22
Appendix
Basic iinformation oon llinear ttemperature
compensation
In order to enable an
approximate
conversion of a
conductivity, measured at any temperature, into
that at the reference temperature (e.g. 25 °C/
+75 °F), the temperature coefficients are used
according to the following equation
(see DIN 38404 part 8):
α is
dependent oon
the
type
and the
concentration
of the ions present in the solution,
but also on
temperature
itself .
In relevant tables (such as Landold Börnstein), α
values can be found for salty, acidic and alcaline
solutions in different types of measuring
conditions.
Should the temperature coefficients be based on
another reference temperature than that required, it
is possible to convert them with the following
equation.
You can also determine temperature coefficients
for your own particular application yourself. For this
you need to measure the conductivity of a given
solution at temperatures T
1
and T
2
, T
2
should be
close to the reference temperature.
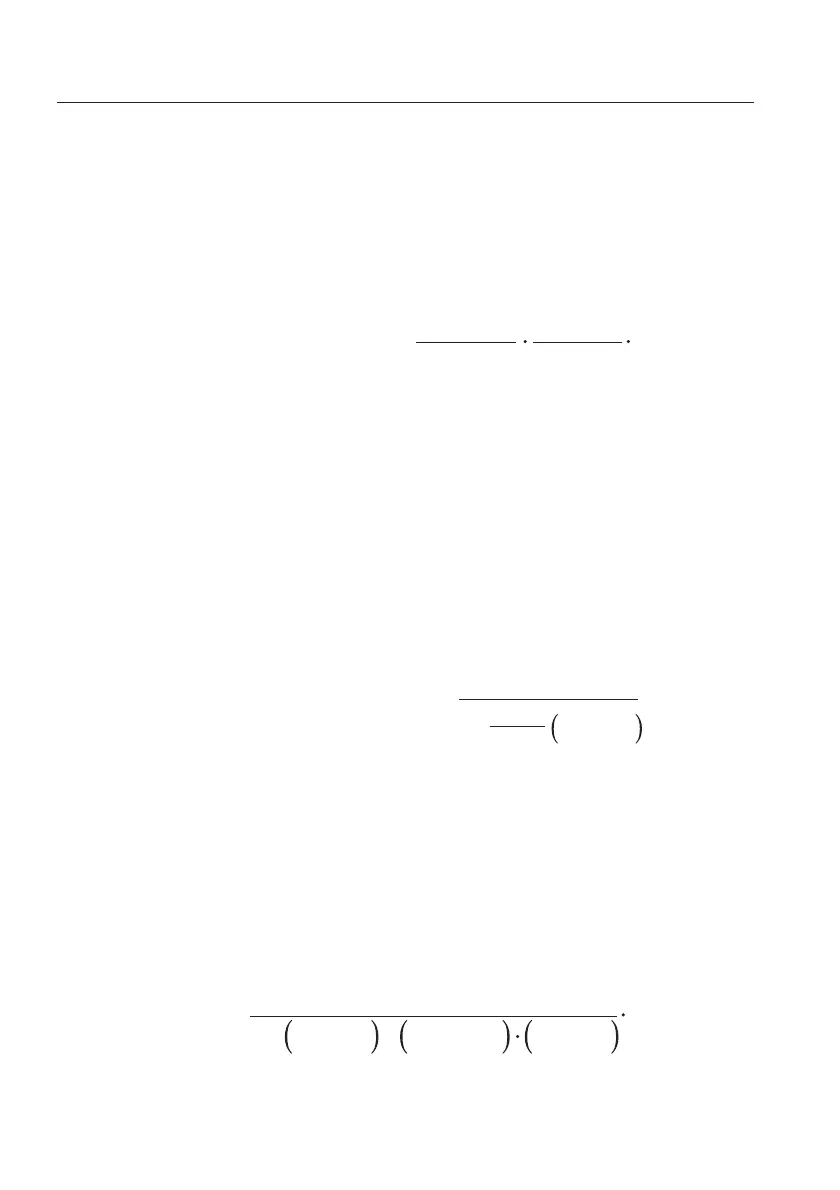
α
TR
can be measured with the equation:
a
=
1
TR
100%
K
TM
K
TR
K
TR
T
M
T
R
a
=
1
TR2
a
TR1
a
TR1
100%
T
R2
T
R1
+
a
=
TR
100%
K
T2
K
T1
T
2
T
1
K
T2
K
T1
K
T1
+
T
R
T
1
α
TR
Temperature coefficient at
the reference temperature
T
R
Reference temperature
(25 °C with
testo
240
)
T
M
Temperature
of the measured sample
K
TR
Electric conductivity at the
reference temperature
K
TM
Electric conductivity at the
temperature of measurement
 Loading...
Loading...