Operation
33
SecoVac 3.3kV-27kV Embedded Pole Vacuum Circuit Breaker
Working Principle
Working Principle of Operating
Mechanism
The vacuum gas pressure inside vacuum interrupter is less than
1.33×10
-3
Pa. Under normal circuit conditions the interrupter is
closed. Arcing is established within the interrupter by withdrawing
the moving contact from stationary contact. This arc burns in
the metal vapor evaporated from local hot spots on the contact
surfaces. The metal vapor continually leaves the inter-contact
region and recondenses on the contact surfaces and surrounding
metal vapor condensation shield. The latter is usually isolated
from both contacts and serves to protect the glass or ceramic
envelope from vapor deposition. At current zero, vapor production
ceases and the original vacuum condition is rapidly approached.
The dielectric strength of the interrupter also increases, and the
circuit is interrupted. Within the contacts in the open position, the
circuit voltage is withstood internally by the inter-contact gap
and externally by the insulating envelope.
The energy that is necessary for closing the circuit breaker is
provided by the closing spring. The energy storage can be done
by the motor or by the manual charging handle.
Motor spring charging
The energy charging mechanism consists of energy storing
motor, gear wheel, cam, holder and closing spring. When the
energy-storing motor (11) is charged, the pinion of output shaft
(12) that is connected to motor will rotateand drive the gear
on the shaft move, which then drive the shaft to rotate, so that
draws out the closing spring (17) for storing energy. When the
block on the gear wheel is pushed away, the clutch is separated
mechanism in charged position, thus completing the charging
operation succeeds.
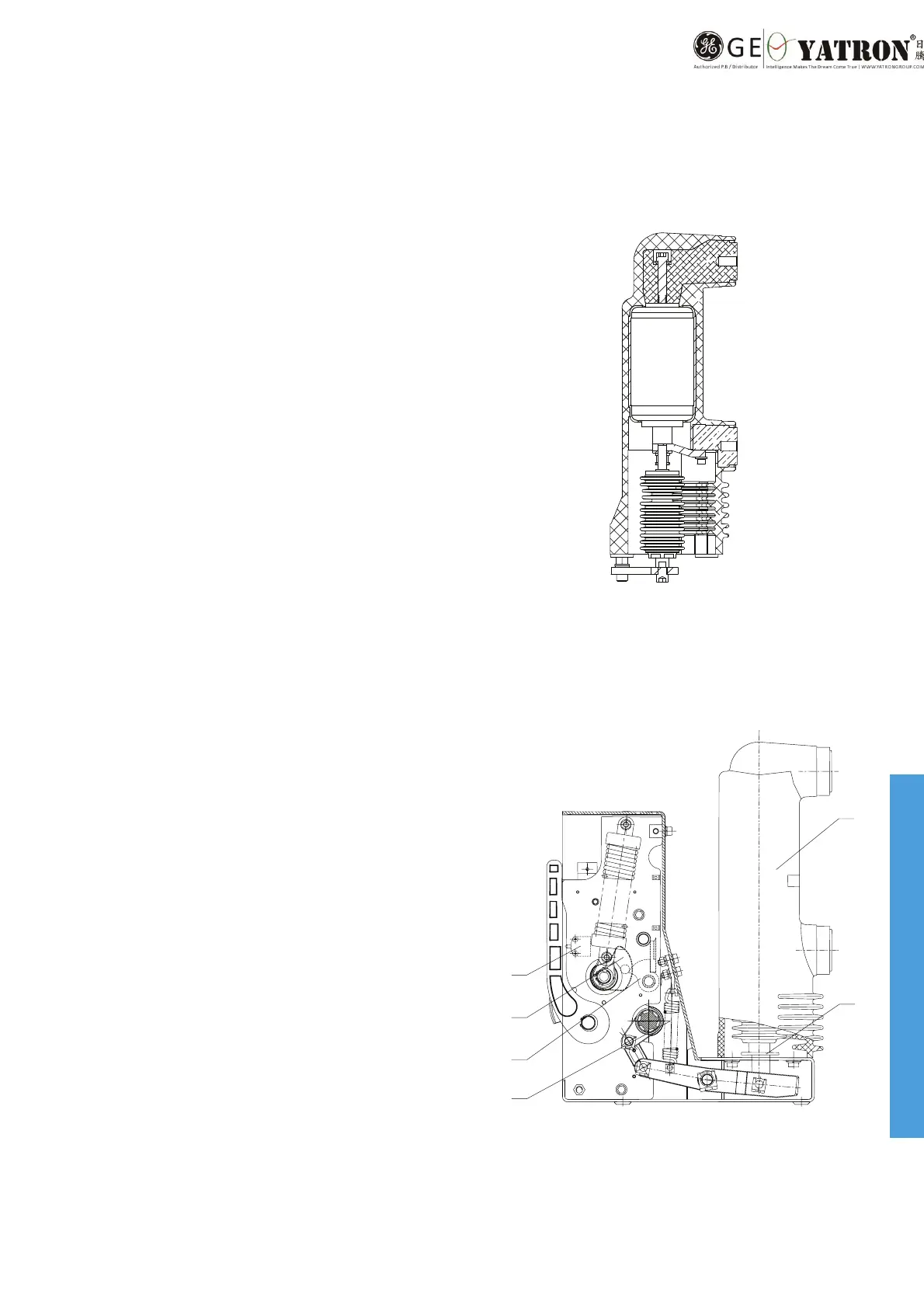
Vacuum interrupter
Motor spring charging
1
2
3
4
5
6
Figure 3.
1 Embedded pole
2 Insulating rod
3 Opening spring
4 Holder
Cam
6 Position switch

 Loading...
Loading...