6VORTEK Doc.# VT5 OM 050499, Rel. 2.1
Chapter 1 Operation
1.3 Operation of VorTek
tm
Sensors
The VorTek Sensing system measures air velocity by a physical principle called
vortex shedding. The vortex shedding phenomena can be witnessed all around
us in everyday life. Swirling vortices, or eddy currents, are generated whenever
air or liquids flow around an obstruction in their flow path. Common examples are
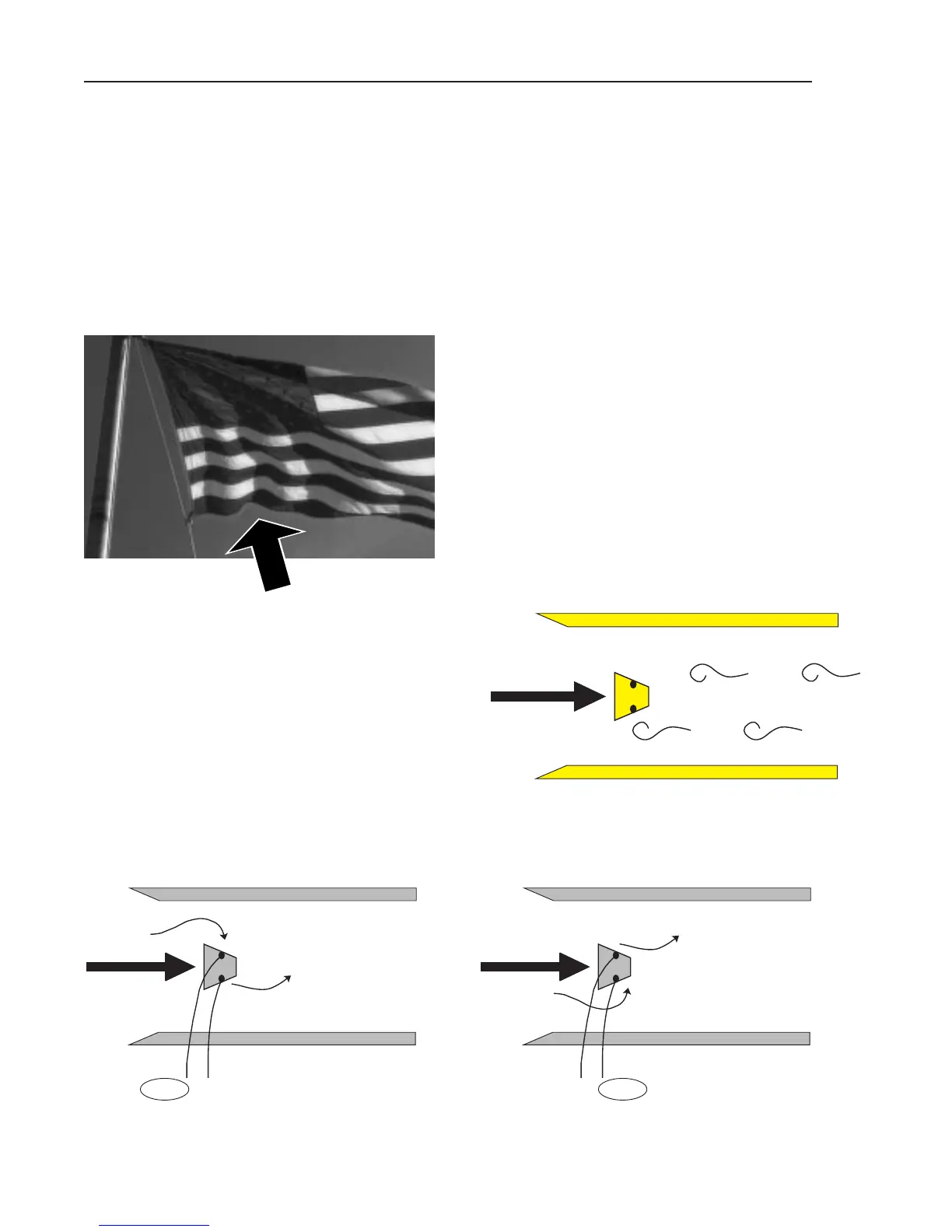
the eddy currents which develop behind rocks in a stream, and in the fluttering of
a flag behind a flag pole. The flag and the flag pole provide the most visual ex-
ample of how vortex shedding works.
The flag pole presents an obstruction in
the path of the airflow, which is the wind.
As the wind passes around the flag
pole, vortices (eddies) are created in the
wake of the pole. These vortices, in
accordance with the laws of nature, are
developed and shed in an alternating
manner, from one side of the flag pole to
the other. The evidence of the shedding
of vortices is in the waving of the flag
itself.
Tek-Air’s unique VorTek flow sensors
use a trapezoidal shaped obstruction
placed in a small tube section to gener-
ate stable vortices over a wide range of
low velocities. Pressure sensors sense
the passing of individual eddies. Multiple
VorTek sensors are mounted on probe
supports to provide ample coverage of
the duct cross section.
AIR FLOW
Low Pressure
High Pressure
Pulse
No Pulse
AIR FLOW
Low Pressure
High Pressure
Pulse
No Pulse
 Loading...
Loading...