Page 8 of 9
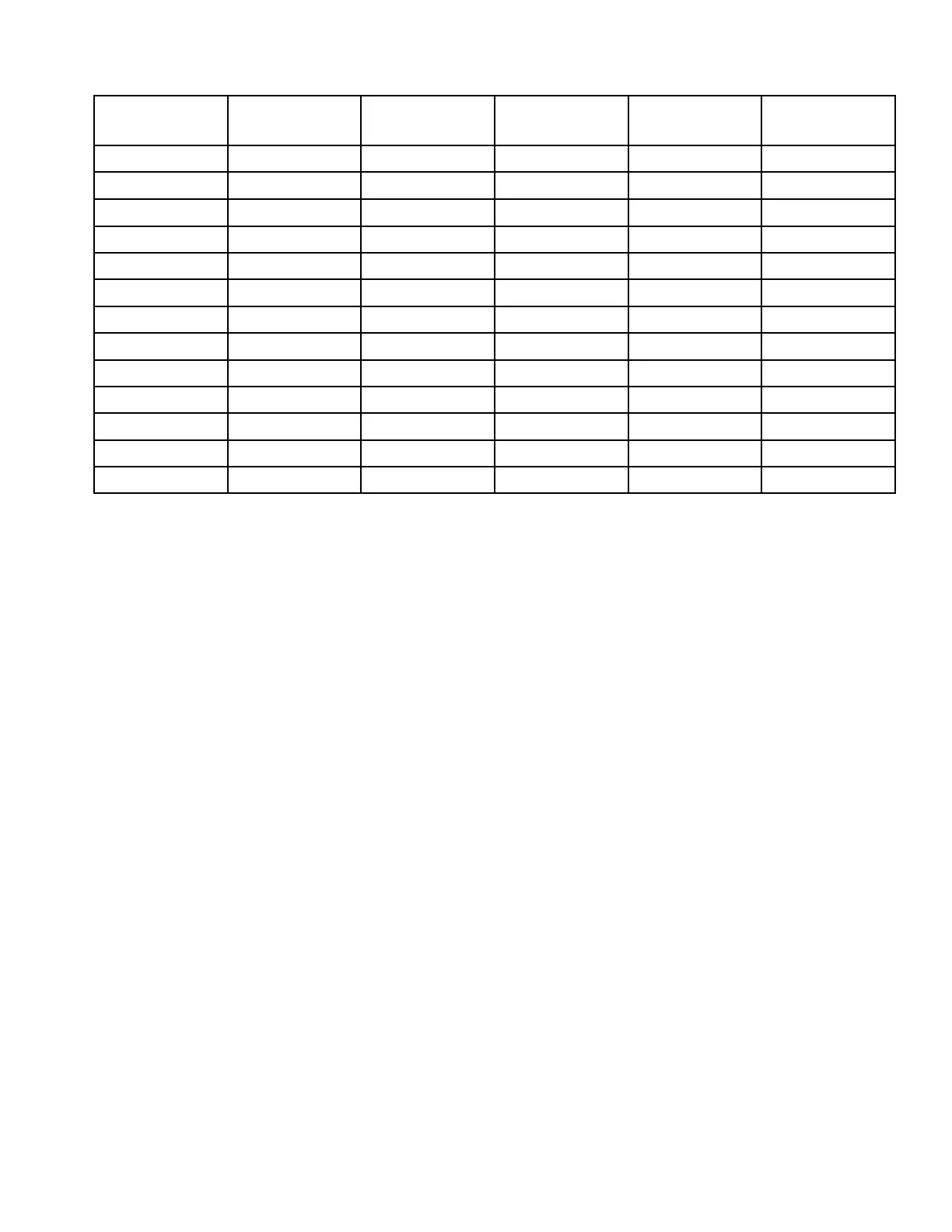
1012 - 1022 Parts List
Item Description Quantity
Drawing
Number
Part
Number
Material
1 Relief Valve 1 A112UK LXUK9219 Various
2 Cover 1 A1066UK 3M35-XUK9014 Cast Iron
3 O’Ring 1 BS046 Neoprene
4 Idler Gear 1 11002-A 3M5-1 Steel/Carbon
5 Body 1 1015-015 Cast Iron
6 Bearing 1 2RLS6/2RS
7 Mechanical seal 1 680-111-23AX12
8 Bearing 1 2RLS6/2RS
9 Circlip 1 NAM300-187
10 Rotor 1 A21445UK Steel
11 Seal Housing 1 1015-012 Cast Iron
12 Shims 2 0.006” Melonex
13 Idler Pin 1 5225-A 3M31 Steel
Field Checklist
1. No Oil is Delivered
• Suction lift too high for vapour pressures of liquid pumped
• While Tuthill Pumps will develop as high as 27 inches of vacuum, it is wise to reduce the vacuum to a minimum
• Bad leaks in suction line or port passages can be detected by submerging pressure line from discharge side of pump into a
pail of oil where the air will be seen in the form of bubbles
• Wrong direction of shaft rotation (In “R” models, check position of cover boss)
• Pump shaft not rotating (Check coupling or drive)
• Relief valve setting too low (Discharging uid through by-pass port)
2. Capacity is too Low
• Suction lift too high
• Air leaks in suction line
• Suction line too small (Can be detected by installing a vacuum gauge directly at the pump suction
• Pump speed too slow
• Filter too small or obstructed
• Suction pipe or port not immersed in the liquid deep enough
• Piping improperly installed, permitting air pocket to form in pump
• Increased clearance or wear in the pump will sometimes cause the pump to deliver an insucient supply of liquid
• A folded gasket or a slight amount of dirt not only will frequently exaggerate the original trouble but will also be the cause
of leakage
Note: The maximum vacuum at the pump suction should never exceed 15 inches of mercury. Not because of the inability of the pump
to handle a higher vacuum, but primarily because the vaporization that is liable to take place at a higher vacuum. Vaporization caused
by higher vacuums will generally result in capacity drop-o.
 Loading...
Loading...











