Theory of thermography
20
where:
W
λb
Blackbody spectral radiant emittance at wavelength λ.
c
Velocity of light = 3 × 10
8
m/s
h Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10
-34
Joule sec.
k
Boltzmann’s constant = 1.4 × 10
-23
Joule/K.
T Absolute temperature (K) of a blackbody.
λ Wavelength (μm).
Note The factor 10
-6
is used since spectral emittance in the curves is expressed in Watt/
m
2
, μm.
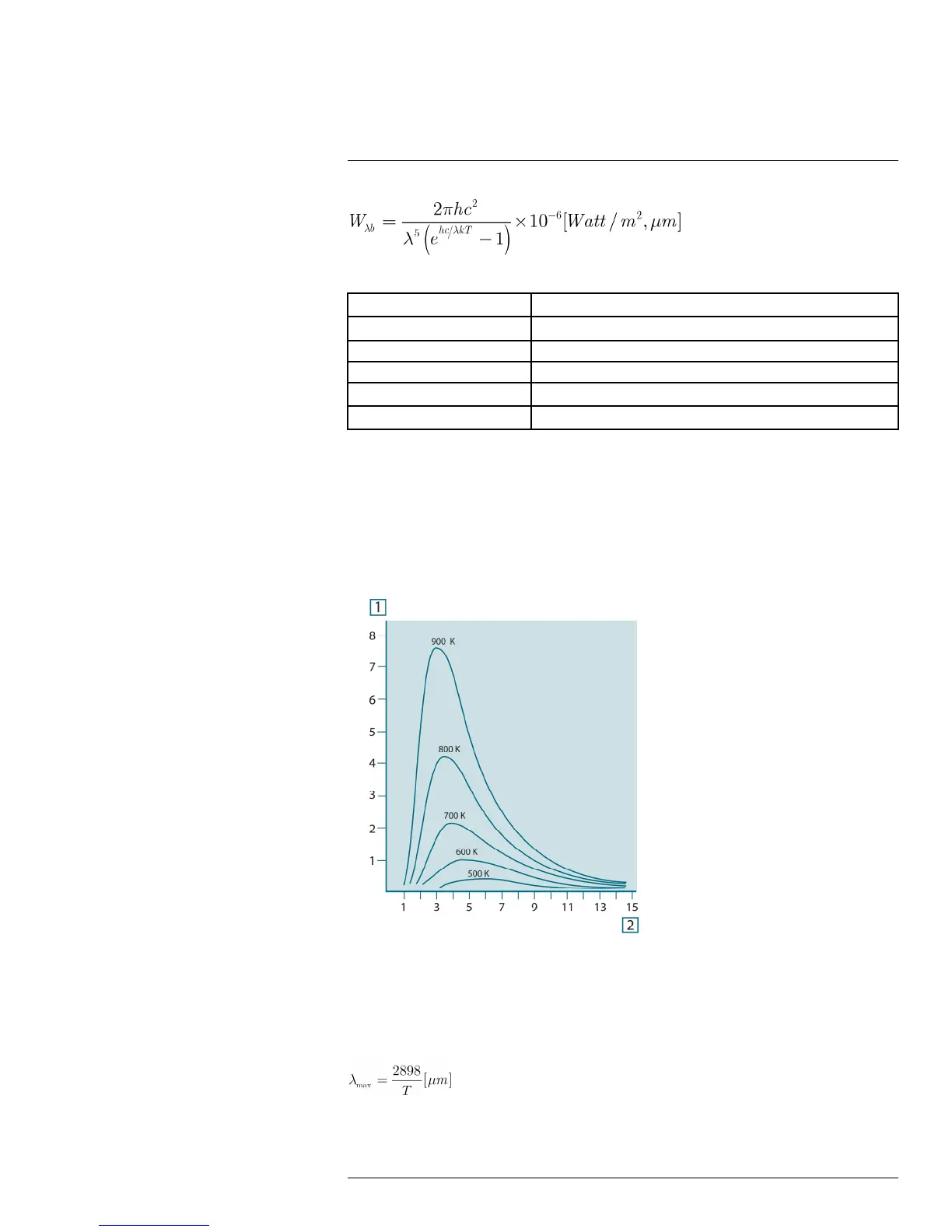
Planck’s formula, when plotted graphically for various temperatures, produces a family of
curves. Following any particular Planck curve, the spectral emittance is zero at λ = 0, then
increases rapidly to a maximum at a wavelength λ
max
and after passing it approaches zero
again at very long wavelengths. The higher the temperature, the shorter the wavelength at
which maximum occurs.
Figure 20.4 Blackbody spectral radiant emittance according to Planck’s law, plotted for various absolute
temperatures. 1: Spectral radiant emittance (W/cm
2
× 10
3
(μm)); 2: Wavelength (μm)
20.3.2 Wien’s displacement law
By differentiating Planck’s formula with respect to λ, and finding the maximum, we have:
#T559770; r. AF/30726/30726; en-US
123

 Loading...
Loading...