Operation Section
1
–
81
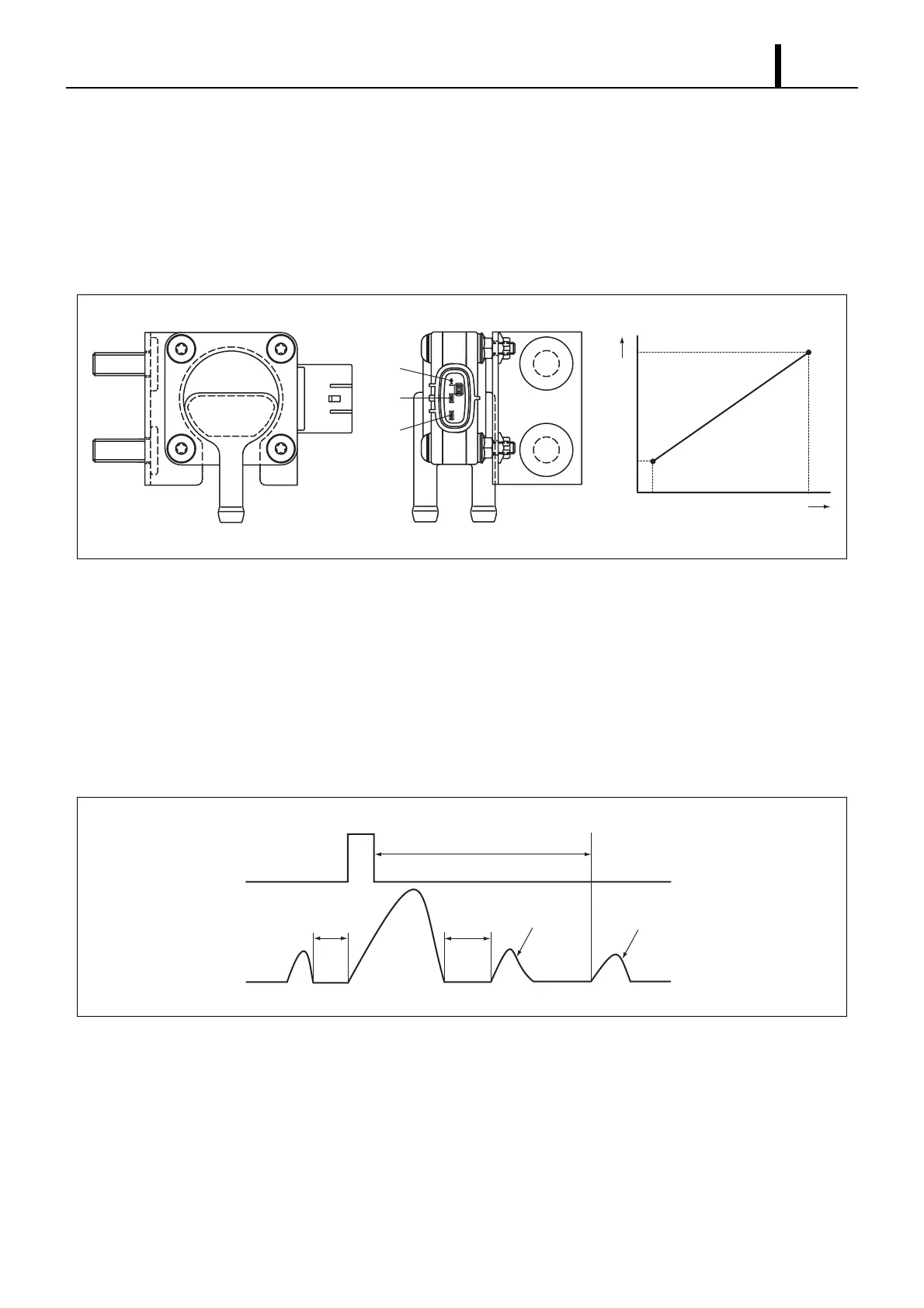
Differential Pressure Sensor
• The differential pressure sensor detects the difference in pressure at the front and rear of the DPF, and outputs a sig-
nal to the engine ECU. The sensor portion is a semiconductor type pressure sensor that utilizes the piezoelectric ef-
fect through a silicon element, and amplifies and outputs the voltage with its IC circuit. When PM is collected and
accumulated in the DPF, the filter clogs and the difference in pressure at the front and rear of the DPF increases.
Therefore, based on the signals from this sensor, the engine ECU judges whether or not to subject PM to combustion
processing.
(4) Operation
• By optimizing the injection pattern and controlling the exhaust gas temperature based on the exhaust gas temperature
and the difference in pressure at the front and rear of the DPF, PM is collected, oxidized, and self-combusted. When
the exhaust temperature is low, adding after-injection after the main injection raises the exhaust gas temperature to
approximately 250?C and promotes oxidation of the PM. When the PM is collected and accumulated, the post-injec-
tion is added and HC is added to the catalyst to raise the catalyst temperature to 600?C, which is the self-combustion
temperature for PM. This combusts the accumulated PM in a short time. The engine ECU controls the A, B, and C
times and the injection times.
Q000910E
GND
V
P
VC
Pressure (kPa)
Output Voltage
VP(V)
TDC A
B
C
After-Injection
Post-Injection
Q000506E
 Loading...
Loading...