Drive arrays and fault-tolerance methods 109
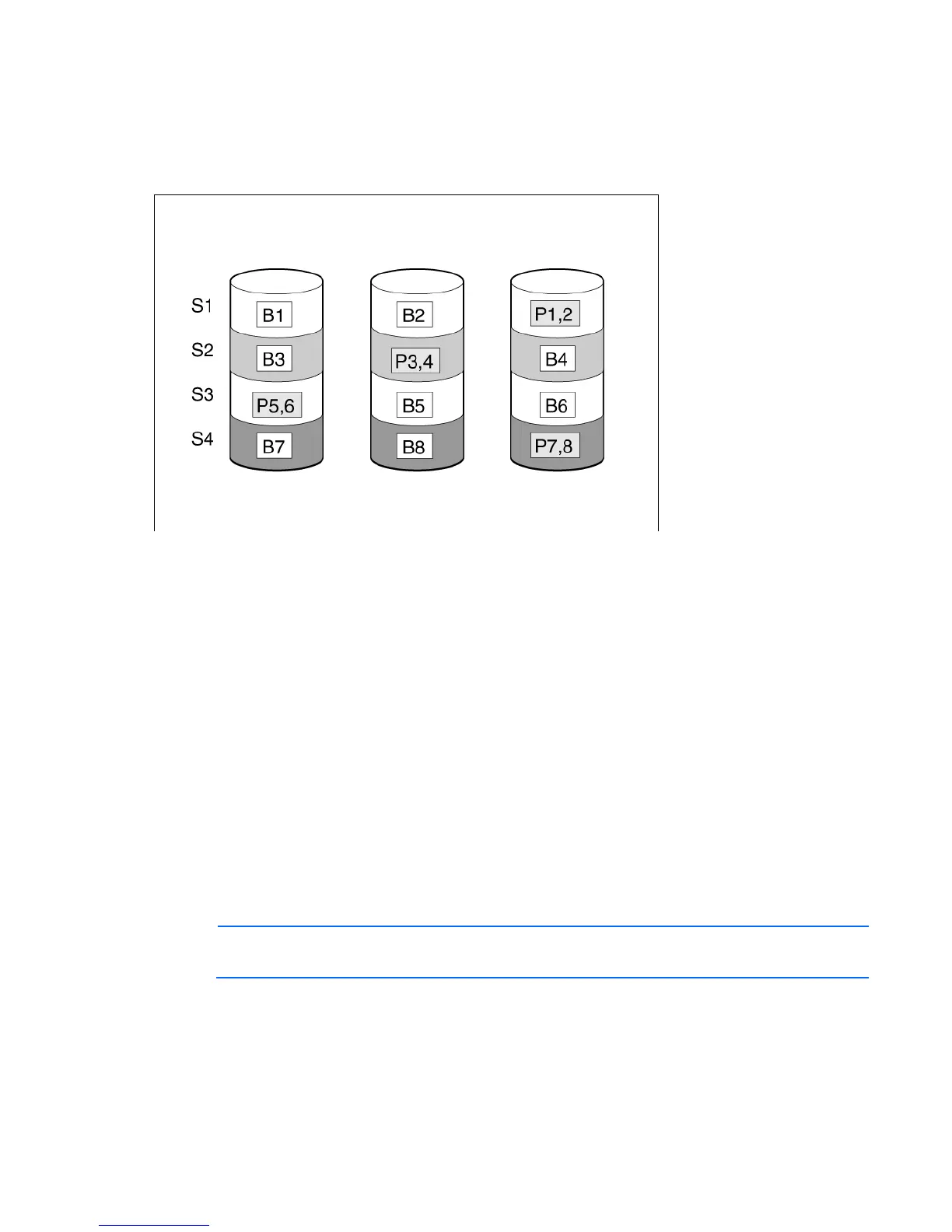
RAID 5—distributed data guarding
In a RAID 5 configuration, data protection is provided by parity data (denoted by Px,y in the figure). This
parity data is calculated stripe by stripe from the user data that is written to all other blocks within that stripe.
The blocks of parity data are distributed evenly over every physical drive within the logical drive.
When a physical drive fails, data that was on the failed drive can be calculated from the remaining parity
data and user data on the other drives in the array. This recovered data is usually written to an online spare
in a process called a rebuild.
This configuration is useful when cost, performance, and data availability are equally important.
Advantages:
• Has high read performance.
• Data is not lost if one physical drive fails.
• More drive capacity is usable than with RAID 1+0—parity information requires only the storage space
equivalent to one physical drive.
Disadvantages:
• Has relatively low write performance.
• Data is lost if a second drive fails before data from the first failed drive is rebuilt.
RAID 6 (ADG)—Advanced Data Guarding
NOTE: Not all controllers support RAID 6 (ADG).

 Loading...
Loading...