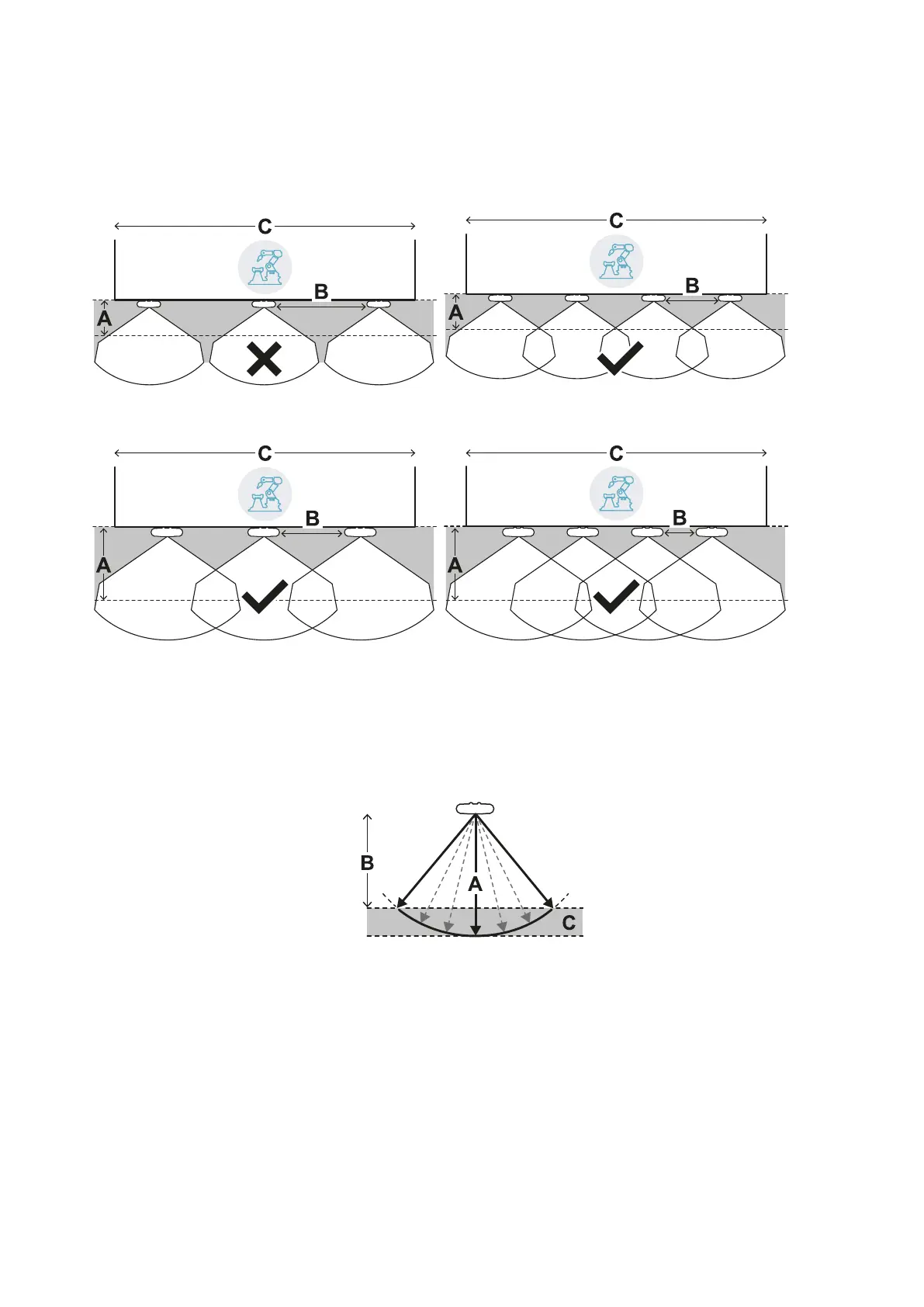
6.3.1 Distance between sensors and number of sensors
The depth of the area to be monitored [A] determines the maximum distance between the sensors [B] and
therefore the number of sensors necessary to cover the width of the dangerous area [C]. The deeper the
area, the greater the possible distance between the sensors, and therefore a lower number of sensors is
necessary.
Example of lower depth
Example of greater depth
6.3.2 Tolerance area
The sensor works in the radial direction, therefore detection distance [A] is the same no matter what angle
the motion is detected from. Defining the dangerous area (and pre-alarm area) with a linear distance [B], a
tolerance area [C] is generated at the periphery of the stopping area (and pre-alarm area) subject to false
alarms because it exceeds the area of interest.
The machinery designer must enclose the tolerance area to prevent transit in the area and thus avoid false
alarms.
The tolerance area is calculated and provided by the Inxpect Safety application.
6. Applications
LBK System| Instruction manual v1.3 SEP 2019 |LBK-System_instructions_en v1.3|© 2018-2019 Inxpect SpA
39
 Loading...
Loading...