Appendix A. EMC Standard Installation GuideVFD-ED
A-4-2 How to Reduce EMC by Shielding
Iron and other metals are high conductivity materials that provide effective shielding at extremely low
frequencies. But conductivity will decrease as:
1. High frequency signals are applied to the conductor
2. Equipment is located in a strong magnetic field
3. The shielding frame is forced into a specific form by machines
It is difficult to select a suitable high-conductivity material for shielding without the help from a shielding
material supplier or a related EMC institution.
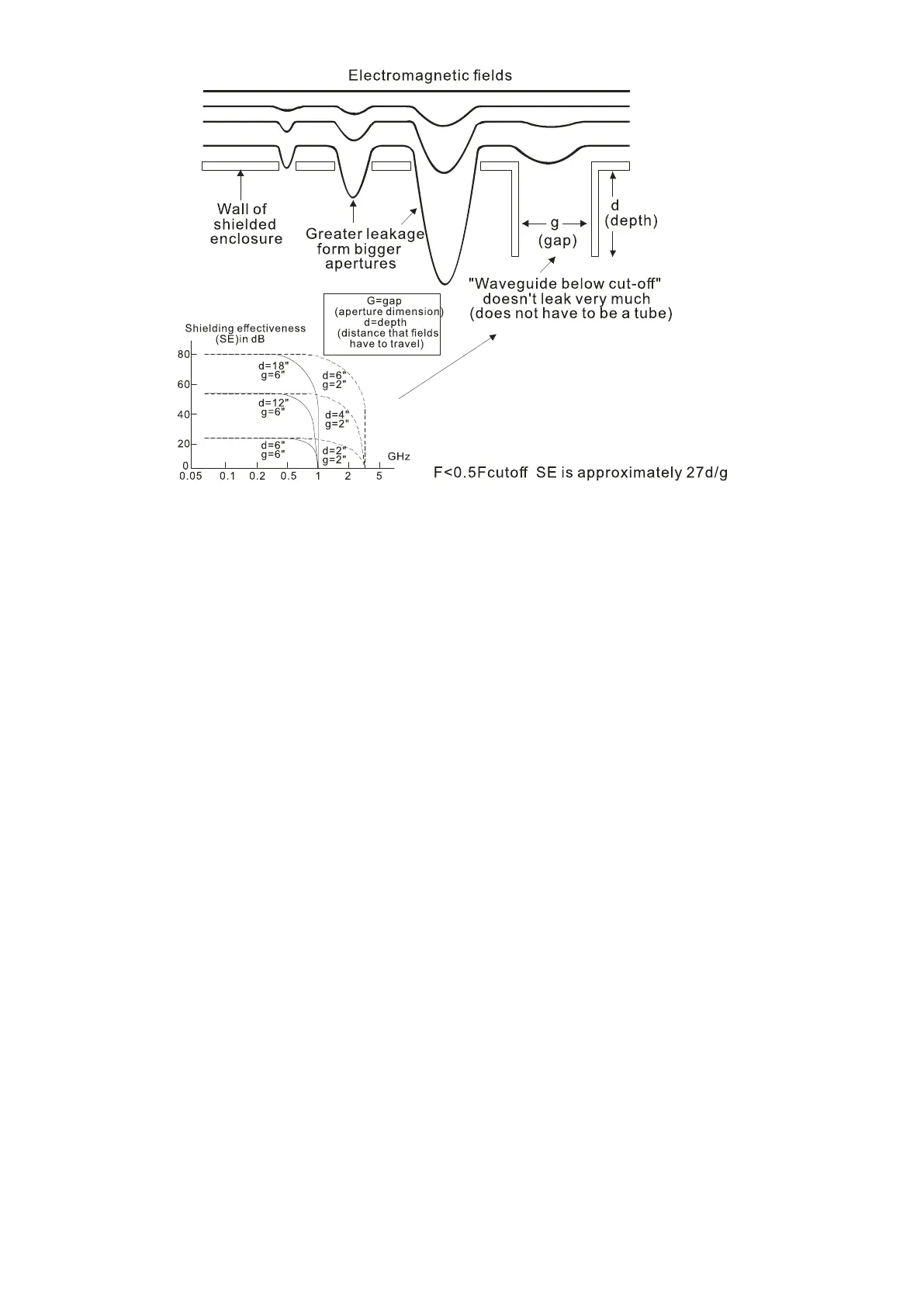
Metallic Shielding Effectiveness
Shielding Effectiveness (SE) is used to assess the applicability of the shielding shell. The formula is:
SEdB=A+R+B (Measures
in dB)
where A= Absorption loss (dB)
R= Reflection loss (dB)
B= Correction factor (dB) (for multiple reflections in thin
shields)
The absorption loss refers to the amount of energy loss as the electromagnetic wave travels through
the shield. The formula is:
AdB=1.314(fσμ) 1/2t where f= frequency (MHz)
μ= permeability relative to copper
σ= conductivity relative to copper
t= thickness of the shield in centimeters
 Loading...
Loading...











