!
Unit Description
8
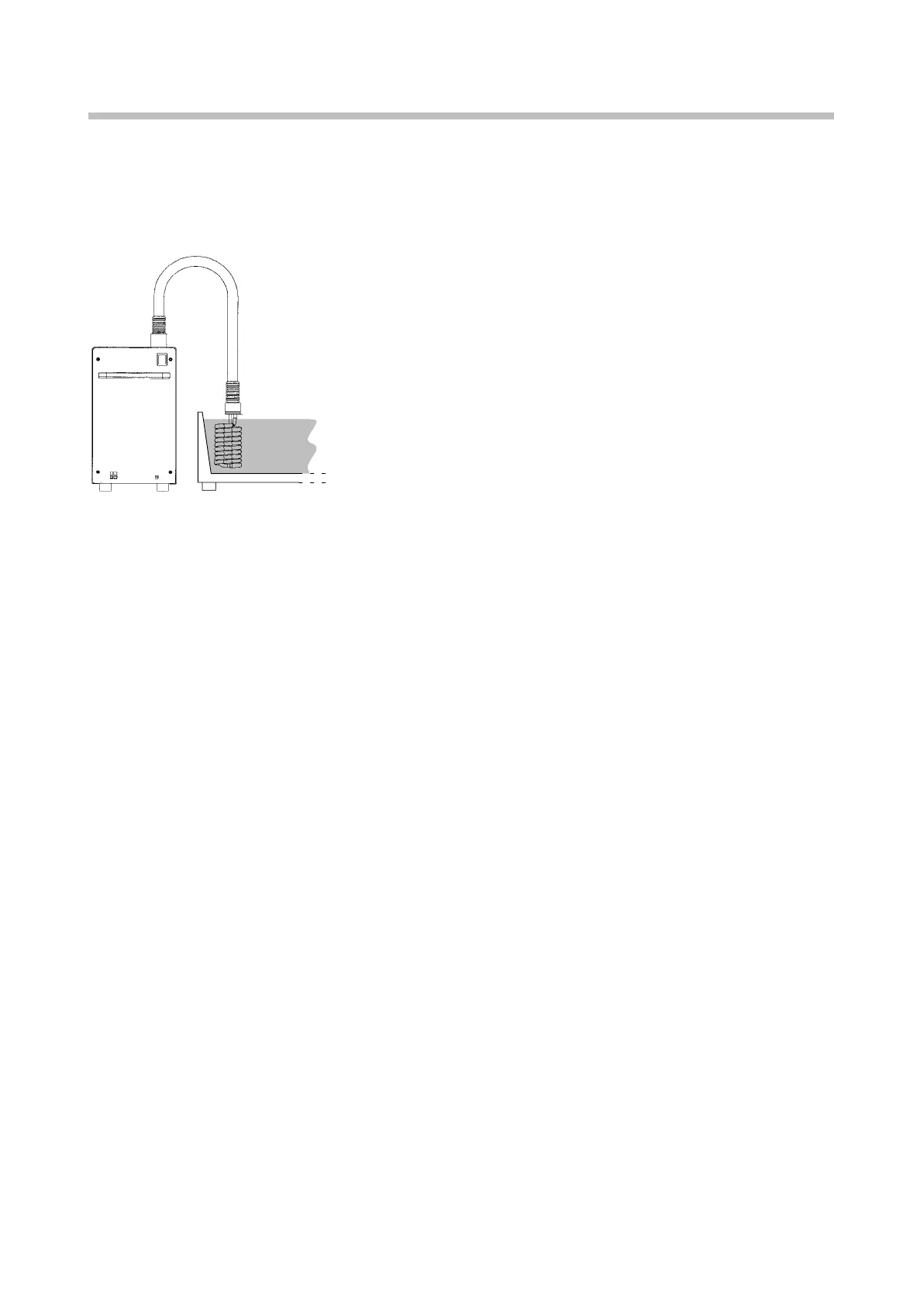
Immersion cooler EK20 and EK30 applications
The external evaporator (cooling coil) is immersed into a
bath and the coil must be completely immersed within the liq-
uid.
The lowest temperature which can be reached in a bath de-
pends on the following factors:
• The volume of heat transfer liquid.
• The bath vessel insulation.
• The heat conductivity of the liquid to be cooled.
• The heat generated within the bath.
It should be differentiated between the two major applica-
tions:
• Cooling a bath vessel:
The units EK20 and EK30 do not have a built-in control-
ler. They will cool the object to the lowest possible tem-
perature, which is governed by the specific properties
of the object. As the liquid is typically not in motion, a
wide temperature distribution has to be expected.
• Cooling open-bath circulators:
Open-bath circulators are equipped with their own
heater and pump. The cooler also operates as a per-
manent cooling source. However as the circulator op-
erates by controlled counter-heating, it is possible to at-
tain both a constant temperature level and an even dis-
tribution throughout the bath.
4.4
Cooling circuits
The cooling capacity for air-cooled units (heat exchanger =
liquefier) depends to a great extent on the free flow of cooling
air through the two ventilation grids.
These grids (one at the front and one at the rear side) must
therefore be kept free of all obstacles at all times!
The cooling capacity is reduced at ambient tem-
peratures of > 30°C!
 Loading...
Loading...