Operation Manual IQ-BASIC-GPS 18
Bräuniger GmbH
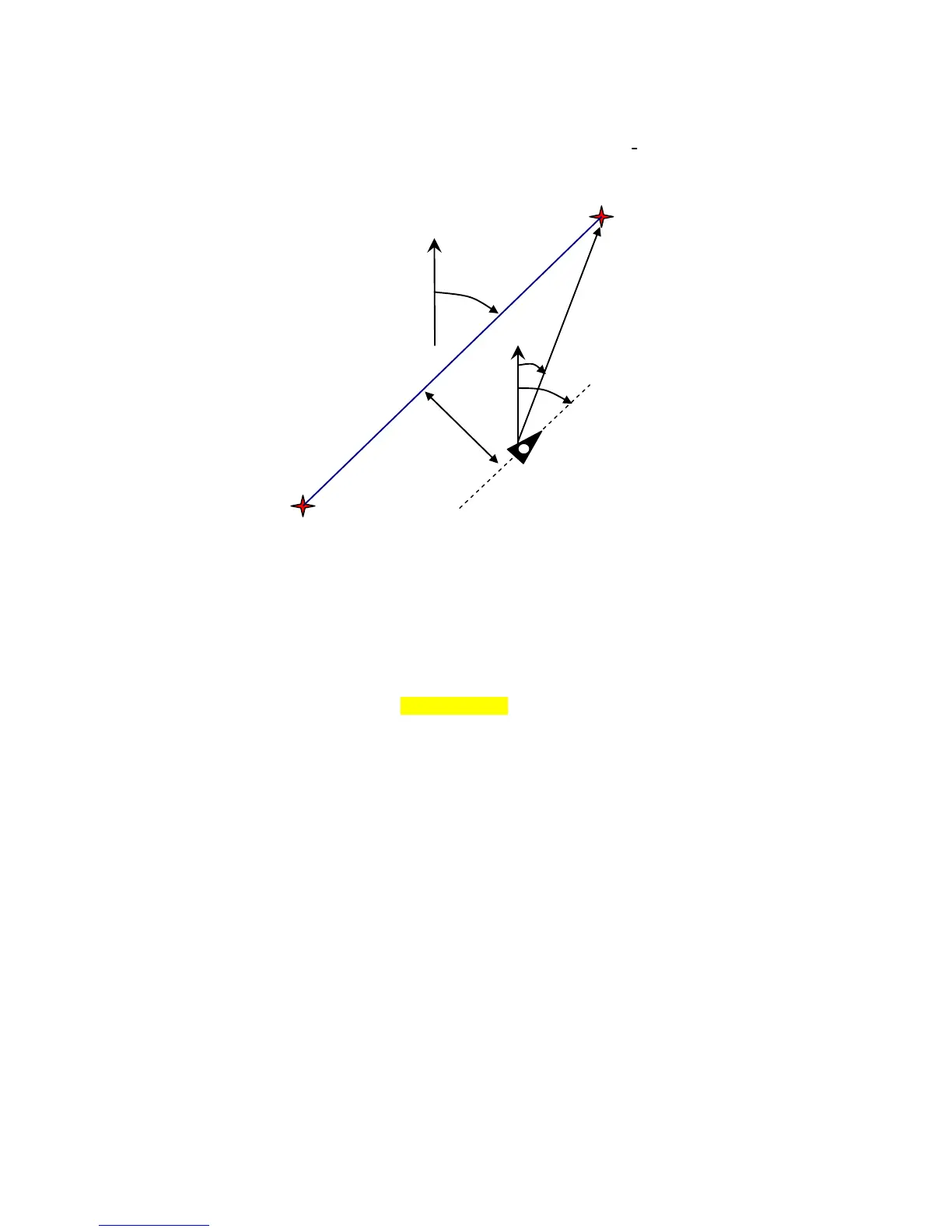
3.2.1 Track and Bearing
Track is the direction into which an aircraft is moving over ground. The geographic true North
is always 0 or 360 degrees. (East = 90 ; South = 180 ; West = 270 Grad)
Bearing is the direction (according to the system described above) to a selected Waypoint seen
from the viewer.
Caution: Track or Tracklog is also called the sequence of recorded positions during one flight.
3.3 Waypoints and Coordinates
A waypoint is any single point on the earth’s surface that you would like to go to.
The IQ-BASIC-GPS can save up to 200 waypoints. Each name of a waypoint can have up to 16
characters, e.g.: "Fiesch Airfield". In determining the waypoint, it is also necessary to enter the
altitude, e.g.: "1123" meters (always above sea level). Now we only need the position of Waypoint
on the earth’s surface. For this purpose the IQ-BASIC-GPS uses the geographical map system
named WGS84 (World Geodetic System 1984). This reference system assumes that latitude is
measured
from the equator to the North Pole, 90 ° N, and to the South Pole - 90 ° S. Longitude is measured
from the Greenwich zero meridian (near London), East is counted positive and West is negative
up to +/-180°.
In Basic Settings / Coordinate Format the data entry format is selectable between:
1) degrees minutes decimal places of minutes (dd°mm.mmm) (factory setting)
2) degrees minutes seconds (dd°mm’ss“)
3) degrees decimal places of degrees (dd.ddddd)
Basically one should always try to use possibility no. 1 (=factory setting), because only this format is
using exactly the same calculation format as the GPS receivers do. With all the other formats rounding
errors could sum up to 20 m.
It is exclusively calculated with the WGS84 system. Differing geodetic systems are no longer
selectable.
 Loading...
Loading...