MAINS OPERATION & RESULTING TEMPERATURE
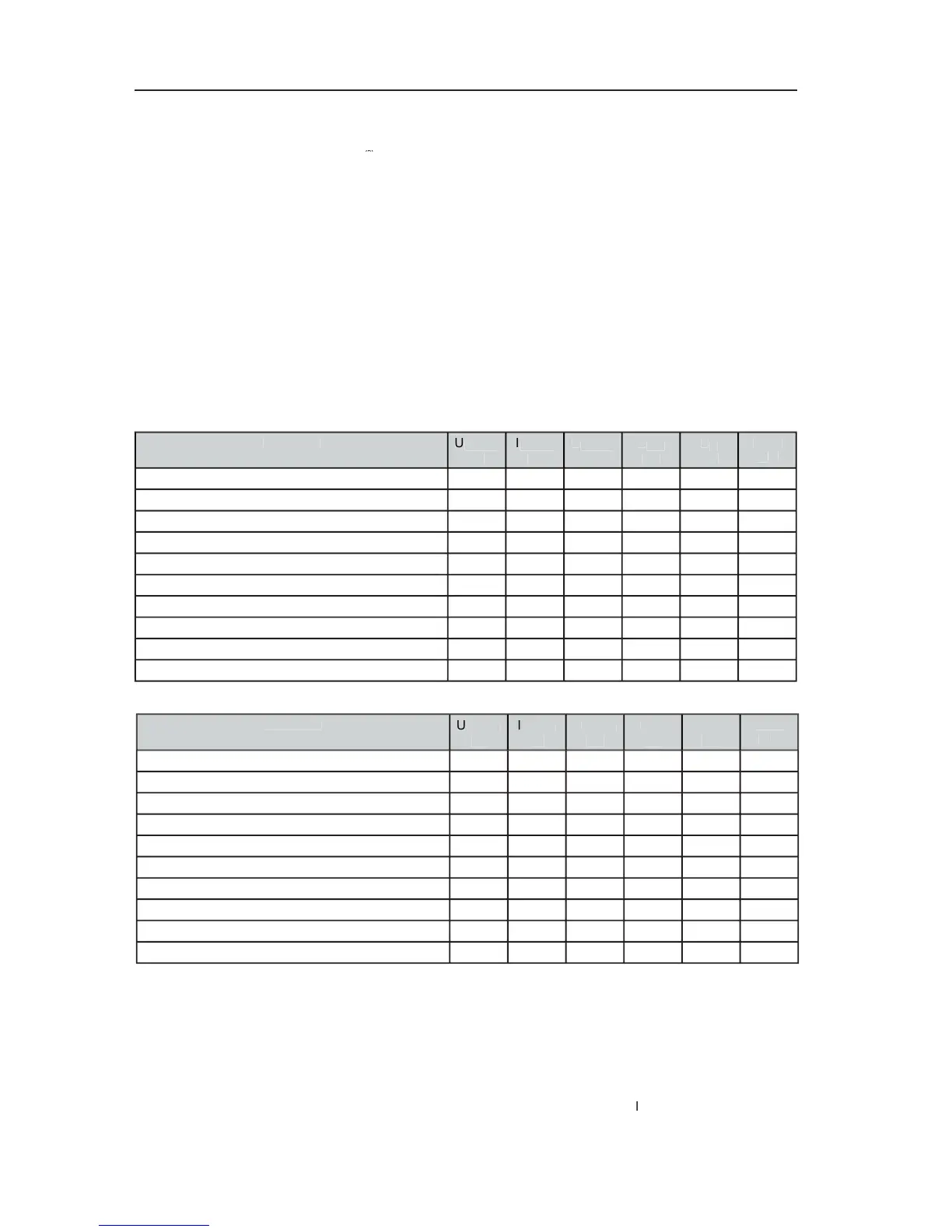
The following tables provide a useful aid in determining power supply and cabling requirements. Column
“1/8 max. output power into 4 ohms
The following tables provide a useful aid in determining power supply and cabling requirements. Column
(2)
The following tables provide a useful aid in determining power supply and cabling requirements. Column
” states the values to be used for normal operation. These results
were measured with the power ampli er being operated at maximum output and a Pink Noise signal
according to EN60065 applied at the input, which approximately represents the strain of an audio signal
driving the power amp at maximum modulation.
Temperatures inside of the power ampli er
The power drawn from the mains network is converted into acoustic output to feed the connected
loudspeaker systems plus heat. The difference between drawn power and dispensed power is referred
to as leakage power or dissipation (P
). The amount of heat resulting from power dissipation might
remain inside of a rack-shelf and needs to be diverted using appropriate measures. The following table
is meant as auxiliary means for calculating temperatures inside of a rack-shelf system/cabinet and the
ventilation efforts necessary.
” lists the leakage power in relation to different operational states. The column “BTU/hr”
shows the dispensed heat amount per hour.
Max. output power into 8ohms
Max. output power into 4ohms
1/3 max. output power into 4ohms
1/8 max. output power into 4ohms
1/8 max. output power into 4ohms
1/8 max. output power into 4ohms
Normal Mode (-10dB) into 4ohms
Rated output power (0dB, rated) into 4ohms
Alert-Mode (-3dB) into 4ohms
Max. output power into 8ohms
Max. output power into 4ohms
1/3 max. output power into 4ohms
1/8 max. output power into 4ohms
1/8 max. output power into 4ohms
1/8 max. output power into 4ohms
Normal Mode (-10dB) into 4ohms
Rated output power (0dB, rated) into 4ohms
Alert-Mode (-3dB) into 4ohms
Pink noise acc. to EN60065
1BTU = 1055.06J = 1055.06Ws
The following factors allow direct proportional calculation of the mains current (
supply voltages: 100V = 2,3; 120V = 1,9; 220V = 1,05; 240V = 0,96

 Loading...
Loading...