178 Diagnosis of Faults on Main Board TM8100 Mobile Radio Service Manual
May 2004 © Tait Electronics Limited
9.2 Interface Circuitry
Introduction This subsection covers the diagnosis of faults involving signals output
from or input to the radio’s internal circuitry via the control-head,
internal options, power, or auxiliary connectors. For most inputs and
outputs, filtering or basic processing is applied between the internal
circuitry and the connectors.
Internal and
Connector Signals
The signals at the internal circuitry and those at the connectors are
distinguished as internal signals and connector signals respectively. On
the circuit diagram for the internal circuitry, dashed lines enclose
connector signals. Internal signals are all named signals outside these
enclosures. In Figure 9.4, which shows part of the internal options
connector as an example,
IOP GPIO7 is a connector signal and ITF IOP GPIO7
is an internal signal.
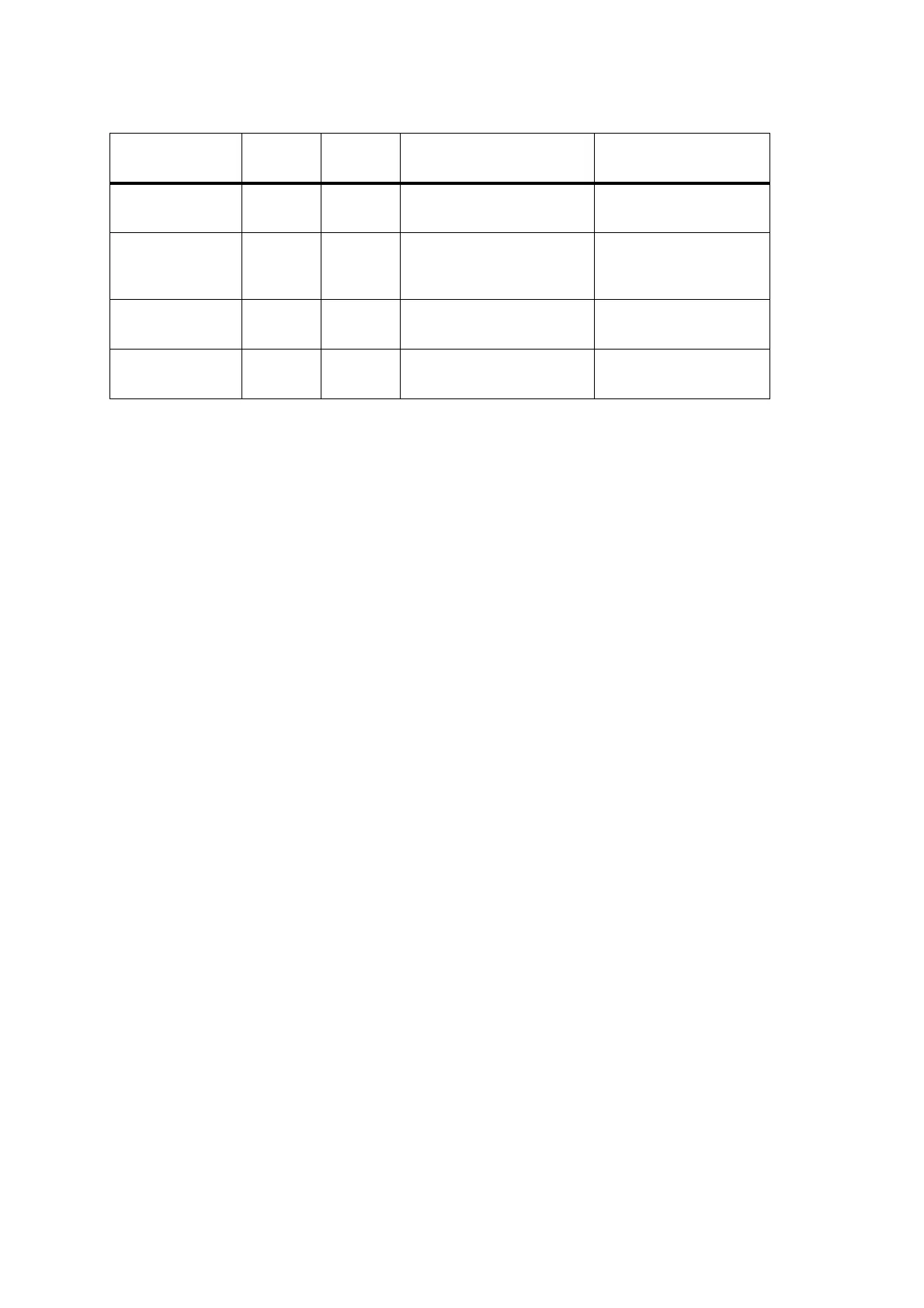
Table 9.1 Implementation of the power-up options
Power-up
option
Link to
insert
Factory
default
Activation mechanism Connector
13V8
power sense
LK1 Link in Connection of 13.8 V supply Power connector
Auxiliary
power sense
LK2 Link in AUX GPI3 line goes high
(If LK1 is in, line floats high;
if LK1 is out, line floats low)
Pin 4 of
auxiliary connector
Emergency LK3 Link in AUX GPI2 line goes low Pin 5 of
auxiliary connector
Internal-options
power sense
LK4 Link out IOP GPIO7 line goes high Pin 15 of
internal options connector

 Loading...
Loading...