GR712RC-QSG
November 2018, Version 1.0
5 www.cobham.com/gaisler
the system clock input through the JP84 jumper in the default configuration 2-3. The on-board soldered 48 MHz
oscillator can be used instead by positioning the JP84 jumper on pins 1-2. Alternatively a custom oscillator can
be installed in X2.
The SpaceWire clock is, by default, driven by an on board additional 100 MHz oscillator. If the user wants to use
the system clock configured in the paragraph above as the source of the SpaceWire clock, then jumper JP88 must
be inserted and the oscillator in socket X5 must be removed.
Refer to Section 2.14 of [RD-1] for further information about oscillators and clock inputs and more information
about the system and SpaceWire clock.
Once the external clock sources are selected, further clock configuration can be done in software. The SpaceWire
external clock source can be used as 1X, 2X or 4X, or the external system clock can be used in its place. This
selection is done by configuring the SoC's General Purpose Register (GPREG). At reset the 1X SpaceWire clock
received from the board is used internally.
For in depth information about configuring the SpaceWire and MIL-STD-1553 clocks through the GPREG, please
refer to Chapter 3 and Chapter 13 of [RD-2].
2.3. I/O Switch Matrix
To overcome the limitation on the number of SoC pins, an internal switch matrix selects the input/output signals
to connect to the pad. Additionally the chip I/O pins are connected to the board's I/O ports through an array of
jumpers. One UART and two SpaceWire interfaces are routed independently of the internal switch matrix and the
jumpers JP3 through JP66. In the default position A of jumpers JP3 through JP66, all multiplexed switch matrix
signals are connected to the board's GPIO pins.
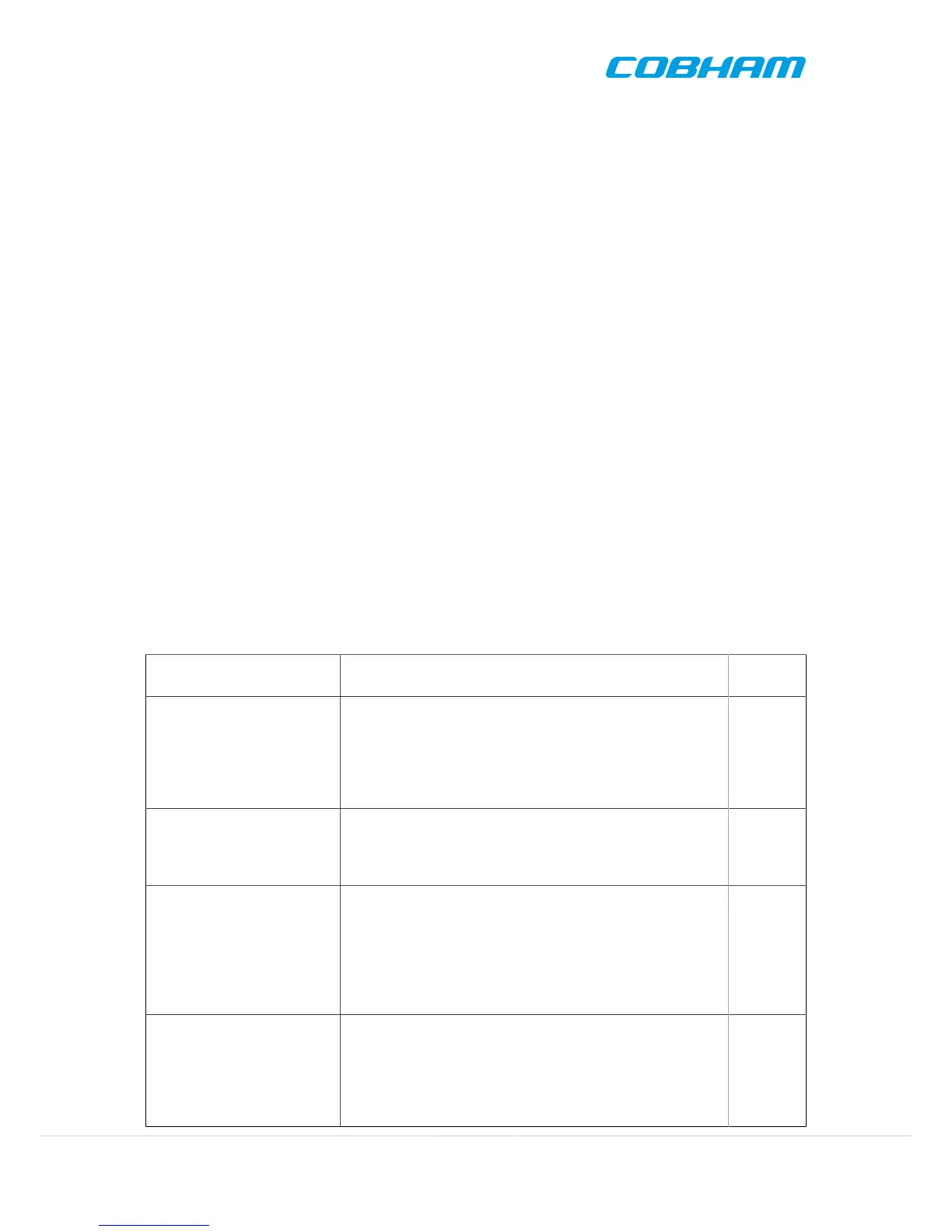
Six basic example configurations are provided to respond to typical use cases, as seen in Table 2.1. To use one of
these configurations, the user has to insert jumpers JP3 through JP66 in the position described in the table. Refer
to [RD-1] and GR712RC Development Board Schematic for more information on signal and GPIO configuration.
Table 2.1. Typical configurations
Cfg. description I/O enabled
Jumper
position
CPU for GEO applications
UART0, UART1, UART2, UART3, UART4, UART5
SpaceWire-0, SpaceWire-1, SpaceWire-2, SpaceWire-3,
SpaceWire-4, SpaceWire-5
Mil-Std-1553-A, Mil-Std-1553-B
SPI
I2C
B
CPU for TMTC applications UART0, UART1, UART2, UART3
SpaceWire-0, SpaceWire-1, SpaceWire-2, SpaceWire-3
SDRAM with optional Reed-Solomon
CCSDS/ECSS TC & TM
C
CPU for LEO applications UART0, UART1, UART2, UART3, UART4, UART5
SpaceWire-0, SpaceWire-1
SDRAM with optional Reed-Solomon
ASCS16
CAN-A, CAN-B
SLINK
I2C
D
Instrument Controller, type A UART0, UART1, UART2, UART3, UART4, UART5
SpaceWire-0, SpaceWire-1
SDRAM with optional Reed-Solomon
CAN-A, CAN-B
SLINK
I2C
E

 Loading...
Loading...