7-6
7.3 Measurement of Electrical Amounts in Main Circuit
Because the voltage and current of the power supply (input) of the main circuit of the inverter and the
output (motor) include harmonic components, the indicated value deviates according to the type of
the meter. Use meters indicated in Table 7.3 when measuring with meters for commercial
frequencies.
The power factor cannot be measured by a commercially available power-factor meter that
measures the phase difference between the voltage and current. To obtain the power factor,
measure the power, voltage and current on each of the input and output sides and calculate in the
following formula.
Three-phase input Single-phase input
%100×
(A)t(V)×Curren×Voltage3
(W)powerElectric
=factorPower
%100×
(A)t(V)×CurrenVoltage
(W)powerElectric
=factorPower
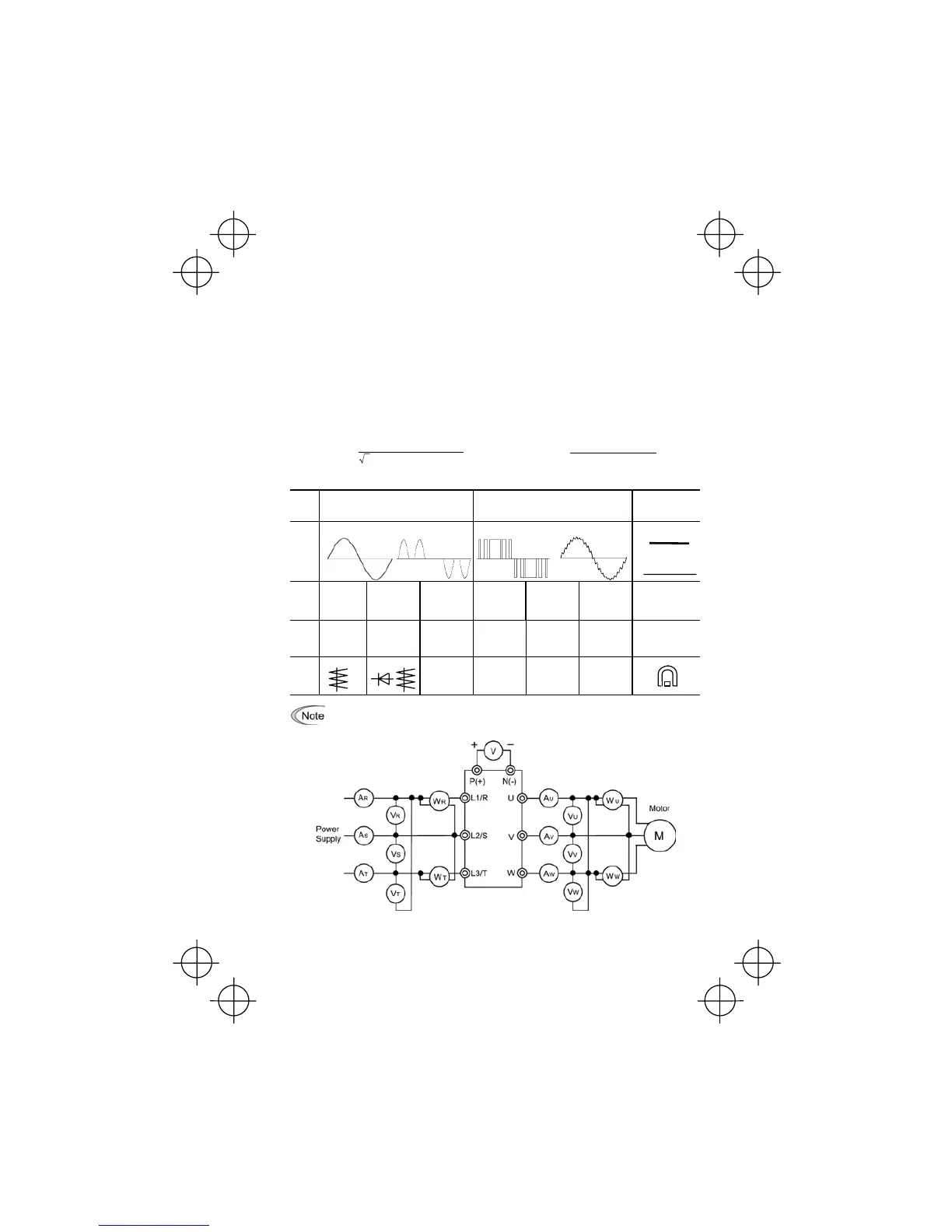
Table 7.3 Meters for Measurement of Main Circuit
Item
Input (power supply) side Output (motor) side
DC link circuit
voltage
(P (+)-N (-))
Waveform
Voltage Current Voltage Current
Name of
meter
Ammeter
A
R
, A
S
, A
T
Voltmeter
V
R
, V
S
, V
T
Wattmeter
W
R
, W
T
Ammeter
A
U
, A
V
, A
W
Voltmeter
V
U
, V
V
, V
W
Wattmeter
W
U
, W
W
DC voltmeter
V
Type of
meter
Moving iron
type
Rectifier or
moving iron
type
Digital power
meter
Digital power
meter
Digital power
meter
Digital power
meter
Moving coil type
Symbol
of meter
When the output voltage is measured by a rectifier type voltmeter, an error may be included
or the voltmeter might be burn out. To measure it with higher accuracy, use a digital AC
power meter.
Figure 7.1 Connection of Meters
 Loading...
Loading...