Implementing Internet Key Exchange Security Protocol on Cisco IOS XR Software
Information About Implementing IKE Security Protocol Configurations for IPSec Networks
SC-23
Cisco IOS XR System Security Configuration Guide
IKE Policy Creation
IKE negotiations must be protected, so each IKE negotiation begins by agreement of both peers on a
common (shared) IKE policy. This policy states which security parameters will be used to protect
subsequent IKE negotiations and mandates how the peers are authenticated.
After the two peers agree on a policy, the security parameters of the policy are identified by a security
association established at each peer, and these security associations apply to all subsequent IKE traffic
during the negotiation.
You can create multiple, prioritized policies at each peer to ensure that at least one policy matches the
policy of a remote peer.
Definition of Policy Parameters
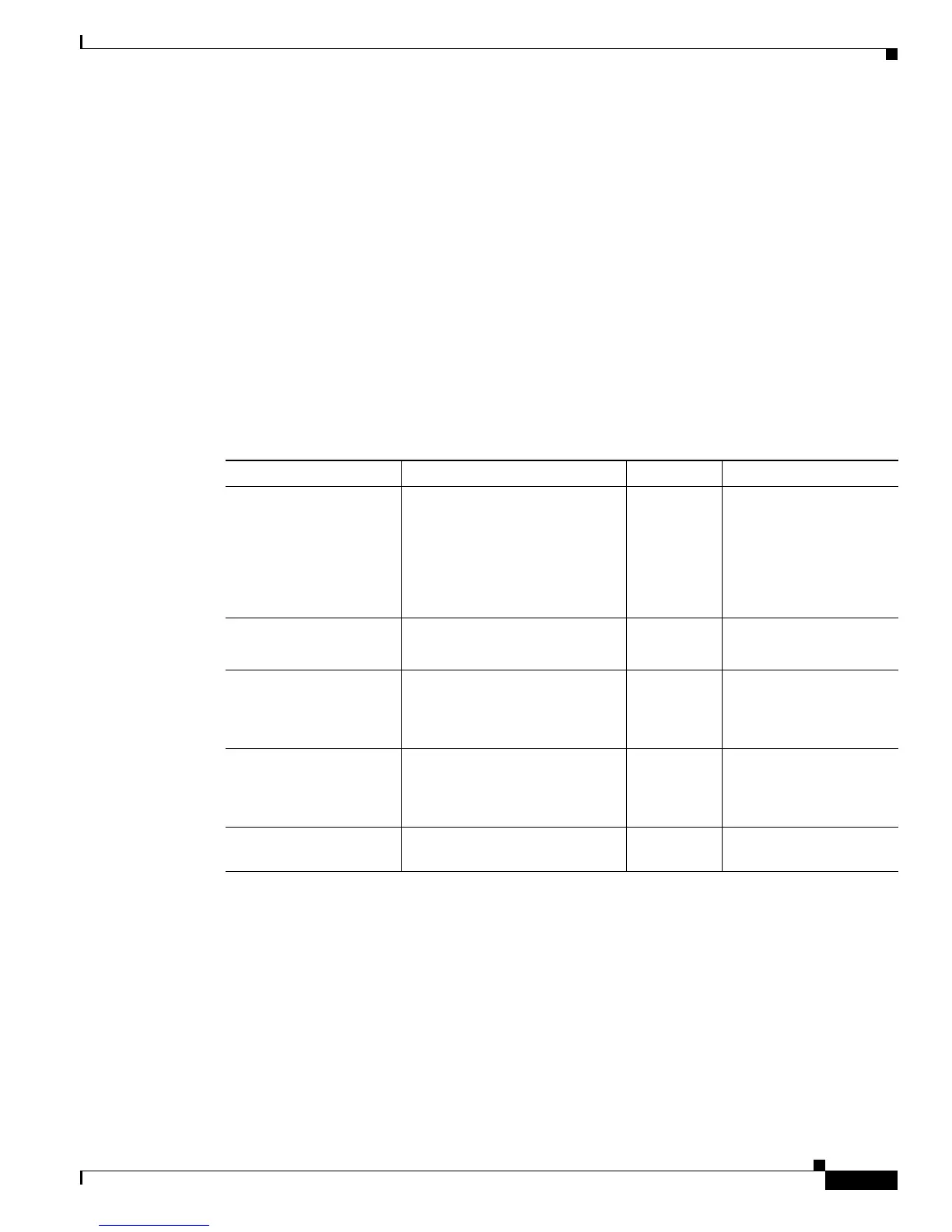
Table 2 lists the five parameters to define in each IKE policy.
These parameters apply to the IKE negotiations when the IKE security association is established.
IKE Peer Agreement for Matching Policies
When the IKE negotiation begins, IKE looks for an IKE policy that is the same on both peers. The peer
that initiates the negotiation will send all its policies to the remote peer, and the remote peer will try to
find a match. The remote peer looks for a match by comparing its own highest priority policy against the
policies received from the other peer. The remote peer checks each of its policies in order of its priority
(highest priority first) until a match is found.
Table 2 IKE Policy Parameter Definitions
Parameter Accepted Values Keyword Default Value
Encryption algorithm 56-bit DES-CBC
168-bit DES
128-bit AES
192-bit AES
256-bit AES
des
3des
aes
aes 192
aes 256
56-bit DES-CBC
Hash algorithm SHA-1 (HMAC variant)
MD5 (HMAC variant)
sha
md5
SHA-1
Authentication method RSA signatures
RSA encrypted nonces
Preshared keys
rsa-sig
rsa-encr
pre-share
RSA signatures
Diffie-Hellman group
identifier
768-bit Diffie-Hellman or
1024-bit Diffie-Hellman
1536-bit Diffie-Helman
1
2
5
768-bit Diffie-Hellman
Lifetime of the security
association
1
1. For information about this lifetime and how it is used, see the command description for the lifetime command.
Any number of seconds — 86400 seconds (1 day)

 Loading...
Loading...











