Calculating charge times
The Chart Method
Use the followingtable to more accurately determine
the time it willtake to bdng a battery to full charge.
First, identify where your battery fits into the chart.
• Small batteries -- motorcycles, garden tractors, etc.
-- are usually rated in Ampere Hours (AH). For
example: 6 to 12 AH, or 12 to 32 AH.
• Batteries in cars and smaller trucks are usually rated
in Reserve Capacity (RC), Cold-Cranking Amps
(CCA), or both.
• Marine, or deep-cycle batteries are usually rated in
Reserve Capacity (RC).
• NR means that the charger setting is NOT RECOM-
MENDED.
Find your battery's rating on the chart below and note
the charge time given for each charger setting. The
times given are for batteries with a 50-percent
charge. Add more time for totally discharged batter-
ies.
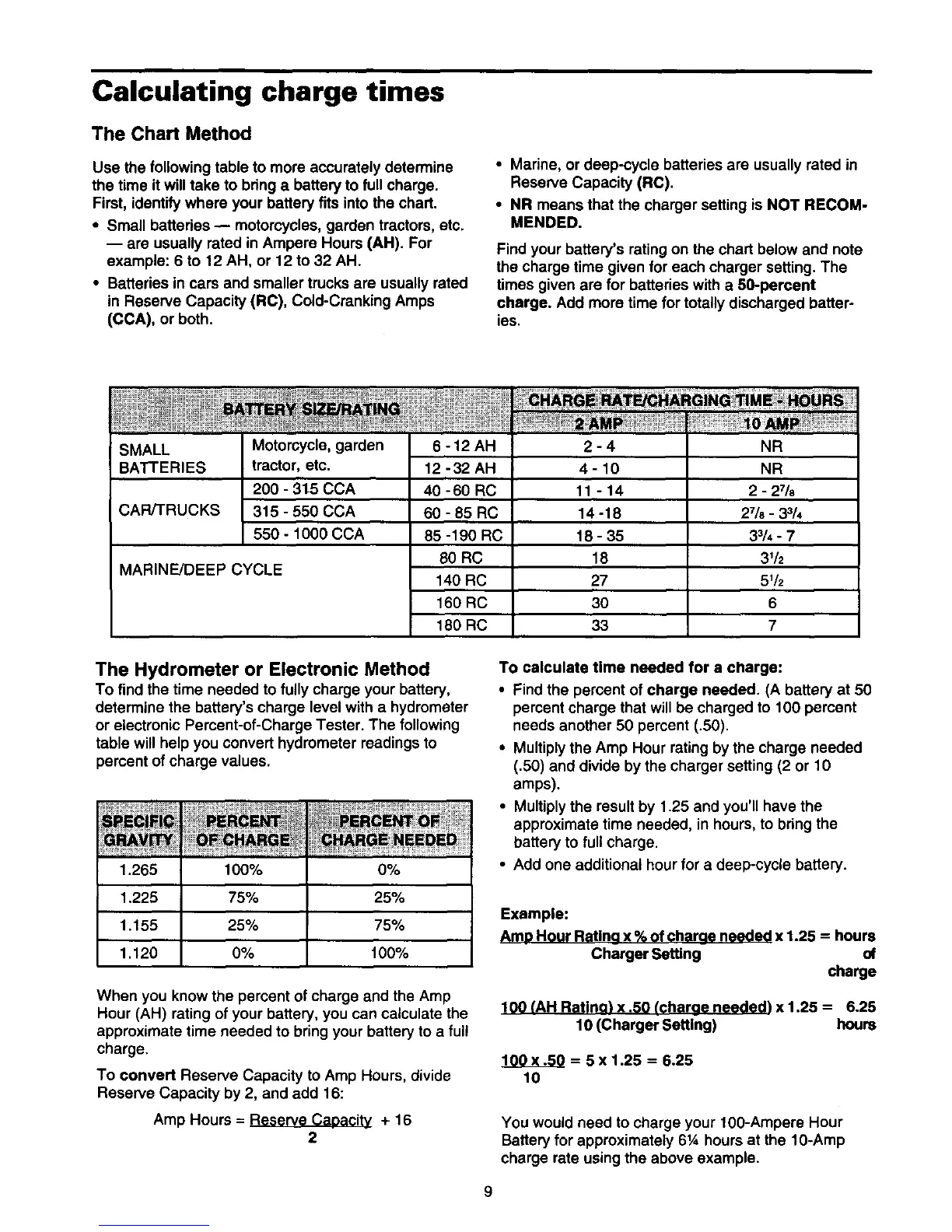
SMALL
BATTERIES
CAR/TRUCKS
Motorcycle, garden
tractor, etc.
200 - 315 CCA
315 - 550 CCA
550 - 1000 CCA
MARINE/DEEP CYCLE
6-12AH 2-4 NR
12-32 AH 4- 10 NR
40 -60 RC 11 - 14 2 - 27/8
60 - 85 RC 14 -18 27/8- 33/4
85 -190 RC 18 - 35 3s/4- 7
60 RC 18 31/2
140 RC 27 51/2
160 RC 30 6
180 RC 33 7
The Hydrometer or Electronic Method
To find the time needed to fully charge your battery,
determine the battery's charge level with a hydrometer
or electronic Pement-of-Charge Tester. The following
table will help you convert hydrometer readings to
percent of charge values.
1.265 100% 0%
1.225 75% 25%
1.155 25% 75%
1.120 0% t00%
When you know the percent of charge and the Amp
Hour (AH) rating of your battery, you can calculate the
approximate time needed to bring your battery to a full
charge.
To convert Reserve Capacity to Amp Hours, divide
Reserve Capacity by 2, and add 16:
Amp Hours = Reserve Caoacity + 16
2
To calculate time needed for a charge:
• Find the percent of charge needed. (A battery at 50
percent charge that will be charged to 100 percent
needs another 50 percent (.50).
• Multiplythe Amp Hour rating by the charge needed
(.50) and divide by the charger setting (2 or 10
amps).
• Multiply the result by 1.25 and you'll have the
approximate time needed, in hours, to bring the
battery to full charge.
• Add one additional hour for a deep-cycle battery.
Example:
Amo Hour Ratino x % of charoe needed x 1.25 -- hours
Charger Setting of
charge
100 (AH Ratlno) x .50 (¢haroe needed) x 1.25 = 6.25
10 (Charger Setting) hours
l_0_0.J_-_.-- 5 x 1.25 = 6.25
10
You would need to charge your 100-Ampere Hour
Battery for approximately 61/_hours at the 10-Amp
charge rate using the above example.

 Loading...
Loading...











