97
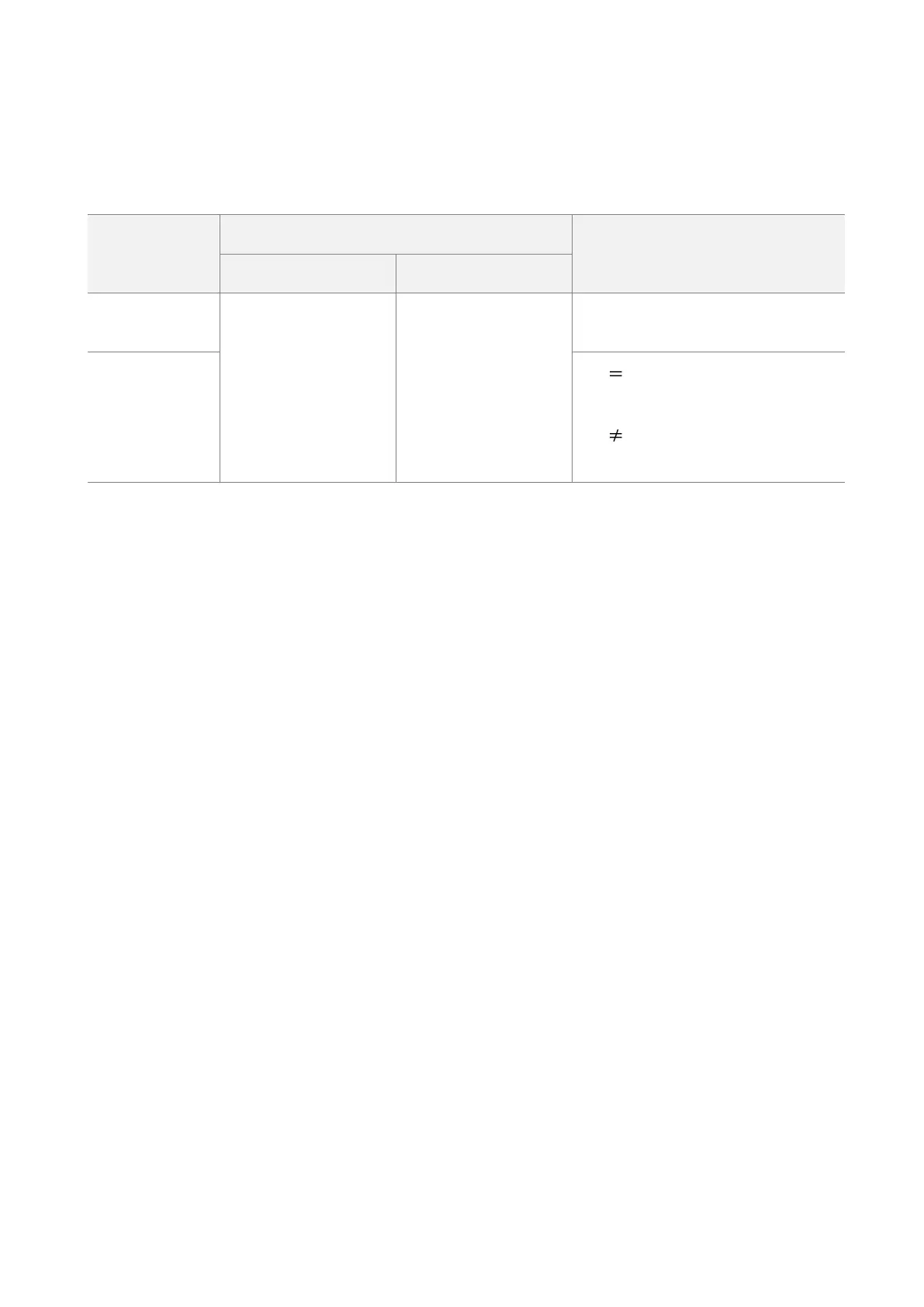
After the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN settings take effect, packet with tag will be forwarded to the ports of
the corresponding VLAN according to the VID of the packet, and packet without tag will be
forwards to the ports of the corresponding VLAN according to the PVID of the port.
The following form shows the details about how different link type ports address received packets:
Forward the data to the
ports of the
corresponding VLAN
based on the VID in the
tag.
Forward the data to the
ports of the
corresponding VLAN
based on the PVID of
ports
Strip the tag in the packet and then
forward it
VID PVID of the port, strip the tag
in the packet and then forward it
VID PVID of the port, retain the tag
in the packet and then forward it
6.5.3 Example of configuring VLAN settings
Networking requirement
You use CPEs to set up CCTV surveillance networks. CPE1 and CPE2 are used to connect to IP
cameras in different places and cannot communicate with each other.
You can assign CPE1 and CPE2 to different VLANs.
Assume that:
− CPE1 is assigned to VLAN10, and CPE2 is assigned to VLAN20.
− The router in the network supports IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and enables two DHCP servers
which belong to VLAN10 and VLAN 20 respectively.

 Loading...
Loading...