10
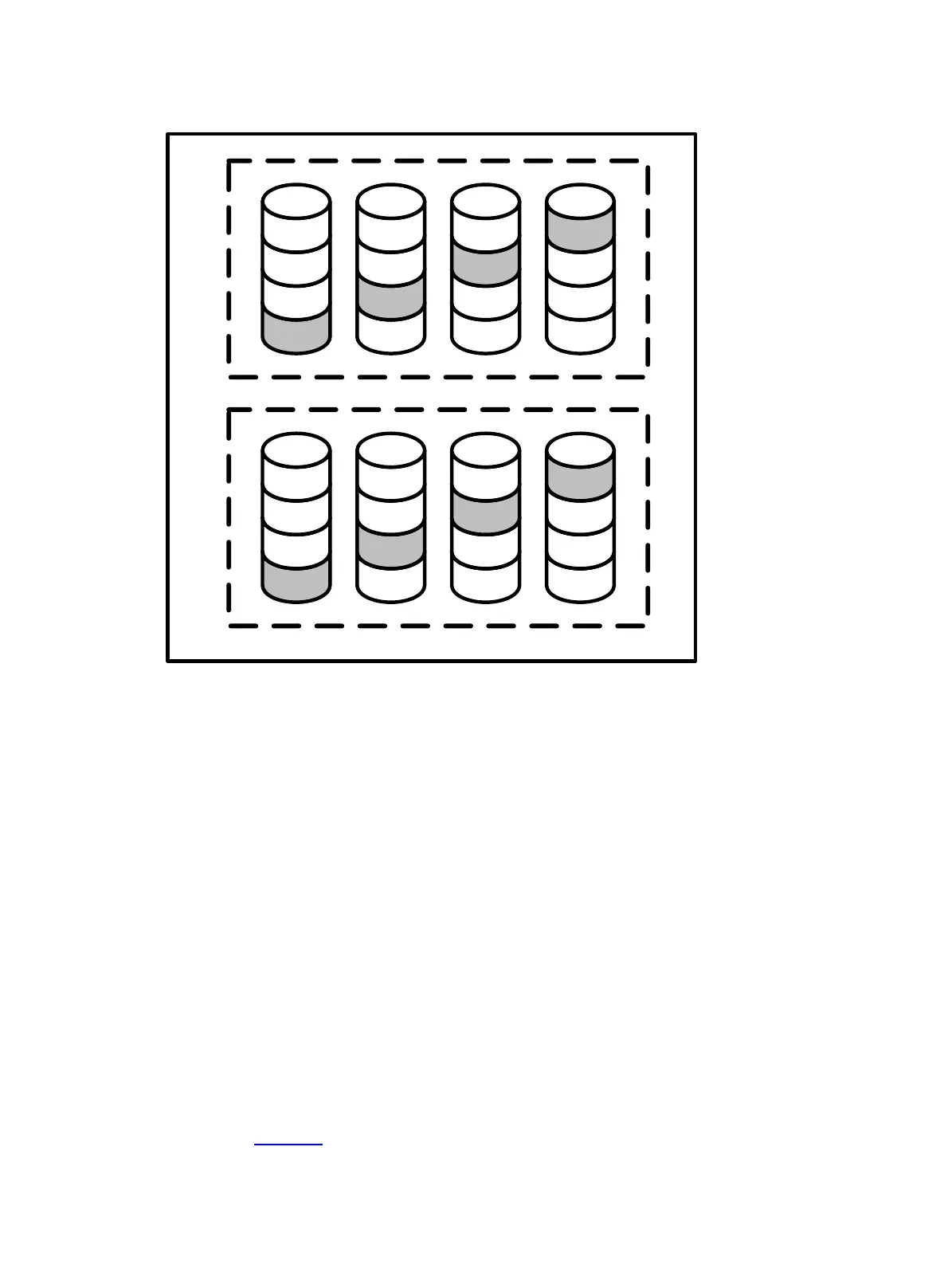
Figure 11 RAID 50
For any given number of drives, when the most parity groups are configured, the data loss
probability is the lowest. For example, if 12 drives are used, configuring four parity groups is more
secure than three parity groups. However, the more parity groups are configured, the less data can
be stored on the array.
Application scenarios
RAID 50 is useful in large-sized databases, file servers, and application servers.
Advantages
Has higher performance (especially write performance) than RAID 5.
Has higher fault tolerance performance than RAID 0 and RAID 5.
No data is lost even up to n (the number of parity groups) physical drives fail as long as the
failed drives are in different parity groups.
Disadvantages
Data is lost if a second drive in a parity group fails before data from the first failed drive in the
parity group is rebuilt.
More drive capacity is used for saving redundant or parity data than non-nested RAID levels.
RAID 60
As shown in Figure 12, RAID 60 is a nested RAID level combining RAID 6 and RAID 0. Member
drives are organized into several same RAID 6 logical drive groups (parity groups). RAID 60
PD
C
1
B1
A1
D
1
PC
B
2
A
2
D
2
C
2
PB
A
3
D
3
C
3
B
3
PA
QD
C
4
B
4
A
4
D
4
QC
B
5
A
5
D
5
C
5
QB
A
6
D
6
C
6
B
6
QA
S
1
S
2
S
3
S
4
S
1
S
2

 Loading...
Loading...