G. Troubleshooting Guide
Appendix G—Troubleshooting Guide
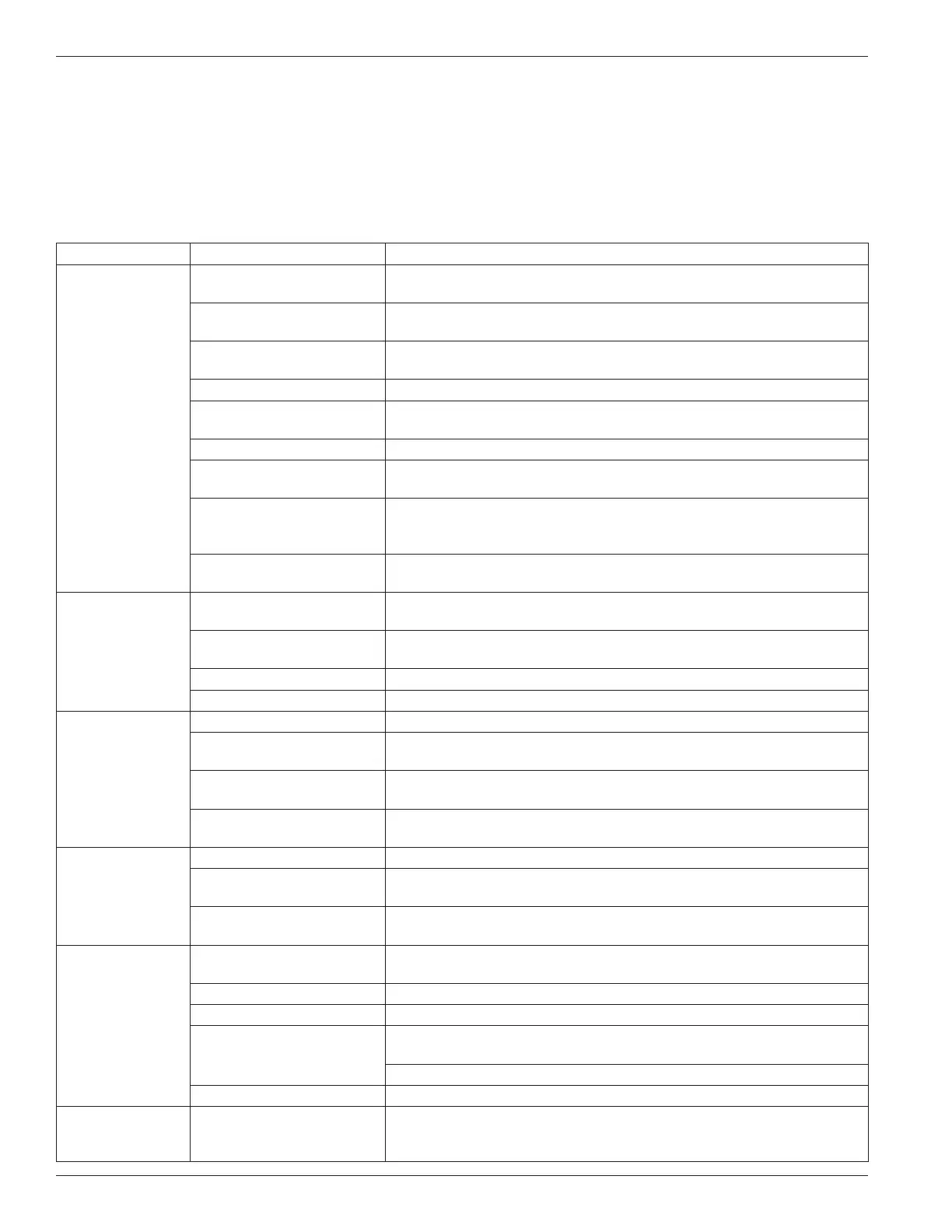
Symptom Probable Cause Remedy
Low capacity Pump speed too slow Check engine speed and PTO ratio. Consult pump performance curve.
Use tachometer on pump if speed is questionable.
High differential pressure Restriction in discharge piping or hose too small. Vapor equalization lines
too small or not used.
External bypass valve stuck
open or set too low
Readjust, repair, or replace valve.
Clogged strainer Clean strainer.
Suction pipe too small or
restricted
Indicated by pump inlet pressure dropping several pounds when pump is
started. Remove restriction or modify piping.
Worn vanes Replace.
Pump without vapor return Without vapor equalization, a pump can remove only about 3% of the truck
tank capacity per minute without severe cavitation and capacity loss.
Worn sideplates Reverse or replace sideplates. Check universal drive assembly to make
sure angularity is within limits, yokes are parallel and slip-joint is greased.
Check bearings.
Vanes sticking Remove vanes and clean out foreign matter (check strainer). Replace
vanes if swollen.
Pump runs but no
flow
Valve closed Check valves. Make sure internal tank excess flow valve is open! Refer to
manufacturer’s instructions.
Excess flow valve slugged Stop pump until valve opens. If problem continues, slow pump down or
install a new or larger excess flow valve.
Broken shaft Disassemble and inspect pump. Repair if necessary.
Defective meter Service meter.
Pump will not turn
or is locked up
Foreign matter in pump Clean out the pump and check strainer in suction line
Vanes broken Clean out pump carefully and replace vanes. Has pump been operated dry?
Then, check for damage to cam and rotor shaft assembly.
Bearing seized Replace pump bearings. Grease monthly. Use ball bearing grease
manufactured for intended service.
Moisture frozen in pump Let thaw and break loose carefully. Add alcohol to tank (on LP-Gas). Check
with product supplier about the possibility of water in the gas.
Will not build
pressure
Poor suction conditions Clean inlet strainer. Increase pipe size.
External bypass valve set
too low
Set valve for higher pressure—see instructions.
Worn vanes and/or
sideplates
Disassemble, inspect and repair as necessary. Do not run pump dry!
Pump is noisy Cavitation from poor suction
conditions
As above.
Vanes sticking As above.
Bearings worn Replace if necessary and grease monthly.
Very high differential Check for restriction in discharge line. Delivery hose too small pressure
and too long. Slow down pump!
Check vapor release float assembly on meter and meter differential valve.
PTO shaft vibration Inspect and repair driveline component.
Pump leaks
around shaft
Seal or O-rings failed Inspect seal assembly and replace if necessary. Keep new seal very
clean when replacing seal. Recommend a light oil film on O-rings. Do not
run pump dry!
In diagnosing pump and system troubles, record the following data during product transfers:
1. Pressure at pump suction.
2. Pressure at pump discharge.
3. Pressure in truck tank.
4. Pressure in tank being filled.
5. Pipe size and length of suction and discharge lines.
6. Size and length of vapor equalizing line.
7. Pump speed if practical.
36
 Loading...
Loading...