6 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
0463 815 101 - 63 - © ESAB AB 2021
6.6 TIG (L-GTAW) basic welding technique
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (L-GTAW) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) is a welding process in which
fusion is produced by an electric arc that is established between a single tungsten (non-
consumable) electrode and the workpiece. Shielding is obtained from a welding grade shielding
gas or welding grade shielding gas mixture which is generally Argon based. A filler metal may
also be added manually in some circumstances depending on the welding application.
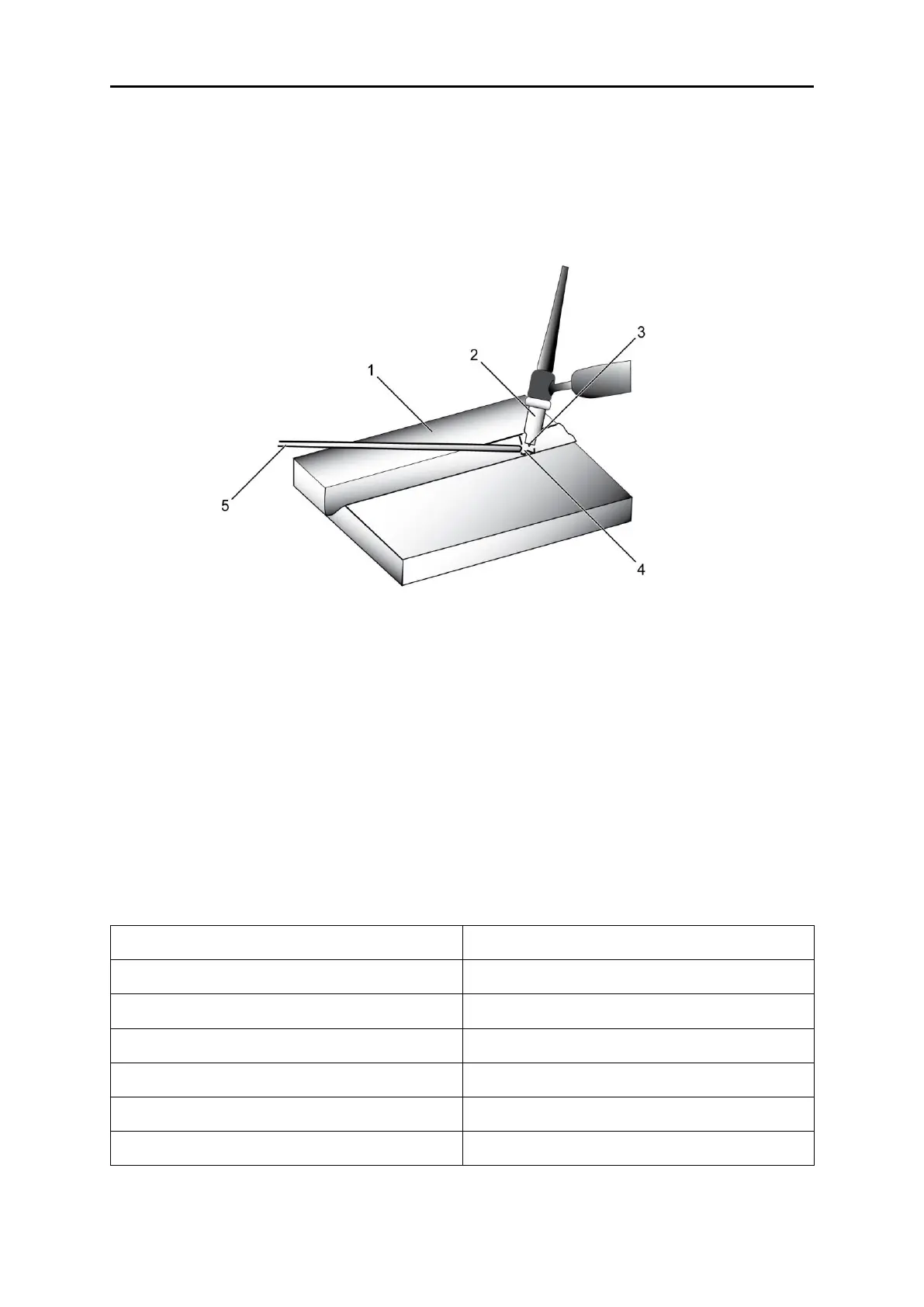
Figure 75: TIG (L-GTAW) welding application
1 Workpiece 4 Inert gas
2 Gas cup 5 Filler metal
3 Tungsten electrode
• Workpiece
Can be any commercial metal
• Gas cup
Either ceramic, high-impact or water cooled metal
• Tungsten electrode Non-consumable • Inert gas
Shields electrode and weld puddle
• Filler metal
Welds are made with or without addition of filler metal
Tungsten electrode current ranges
Table 15: Current ranges for various tungsten electrode sizes
 Loading...
Loading...