Figure 5- 41
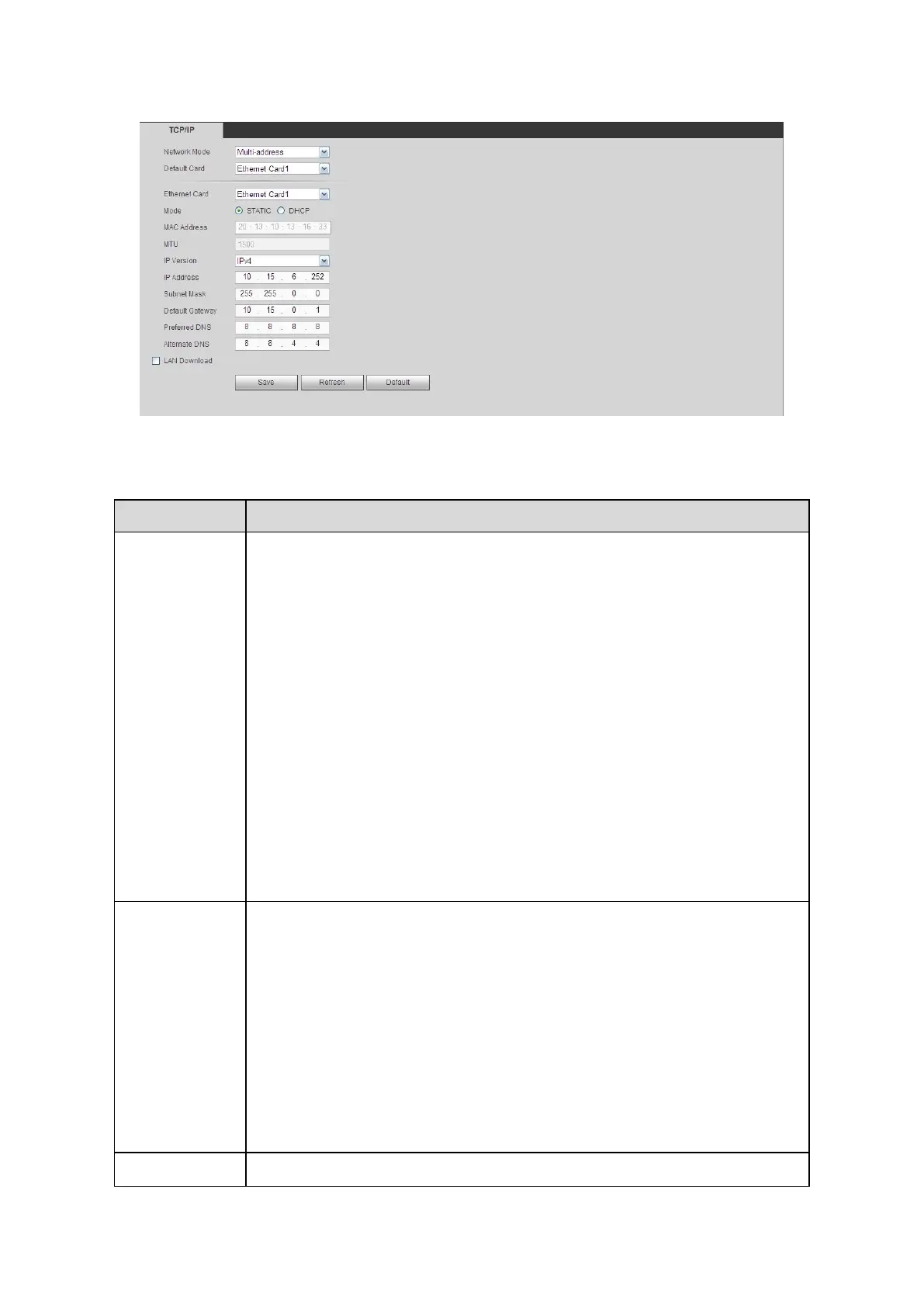
Please refer to the following sheet for detailed information.
It includes: single multiple-address, fault tolerance, load balance.
Multiple-address: eth1/eth2 operates separately. You can use the
services such as HTTP, RTP service via eth1/eth2. Usually you need to
set one default card (default setup is eth1) to request the auto network
service from the device-end such as DHCP, email, FTP and etc. In
multiple-address mode, system network status is shown as offline once
one card is offline.
Fault-tolerance: In this mode, device uses bond0 to communicate with
the external devices. You can focus on one host IP address. At the
same time, you need to set one master card. Usually there is only one
running card (master card).System can enable alternate card when the
master card is malfunction. The system is shown as offline once all
cards are offline. Please note all cards shall be in the same LAN.
Load balance: In this mode, device uses bond0 to communicate with
the external device. The all cards are working now and bearing the
network load. Their network load are general the same. The system is
shown as offline once all cards are offline. Please note all cards shall be
in the same LAN.
There are two modes: static mode and the DHCP mode.
The IP/submask/gateway are null when you select the DHCP mode to
If you select the static mode, you need to set the IP/submask/gateway
If you select the DHCP mode, you can view the IP/submask/gateway
If you switch from the DHCP mode to the static mode, you need to reset
Besides, IP/submask/gateway and DHCP are read-only when the
It is to display host Mac address.
 Loading...
Loading...











