New Shallow Well Convertible Pump Installation 5
Shallow Well Installations
1. Remove the pressure regulator from the pump body. Replace it with a
1” NPT close nipple, a 1”x1”x3/4” NPT Tee, and a 1” NPT pipe plug).
Install the pressure gage in the plugged hole in the pump body (see
Figure 1).
2. Install the ejector kit. Follow the instructions provided with the kit.
Align the venturi with the top hole on the front of the pump (see
Figure3).
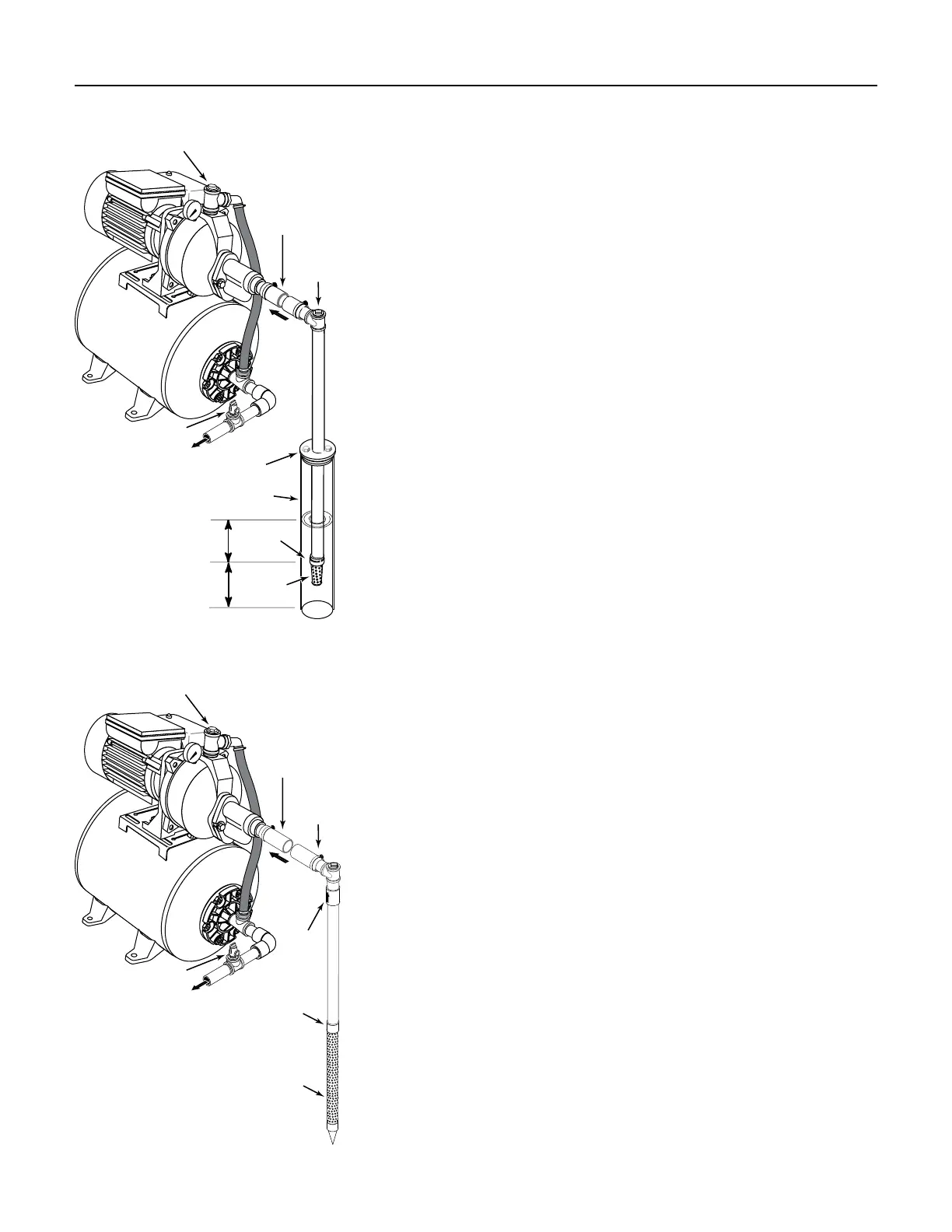
Cased Well Installation, 2” or Larger Casing)
3. Mount the pump as close to the well as possible. Connect the pipe
from the well to the pump suction port, using the fewest possible
fittings – especially elbows – as fittings increase friction in the pipe.
4. Assemble the foot valve, strainer, and well pipe (see Figure 5). Make
sure that the foot valve works freely.
5. Lower the pipe into the well until the strainer is five feet above the
bottom of the well. It should also be at least 10 feet below the well’s
water level while the pump is running in order to prevent the pump
from sucking air. Install a sanitary well seal.
Driven Point Installation
3. Drive the well, using “drive couplings” and a “drive cap”. “Drive
fittings” are threaded all the way through and allow the pipe ends to
butt against each other so that the driving force of the maul is carried
by the pipe and not by the threads. The ordinary fittings found in
hardware stores are not threaded all the way through the fitting and can
collapse under impact. “Drive fittings” are also smoother than standard
plumbing fittings, making ground penetration easier.
4. Mount the pump as close to the well as possible. See Figure 5.
5. If one well point does not supply enough water, consider connecting
two or three well points to one suction pipe.
All Shallow Well Installations
6. Install a priming tee, priming plug, and suction pipe to the pump (see
Figures 4 and 5). Connect the pipe from the well to the pump suction
port, using the fewest possible fittings – especially elbows – as fittings
increase friction in the pipe. The priming tee is optional.
• The suction pipe should be at least as large as the suction port on
the pump (include a foot or check valve – see Figures 4 and 5).
• Support the pipe so that there are no dips or sags in the pipe, so it
doesn’t strain the pump body, and so that it slopes slightly upward
from the well to the pump (high spots can cause air pockets which
can air lock the pump).
• Seal the suction pipe joints with PTFE pipe thread sealant tape or
a PTFE-based pipe joint compound. Joints must be air- and water-
tight. If the suction pipe can suck air, the pump cannot pull water
from the well.
7. Run piping from the discharge tee in the tank flange to the household
piping. The discharge piping must be at least as large as the tank tee.
Install a relief valve in the discharge pipe capable of passing the entire
pump flow at 75 psi. Run a pipe from the relief valve to a floor drain or
some other convenient place to carry off the water.
You have just completed the piping for your new pump/tank system. Please
go to Electrical for electrical connections.
To Household
Water System
Suction Pipe
From Well
Regulator with
Priming Te e
(see fig. 1)
Priming
T
Plug
Relief Valve
Drive
Coupling
Drive
Point
Check
Valve
Figure 5 - Driven Point Installation
To Household
Water System
Suction Pipe
From Well
Priming
T
Plug
Well
Casing
Foot
Valve
Sanitary
Well Seal
Strainer
5-10'
At least
10'
Relief Valve
Regulator with
Priming Te e
(see fig. 1)
Figure 4 - Cased Well Installation

 Loading...
Loading...