29
www.agilent.com/find/esg
Creating Signals
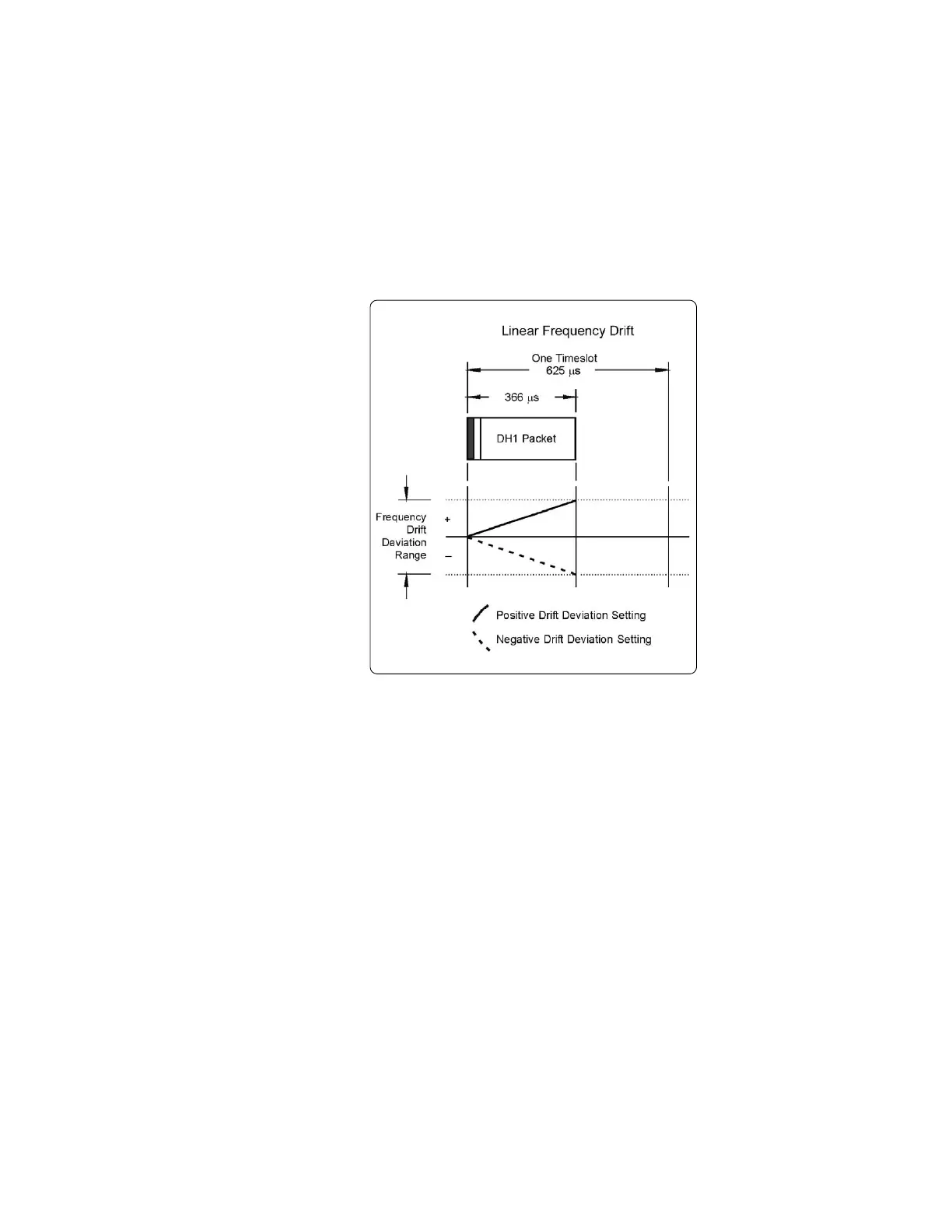
Linear drift
The two different carrier frequency drift types that are available in the menu are sine and
linear. When linear drift is selected, the carrier frequency deviates from the center carrier
frequency in a positive or negative linear direction, depending on the drift deviation set-
ting. For example, a drift deviation setting of –15 kHz would cause the carrier frequency
to drift in a linear fashion from 0 to 15 kHz below the intended carrier frequency.
The drift is over the duration of the packet and returns to the start value after each packet.
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN)
This impairment adds noise to the Bluetooth signal. Although not required by the
Bluetooth RF test specification, this impairment enables the simulation of non-ideal
environments for receiver performance evaluation. The carrier-to-noise ratio and the
noise seed are user defined. The noise seed initializes the 16-bit shift register used for
noise generation. When repeating measurements, using the same noise seed for each
measurement iteration increases the probability of replicating test results.
Figure 33. Linear frequency drift impairment

 Loading...
Loading...

















