Operation Section
1
–
4
2.5 Operation
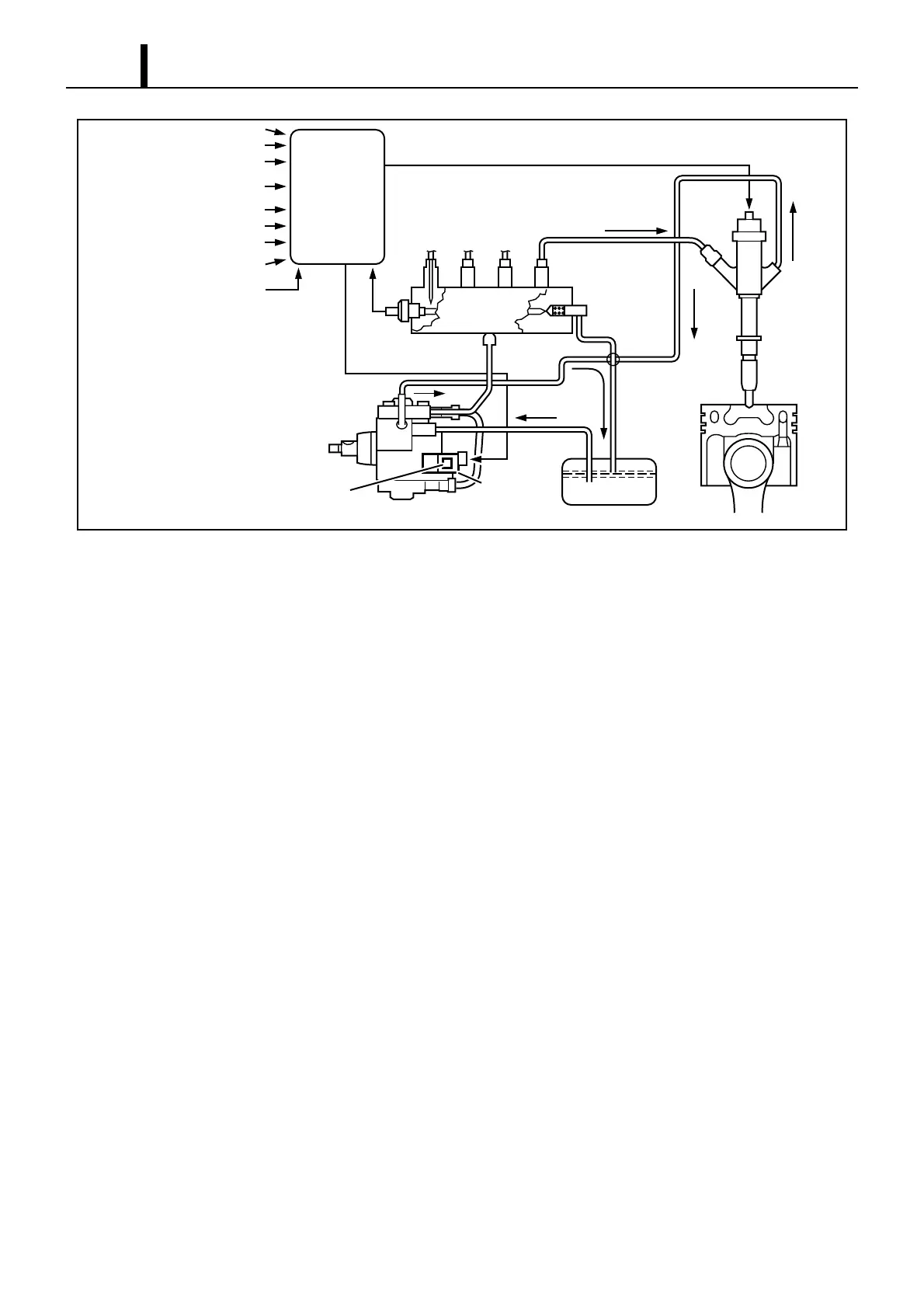
(1) Supply Pump (HP3)
• The supply pump draws fuel from the fuel tank, and pumps the high pressure fuel to the rail. The quantity of fuel discharged from the
supply pump controls the pressure in the rail. The SCV (Suction Control Valve) in the supply pump effects this control in accordance
with commands received from the engine ECU.
(2) Rail
• The rail is mounted between the supply pump and the injector, and stores the high-pressure fuel.
(3) Injector (G2 type)
• This injector replaces the conventional injection nozzle, and achieves optimal injection by effecting control in accordance with signals
from the engine ECU. Signals from the engine ECU determine the duration and timing in which current is applied the injector. This
in turn, determines the quantity, rate and timing of the fuel that is injected from the injector.
(4) Engine ECU
• The engine ECU calculates data received from the sensors to comprehensively control the injection quantity, timing and pressure, as
well as the EGR (exhaust gas recirculation).
2.6 Fuel System
z This system comprises the route through which diesel fuel flows from the fuel tank via the rail to the supply pump, and is injected
through the injector, as well as the route through which the fuel returns to the tank via the overflow pipe.
2.7 Control System
z In this system, the engine ECU controls the fuel injection system in accordance with signals received from various sensors. The com-
ponents of this system can be broadly divided into the following three types: (1) sensors; (2) ECU; and (3) actuators.
Fuel Temperature
Accelerator Opening
Turbo Pressure,
Atmospheric Air Pressure
Intake Airflow Rate
Rail Pressure
Sensor
Rail
Engine ECU
Fuel Temperature Sensor
Supply Pump
Fuel Tank
Injector
Pressure
Limiter
SCV
(Suction
Control Valve)
Intake Air Temperature
Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft position
Cylinder Recognition Position
Q001226E
Engine Speed
 Loading...
Loading...