35
Transcoding
The 2192 can transcode (convert) digital audio data between AES/EBU, S/PDIF, and ADAT S-
MUX formats in realtime. The transcoded digital audio input signal is output to all of the other
digital audio outputs simultaneously.
Transcoding can be performed using any of the available clock sources. The 2192 does not
perform sample rate conversion.
Note: You cannot clock to S/PDIF while listening to AES/EBU or vice versa.
To hear analog audio during transcoding, set the Analog Outputs knob to the digital audio
source.
Transcoding can be performed using either the internal clock, the digital audio source clock, or
an external clock master. Each operation is detailed below.
Important: Do not change any front panel knob or switch settings while transcoding is
in process. The signal is briefly interrupted when new settings are applied.
Transcoding Using Internal Clock
In this configuration, the 2192 is the master system clock.
To perform transcoding using the internal clock:
1. Connect the digital output from the external digital audio source device to the desired 2192
digital input using the appropriate digital cable.
2. Connect the 2192 digital output(s) to the digital input(s) on any external device(s) that will
receive the transcoded digital audio signal using the appropriate digital cable(s).
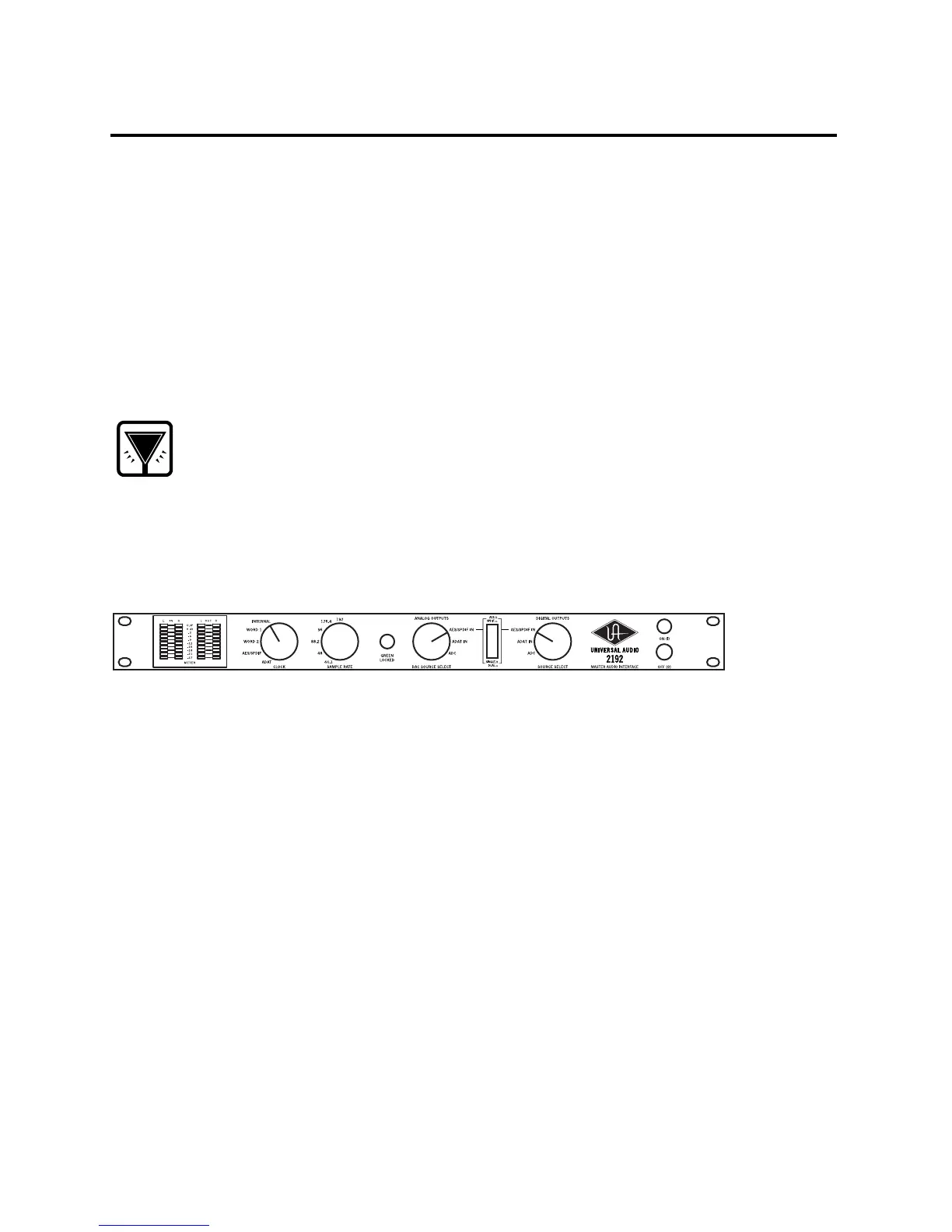
3. Set the 2192 Clock knob to Internal.
4. Set the 2192 Sample Rate knob to match the sample rate of the digital audio source signal.
5. Set the 2192 Digital Outputs knob to the digital audio source input (AES/SPDIF or ADAT). If
the Digital Outputs knob is set to AES/SPDIF, use the AES/SPDIF switch to specify AES/EBU
or S/PDIF.
6. Set the digital audio source device to transmit digital audio and to synchronize to either the
external master clock or to the 2192.
Transcoding is continuous as long as the digital audio source is transmitting.

 Loading...
Loading...