data length. Receiver and transmitter data lengths can therefore be
different, as well as the right and left data lengths.
WS is synchronized to either the rising or the falling edge of SCK and precedes the MSB by
one SCK period in order to have enough time to store and shift operations.
As in most communication protocols, there must be a master and a slave. The master
provides and controls the SCK clock and the WS signal, while the slave only sends or
receives data. The master can be the receiver, the transmitter or a third element (Controller).
Refer to Figure 2.
Figure 1. I
2
S Phillips protocol waveforms 16/32-bit
Transmission Reception
CK
WS
SD
MSB MSBLSB
16-bit or 32-bit
Left channel Right channel
ai15112

 Loading...
Loading...