Hytera DMR System Planner
14
the repeater and the public switched telephone network (PSTN) respectively,
achiving its communications with a specific phone. The call ends when the radio
sends the de-access code or when the phone is hung up. Like the call between
the radios, the call between the radio and the phone is subject to time limit.
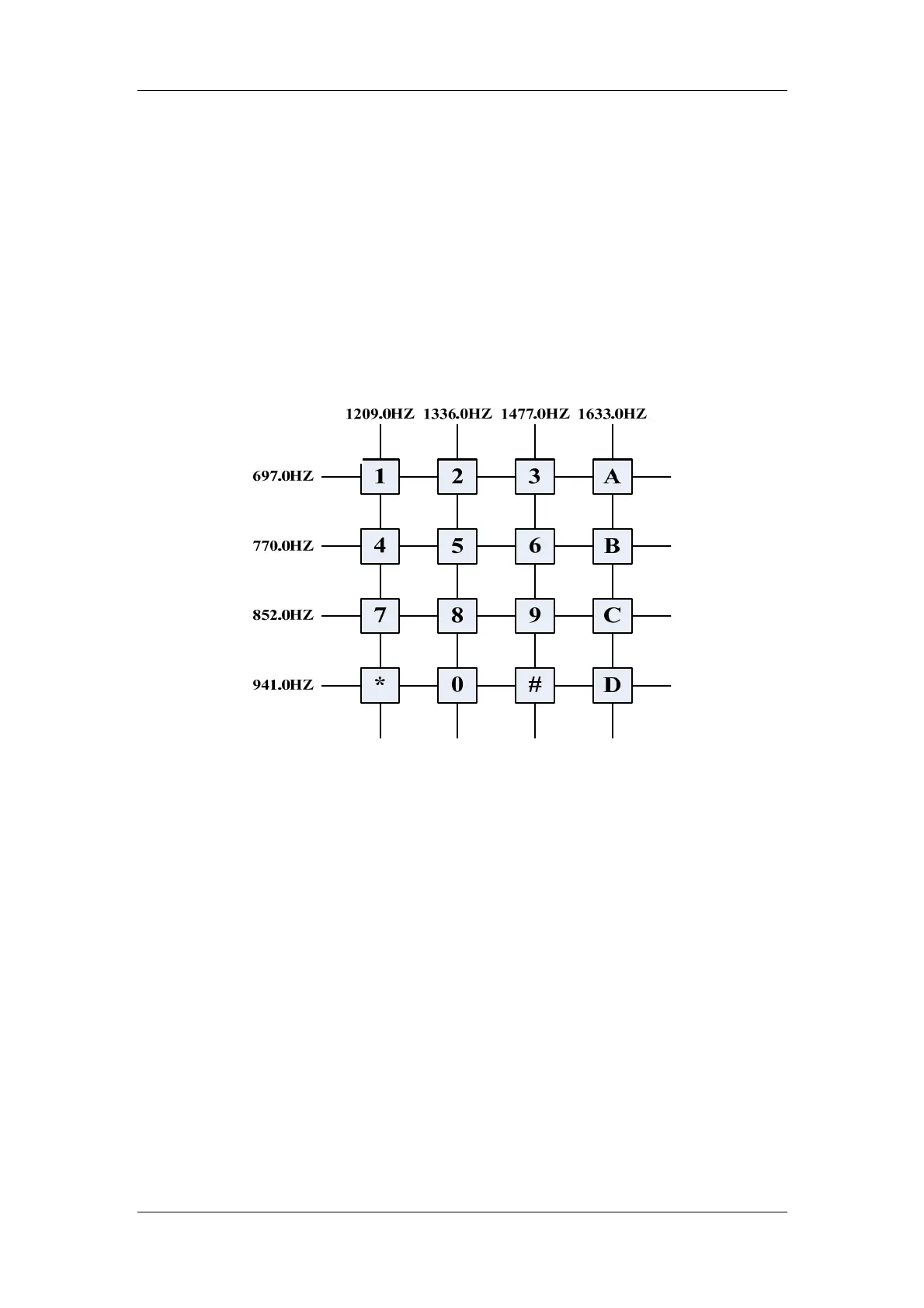
The DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) encoding technology uses two sepcific
tones (high and low) to represent a number (as shown in the following figure), so as
to realize some features. It is often designed with 16 keys (numeric keys 0~9 and
function keys *, #, A, B, C and D). As the DTMF code consists of a high frequency
(f1) and a low frequency (f2), the equation of corresponding signal is:
F(t)=A.sin(2.pi.f1.t)+A.sin(2.pi.f2.t).
Figure 2.2.4-3: Tone Combination for DTMF
Note: A, B, C, D, and the pause code (“P”) only can be input via the CPS.
There are two dialing methods including live dial and buffer dial.
Live Dial: During the voice transmission via PTT, the radio will send the
corresponding DTMF code immediately after you enter a digit via the keypad, like
dialing the number on the phone. When you release PTT, the radio will stop the
transmission. When making Live Dial operation, press the programmed key to
transmit the access code.
Buffer Dial: Enter the needed DTMF code and then hold down PTT to transmit it,
like dialing on the mobile phone. This method works only when you enable the
DTMF keypad mode. You can enable the DTMF keypad via the CPS or the radio
menu.
In analog mode, the radio will load the carrier with the DTMF code and transmit the
Low frequency
High frequency

 Loading...
Loading...