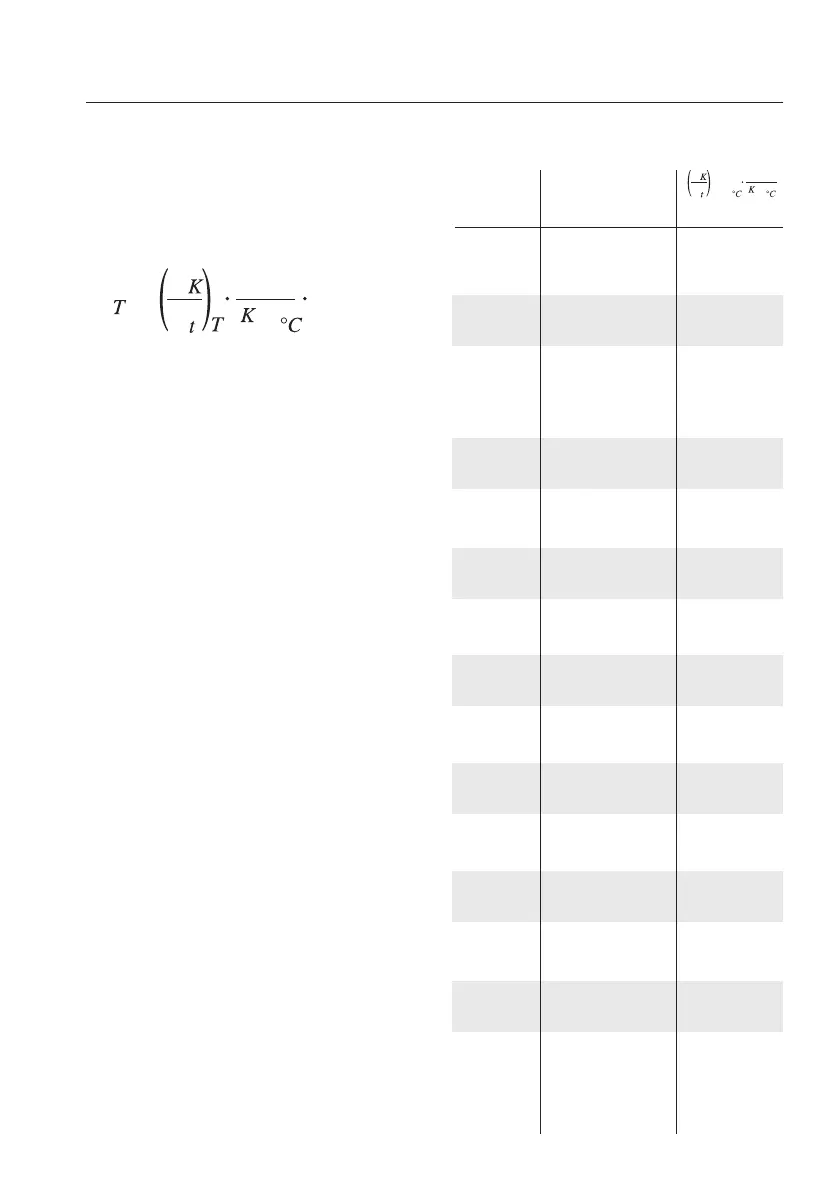Appendix
Temperature ccoefficients oof sselected ssolutions
concentration
c
in
Mol/l
Compound
p
in
weight.-%%
in
%/°C
HCI c = 1.405 1.42
4.420 1.40
11.303 1.37
HNO
3
c = 1.017 1.33
5.873 1.27
13.640 1.41
H
2
SO
4
p = 96.00 2.13
99.66 2.61
99.98 2.55
(excess 100.14 2.48
SO
3
) 101.12 2.55
NaOH c = 0.641 1.71
6.122 2.47
15.323 4.66
KOH c = 0.777 1.65
5.583 1.82
10.695 2.36
NaCl c = 0.884 1.88
3.924 1.88
5.421 2.00
KCI c = 0.691 1.76
2.208 1.59
3.213 1.49
NaNO
3
c = 0.607 1.91
2.688 1.87
4.329 1.91
KNO
3
c = 0.509 1.82
1.626 1.77
2.496 1.71
Na
2
SO
4
c = 0.25 2.06
1.0 2.13
1.206 2.17
K
2
SO
4
c = 0.298 1.88
0.5 1.81
0.620 1.78
NH
4
OH c = 0.059 2.10
2.307 2.13
8.87 2.49
NH
4
Cl c = 0.984 1.74
2.924 1.53
5.003 1.39
NH
4
NO
3
c = 0.637 1.78
2.711 1.59
7.664 1.41
(NH
4
)
2
SO
4
c = 0.25 1.89
1.0 1.77
1.5 1.72
¶
25
(22 ±4)
The temperature coefficient α
T
is defined
as the change in the specific conductivity,
in relation to the conductivity of the refe-
rence temperature (25 °C/+75°F):
The values in the table opposite are mean
temperature coefficients for 18 °C T
26 °C. They have been converted to a
reference temperature of 25 °C (see
"Basic information on linear temperature
compensation"), so that you can enter
them in your Testo instrument without fur-
ther ado.
Source of literature:
Table from Landold-Börnstein, "Zahlen-
werte und Funktionen"
a
=
¶
¶
1
25
100%
21
 Loading...
Loading...