E-18
A
Notes
• These functions can be used in the CMPLX Mode, as long as a complex number is not
used in the argument. A calculation like
i
× sin(30) is supported for example, but sin(1 +
i
)
is not.
• The angle unit you need to use in a calculation is the one that is currently selected as the
default angle unit.
k
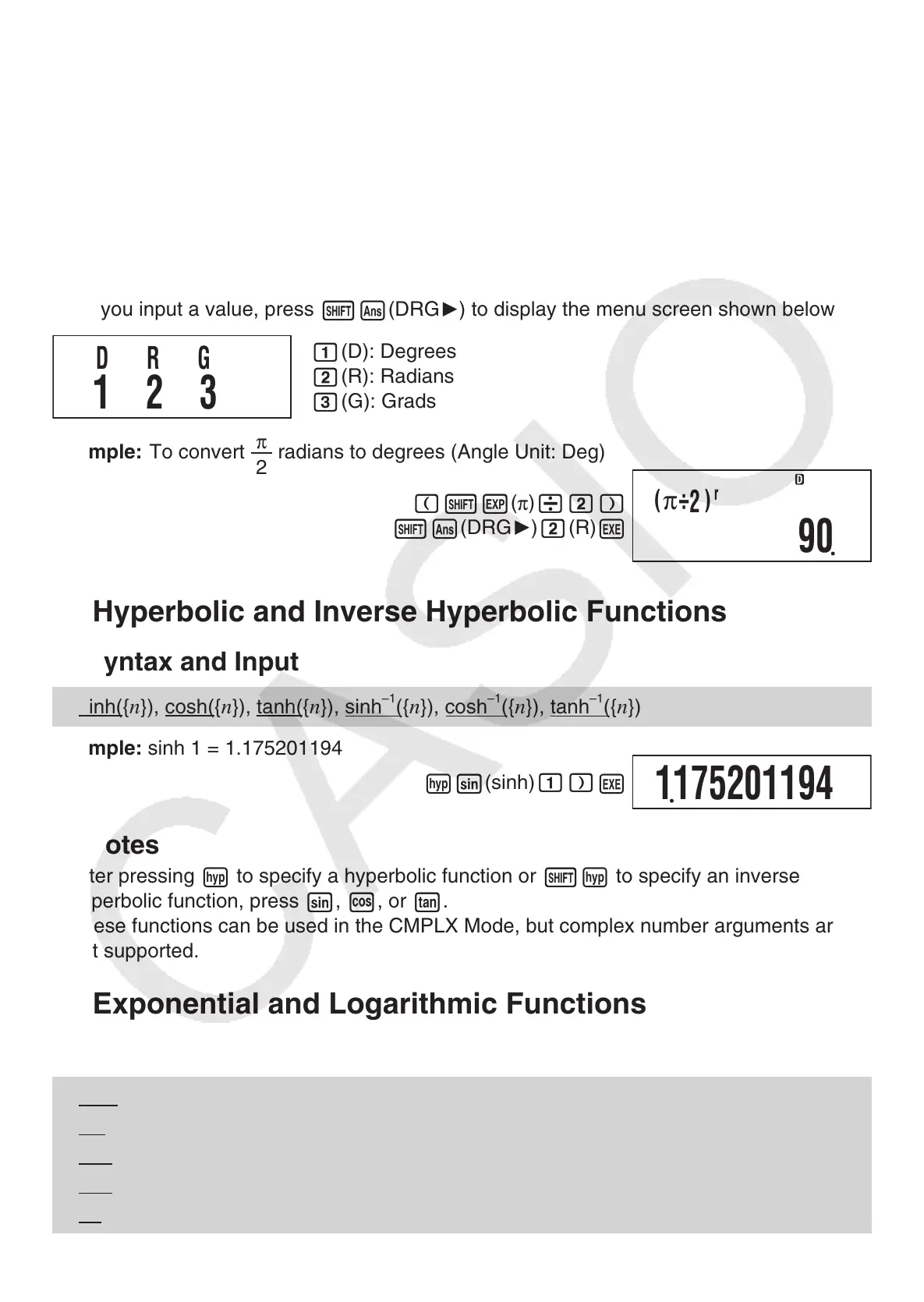
Angle Unit Conversion
You can convert a value that was input using one angle unit to another angle unit.
After you input a value, press
1G
(DRG
'
) to display the menu screen shown below.
1
(D): Degrees
2
( R
): Radians
3
( G
): Grads
Example: To convert
π
2
radians to degrees (Angle Unit: Deg)
(
1e
(
π
)
/2)
1G
(DRG
'
)
2
( R
)
E
k
Hyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
A
Syntax and Input
sinh({
n
}), cosh( {
n
}), tanh( {
n
}), sinh
–1
({
n
}), cosh
–1
({
n
}), tanh
–1
({
n
})
Example: sinh 1 = 1.175201194
w
s
(sinh)
1)
E
A
Notes
• After pressing
w
to specify a hyperbolic function or
1w
to specify an inverse
hyperbolic function, press
s
,
c
, or
t
.
• These functions can be used in the CMPLX Mode, but complex number arguments are
not supported.
k
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
A
Syntax and Input
10^( {
n
}) .......................... 10
{
n
}
e
^({
n
}) .............................
e
{
n
}
log( {
n
}) ........................... log
10
{
n
} (Common Logarithm)
log( {
m
},{
n
}) ..................... log
{
m
}
{
n
} (Base {
m
} Logarithm)
ln( {
n
}) ............................. log
e
{
n
} (Natural Logarithm)
DRG
312
(
π
÷
2
)
r
90
1175201194

 Loading...
Loading...











