22 Theory of thermography
22.1 Introduction
The subjects of infrared radiation and the related technique of thermography are still
new to many who will use an infrared camera. In this section the theory behind ther-
mography will be given.
22.2 The electromagnetic spectrum
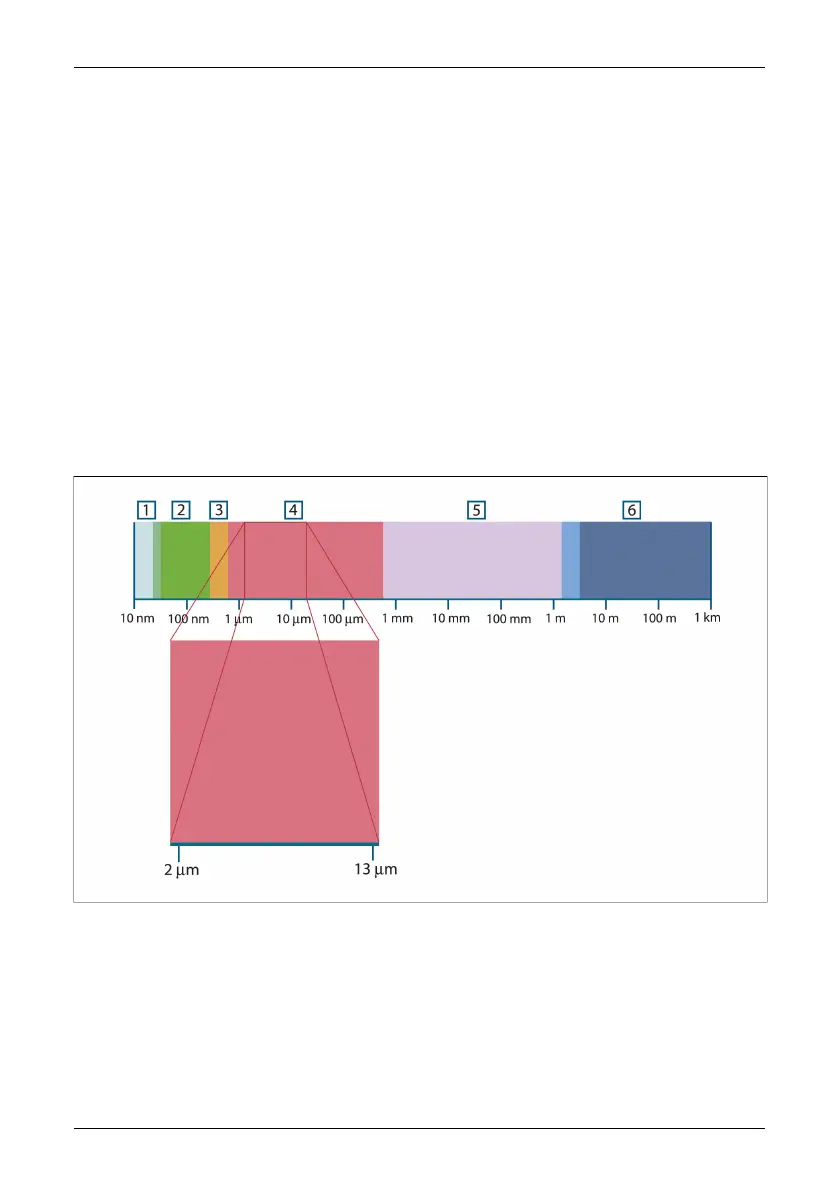
The electromagnetic spectrum is divided arbitrarily into a number of wavelength re-
gions, called bands, distinguished by the methods used to produce and detect the
radiation. There is no fundamental difference between radiation in the different bands
of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are all governed by the same laws and the
only differences are those due to differences in wavelength.
10067803;a1
Figure 22.1 The electromagnetic spectrum. 1: X-ray; 2: UV; 3: Visible; 4: IR; 5: Microwaves; 6: Radiowaves.
Thermography makes use of the infrared spectral band. At the short-wavelength end
the boundary lies at the limit of visual perception, in the deep red. At the long-wave-
length end it merges with the microwave radio wavelengths, in the millimeter range.
The infrared band is often further subdivided into four smaller bands, the boundaries
of which are also arbitrarily chosen. They include: the near infrared (0.75–3 μm), the
middle infrared (3–6 μm), the far infrared (6–15 μm) and the extreme infrared (15–100
136 Publ. No. T559382 Rev. a358 – ENGLISH (EN) – June 23, 2009

 Loading...
Loading...