Addressing Modes for Your Remote I/O
Chapter 3
3-16
Module Placement with 1slot Addressing
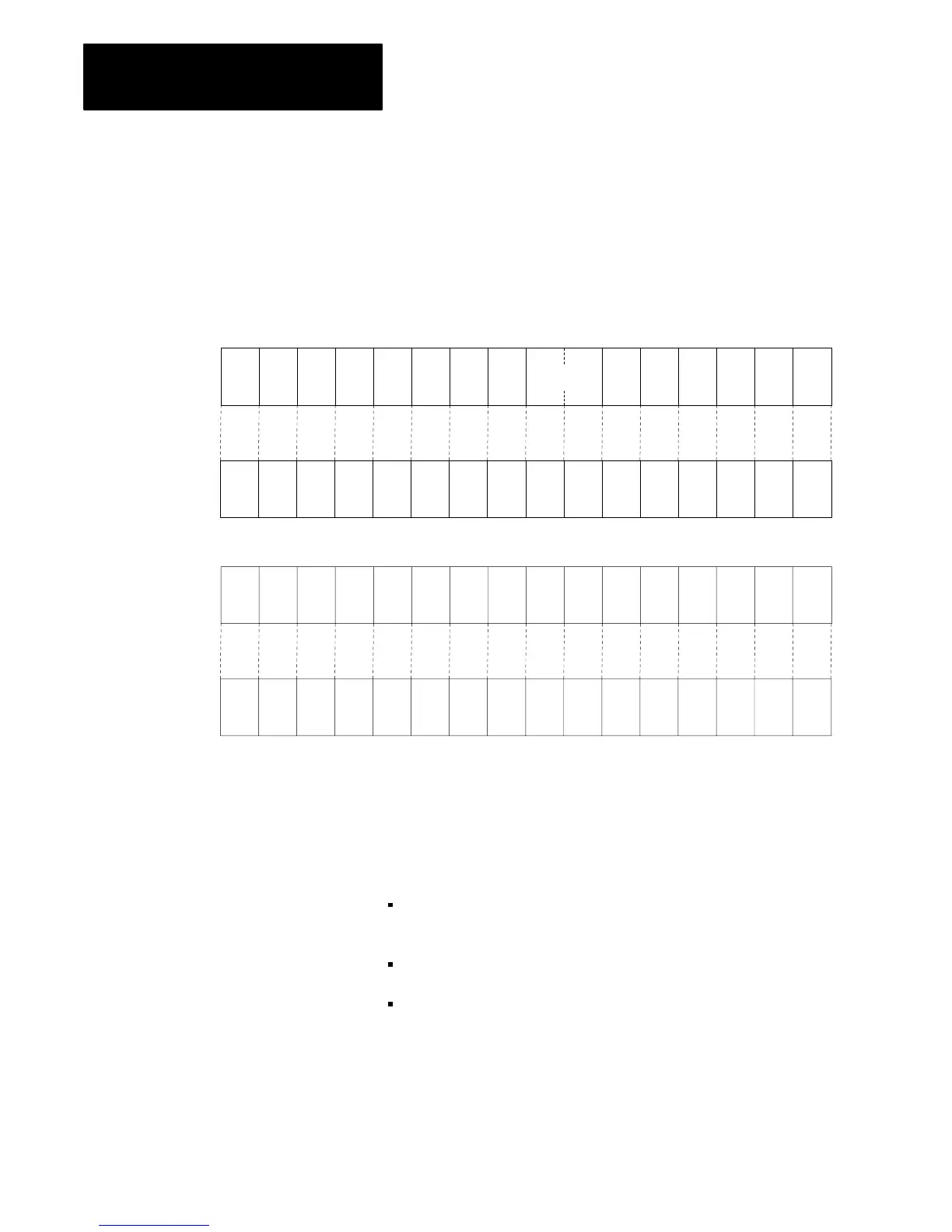
Figure 3.14 shows possible module placement for complementary I/O with
1-slot addressing.
Figure 3.14
Complementary
I/O Configurations with 1slot Addressing
IIO IOO
O
Double-slot
BT
E
M
P
T
Y
021 34567
Example A
Example B
Primary 16-slot
Chassis
I/O G roup
Number
Complementary
16-slot Chassis
Primary 16-slot
Chassis
I/O G roup
Number
Complementary
16-slot Chassis
I = Input Module (8-or 16-point)
O = Output Module (8-or 16-point)
BT = Block transfer Module
1 Output modules use the same output image table bits
2 Can be input or output module (8-or 16-point) single-slot block tran fer module
3 Must be empty if corresponding primary slot is block transfer module
12
BT
OI I I OO
E
M
P
T
Y
OO I I O OI
I, O,
BT
IIIOOO
01234567
021 34567
01234567
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
13080
1
3
3
s
Follow these guidelines when you select 1-slot addressing:
Place input modules opposite output modules; place output
modules opposite input modules.
You can use 8-point or 16-point I/O modules.
Output modules placed opposite output modules reflect the same
bits in the output image table.
You can use block-transfer modules in a complementary I/O configuration
with 1-slot addressing. Remember that when you select 1-slot addressing,
an I/O group is one module slot. Use block-transfer modules with these
restrictions:

 Loading...
Loading...











