E-54
• As shown in the examples below, multiplication where the sign is omitted is given higher priority
than signed multiplication and division.
1 ÷ 2
π
=
1
2
π
= 0.159154943
1 ÷ 2 ×
π
=
1
2
π
= 1.570796327
k
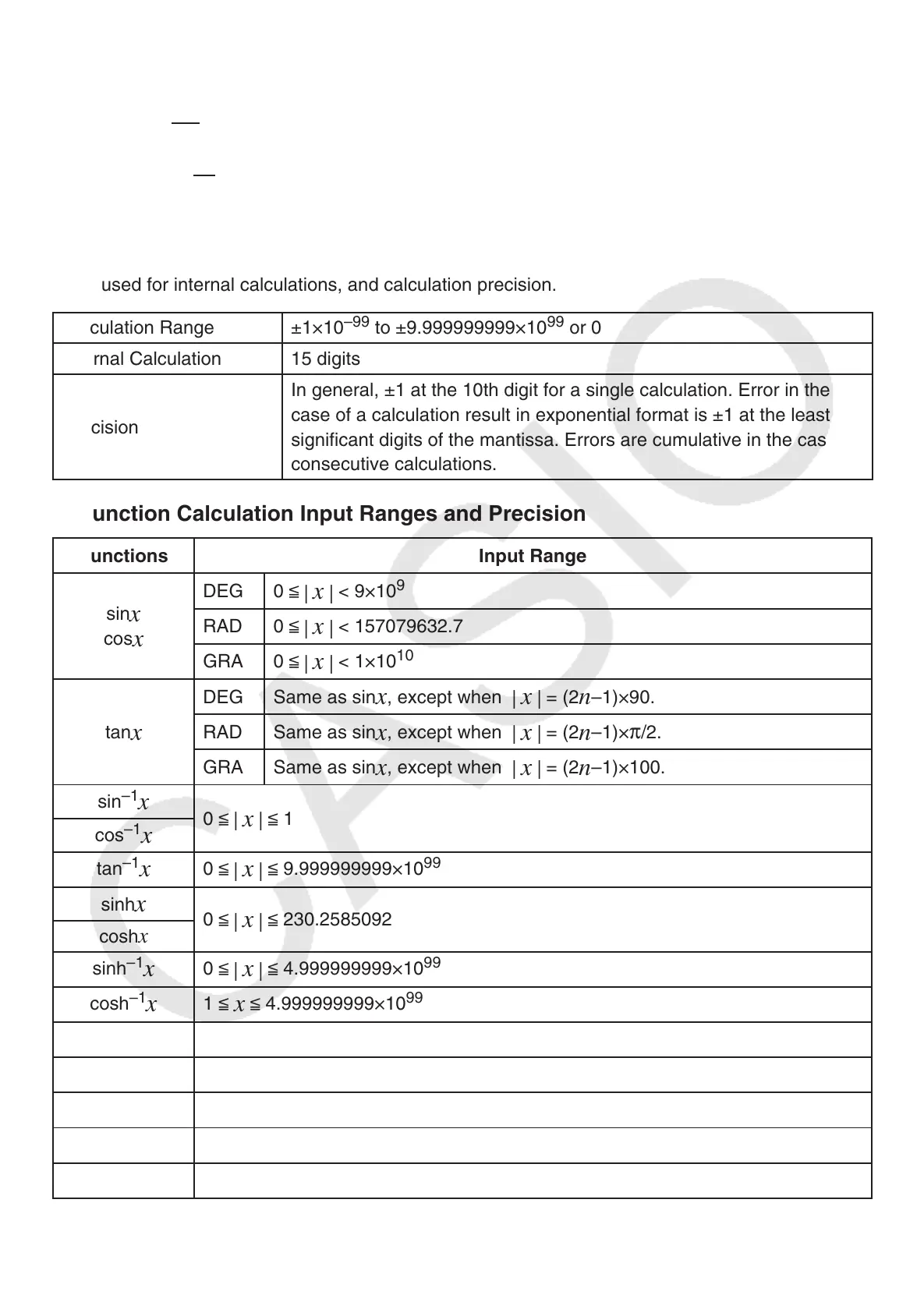
Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
The following table shows the general calculation range (value input and output range), number of
digits used for internal calculations, and calculation precision.
Calculation Range ±1×10
–99
to ±9.999999999×10
99
or 0
Internal Calculation 15 digits
Precision
In general, ±1 at the 10th digit for a single calculation. Error in the
case of a calculation result in exponential format is ±1 at the least
signifi cant digits of the mantissa. Errors are cumulative in the case of
consecutive calculations.
A
Function Calculation Input Ranges and Precision
Functions Input Range
sin
x
cos
x
DEG 0
<
|
x
|
< 9×10
9
RAD 0
<
|
x
|
< 157079632.7
GRA 0
<
|
x
|
< 1×10
10
tan
x
DEG Same as sin
x
, except when
|
x
|
= (2
n
–1)×90.
RAD Same as sin
x
, except when
|
x
|
= (2
n
–1)×
π
/2.
GRA Same as sin
x
, except when
|
x
|
= (2
n
–1)×100.
sin
–1
x
0
<
|
x
|
<
1
cos
–1
x
tan
–1
x
0
<
|
x
|
<
9.999999999×10
99
sinh
x
0
<
|
x
|
<
230.2585092
cosh
x
sinh
–1
x
0
<
|
x
|
<
4.999999999×10
99
cosh
–1
x
1
<
x
<
4.999999999×10
99
tanh
x
0
<
|
x
|
<
9.999999999×10
99
tanh
–1
x
0
<
|
x
|
<
9.999999999×10
–1
log
x
/ln
x
0 <
x
<
9.999999999×10
99
10
x
–9.999999999×10
99
<
x
<
99.99999999
e
x
–9.999999999×10
99
<
x
<
230.2585092

 Loading...
Loading...











