– 79 –
5V
Reset circuit
Reset voltage
Peak current cut
off circuit
Trip signal
synthesis circuit
Chopper signal
Chopper
signal
Reset Signal
Ip signal (interrupt signal)
Overload external
set value circuit
DC current level
Voltage amp.
circuit
Detection
resistor
R806
DC current
Outdoor
micro
computer
(AX-8E21)
Drive
signal
Com-
pressor
motor
DC current
Power module
photocoupler
DC 260V
_
290V
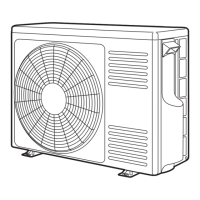
Fig. 8 - 2
18A
0.9V
Voltage at point
Micro computer
Voltage at pin
Voltage at point
DC current (ld)
POR
Ip
Micro
computer
AX-8E21
chopper
23
22
5V
0V
0V
C
B
A
Q1
(A)
57
45
44
30
56
7
32
0V
0V 0V
A
0V
0V
5V
5V
R1
Normal Hi
Upper arm Drive circuit
Lower arm Drive circuit
DC current
(current detection
resistor)
0V
0V
COM 1 (2/4)
0V
R202
R201
Normal Hi
5V
R806
D201
C202
31
23
C
HIC - 1
Fig. 8 - 3 Peak current cut off circuit and Waveforms at Each Section
+
-
+
-
!
@
● The following describes the operations of each circuit in detail.
(1) Peak current cut (Ip) off circuit
Fig.8-3 shows the Peak Current Cut off Circuit and Waveforms at Each Section.
● Ip cut off circuit detects an instantaneous large current and stops drive output signal to protect parts such
as power module, etc.
● As shown in the figure, when current exceeding 18A flows, voltage at point A detected by detection
resistor is input to e terminal of COM (A). If it exceeds d terminal voltage, which is the set value, output
pin voltage (point B) of COM (A) changes from Lo to Hi. Thus, Q1 is turned ON to stop drive curcuit and,
at the same time, voltage at point C changes from Hi to Lo to send Ip signal to pin ™ of microcomputer
(observed by pin º of HIC) and microcomputer stops drive.
● On the other hand, e terminal voltage is pulled up by R1, and DC current becomes 0A. Even when voltage
at point A returns to 0V, (power is not supplied - current value of zero), Output is temporarily held in Hi
state since voltage at - terminal is high. (memory function).
● Just before drive signal is output the next time, Microcomputer switches pin £ from Hi to Lo (observed
by pin ⁄ of HIC), so that e terminal voltage < d terminal voltage to release memory function and return
to initial state.
 Loading...
Loading...