Principles of Operation 83
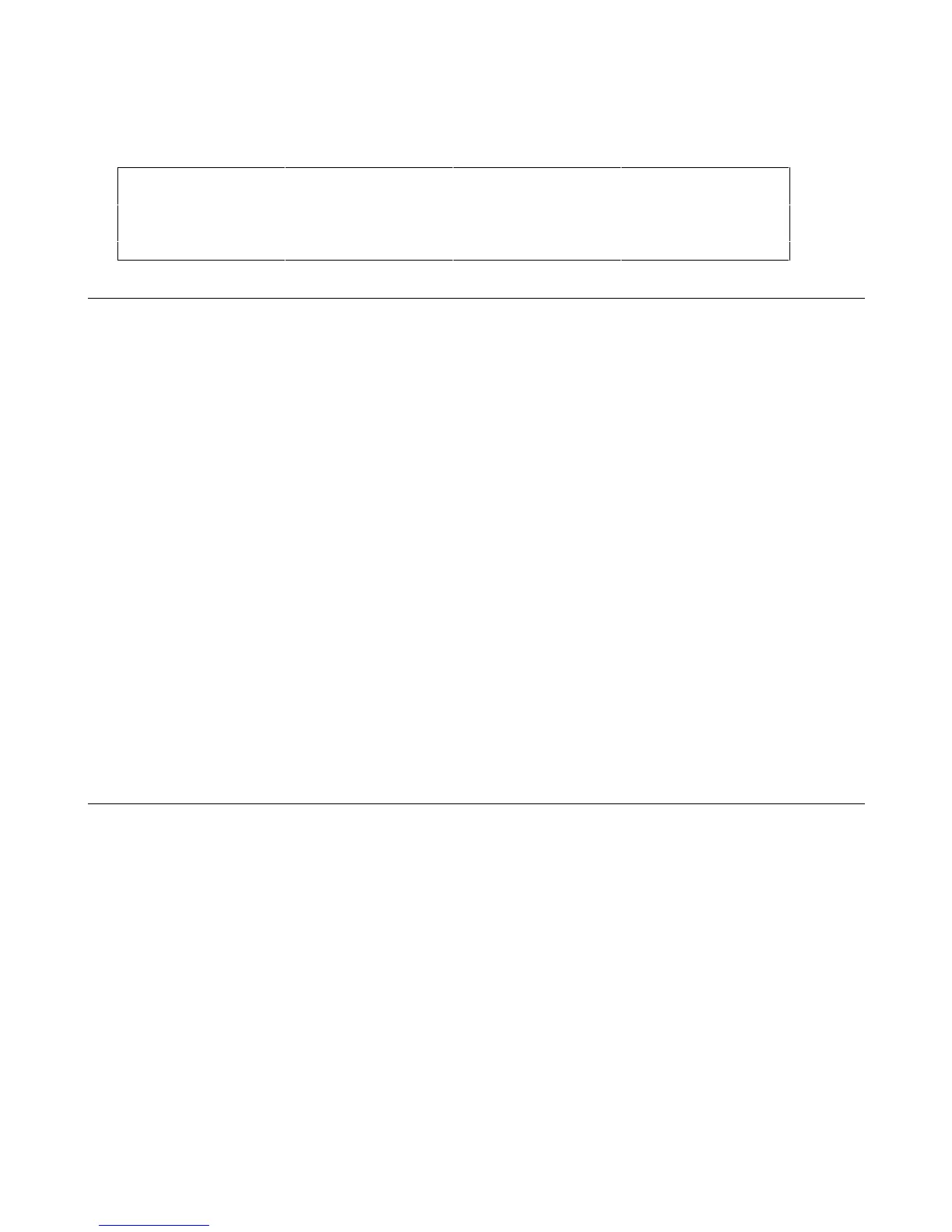
Table 4-2. Digital CNTL Signals
PIN Digital I/O Relay Link Fault/Isolation
Pin 1 OUT 0 RLY SEND FLT Output
Pin 2 OUT 1 NC FLT Common
Pin 3 IN/OUT 2 RLY RTN INH Input
Pin 4 Common Common INH Common
Overall Block Diagram (Figure 4-2)
All of the Agilent Technologies power supplies covered in this service manual consist of four major functional circuit
groups. They are:
1. Secondary Interface Circuits on the A1 Main Board. .
2. Output Power and Control Circuits on the A1 Main Board.
3. A3 Front Panel Board Circuits (part of the Front Panel Assembly).
4. Either the A2 GPIB Board Circuits (primary interface) for models 664xA and 665xA, or the A2 Isolator Board Circuits
for models 654xA or 655xA.
In addition, for all models, the primary power transformer is mounted inside and at the bottom of the power supply chassis.
Note the following comments regarding circuit differences in Figure 4-2.
1. In the 200 watt models (654xA and 664xA), the heat sink assembly is part of the Al main board. But, in the 500 watt
models (655xA and 665xA), the heat sink assembly is external to the A1 Main Board mounted at the bottom of the
power supply chassis itself.
2. In the 200 watt models (654xA and 664xA), separate switches located on the main board are used to set the appropriate
input AC voltage. In the 500 watt models (655xA and 665xA), appropriate wire connections at the power transformer
are set according to the applied input AC voltage.
3. In models 664xA and 665xA, the A2 Board is the GPIB board, and a GPIB interface connector is used to transfer data
between the power supply and an external computer. In models 654xA and 655xA, the A2 Board is the A2 Isolator
Board and the GPIB connector (primary interface) is not applicable.
4. Other differences across Agilent models are described in the text.
Detailed Block Diagram Discussion
The simplified block diagrams in this section show the major signals between circuits. The simplified block diagrams also
show the reference designations of the components that comprise a functional circuit. These same reference designators are
shown in the schematic diagrams in Section 6.
Secondary Interface Circuits (Figure 4-3)
The secondary interface circuits are also located on the Al main board. These circuits include a secondary microprocessor,
programmed GAL, three DAC/Op amp circuits, and analog comparator circuits. The secondary microprocessor translates
the serial data received from the A2 board into a parallel 12-bit data bus. The data bus is connected directly to three
DAC/Op amplifier circuits. Under control of the microprocessor, the selected DAC converts the data on the bus into an
analog signal. The DAC reference circuit provides a +10 V Ref for the CV and CC DACs, and a -11.5 V Ref for the
readback DAC.

 Loading...
Loading...











