- 90 -
LP Engine G430(3.0L) LP Fuel System (Low Emission Version)
Engine Control Unit (ECU)
In order to obtain maximum effect from the catalyst,
an accurate control of the air fuel ratio is required.
The engine control unit (ECU) uses an exhaust gas
oxygen sensor (EGO) in the exhaust system to
send information about exhaust gas content to the
controller. The controller then calculates any
corrections that may need to be made to the air fuel
ratio. The controller makes these corrections to the
air fuel ratio by manipulating the inlet fuel pressure
to the carburetor through the fuel control valve(s)
(FCV). Reducing the fuel pressure leans the air/fuel
mixture. Increasing the fuel pressure richens the
air/fuel mixture.
The controller uses engine exhaust gas oxygen
sensor (EGO), engine speed (tachometer signal)
and manifold absolute pressure sensors (MAP), to
regulate the air/fuel mixtures, correcting for proper
air/fuel ratios on different system configuration and
in different operating modes. The fuel control valve
(FCV) meters air valve vacuum (AVV) into the
atmospheric reference side of the secondary
regulator diaphragm. The atmospheric reference
vent orifice allows for the controlled depletion of the
vacuum over the diaphragm, this assists the
dynamic response of the diaphragm.
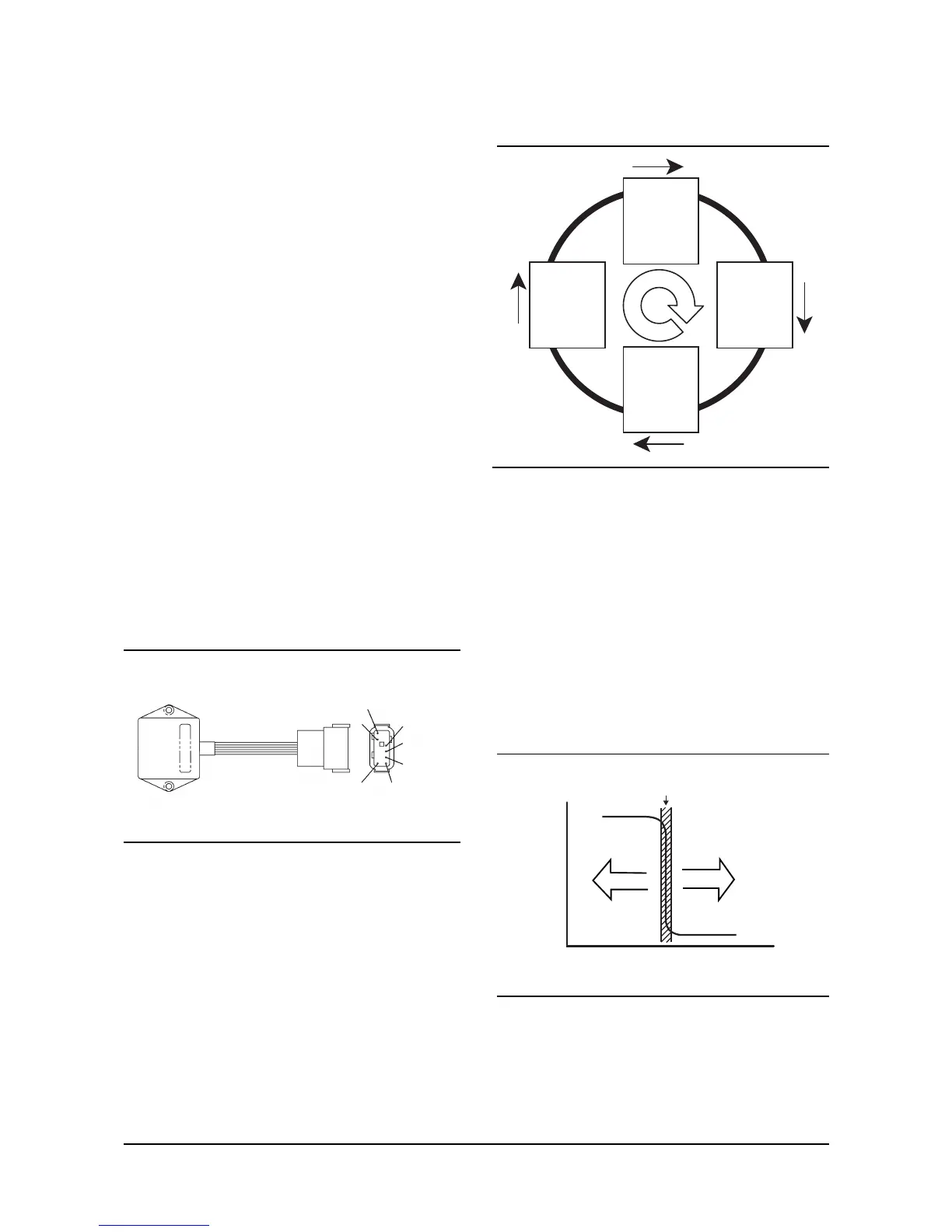
When the EGO sends a voltage signal above 500
mv the controller interprets the fuel mixture to be
rich. The controller increases the duty cycle of the
FCV allowing more AVV to act on the atmospheric
side of the secondary regulator diaphragm, which
causes a reduction in regulator output pressure. As
the regulator output pressure is reduced the air/fuel
mixture is enleaned.
When the EGO sensor sends a voltage signal less
than 500 mv the controller interprets the fuel
mixture to be lean. The controller decreases the
duty cycle of the FCV lowering the amount of AVV
acting on the atmospheric side of the secondary
regulator diaphragm, which causes an increase in
the regulator output pressure. As the regulator
output pressure is
increased, the air/fuel mixture becomes enriched.
The closed loop fuel controller is constantly
targeting the ideal air/fuel mixture.
The electronic closed loop system utilizes a
feedback (FB) mixer. FB mixers are engineered
slightly rich of stoichiometric and the air/fuel mixture
is pulled back lean by manipulating the regulator
output pressure with the variable vacuum signal
from the FCV.
 Loading...
Loading...