Quick Results Guide 9
NOTE
Ohms guard cannot be used for high current (>100mA) ranges. Ohms guard cannot
be selected if already on a high current range. Conversely, if ohms guard is already
selected, a high current range cannot be selected.
The following menu sequence selects ohms guard:
Press CONFIG > press MEAS
Ω
(or SOURCE V or SOURCE I) > select GUARD > select
OHMS
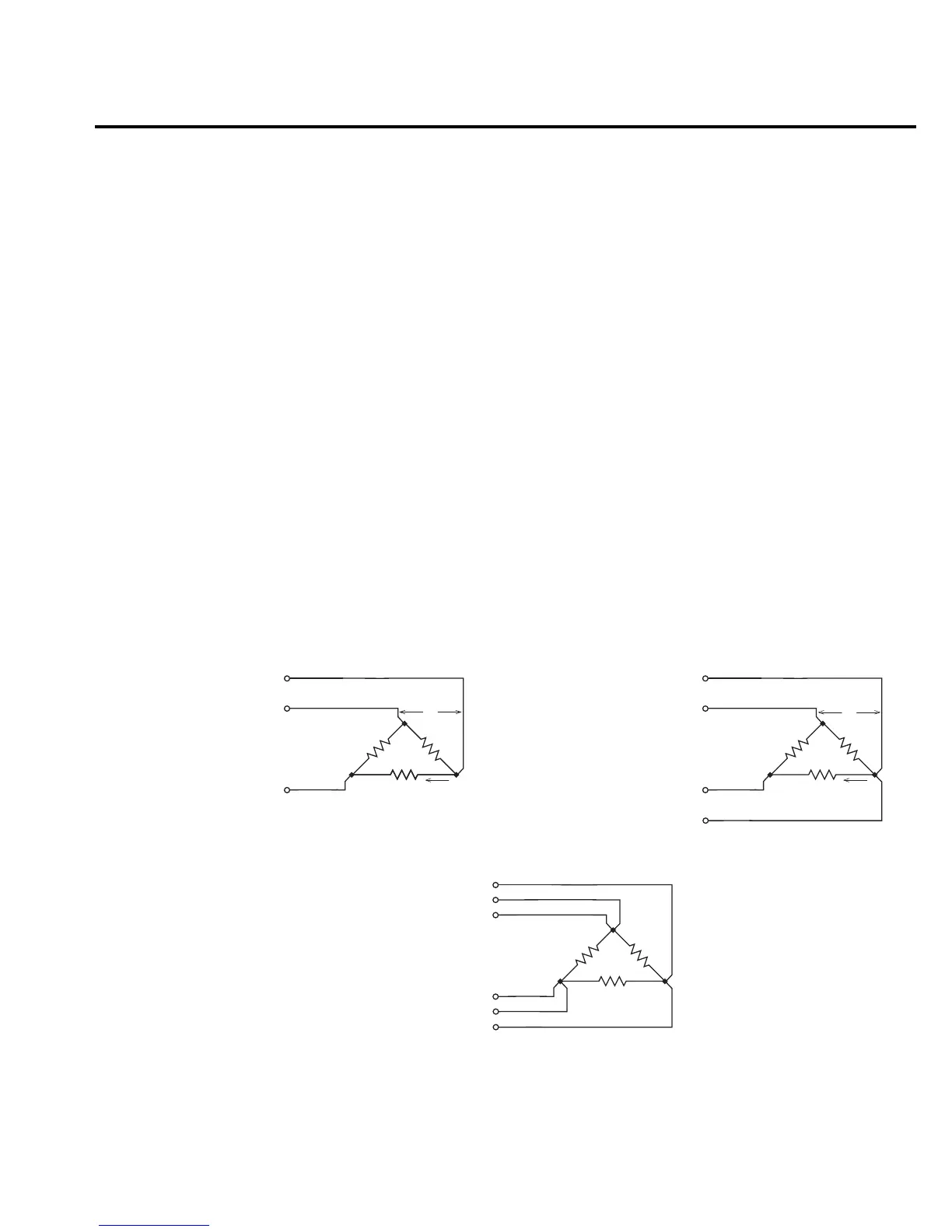
Basic connections for ohms guard is shown in Figure 6A. With V,
Ω
Guard and In/Out HI at
virtually the same potential, the voltage drop across R will be 0V, and therefore, the current
through R will be 0A. Virtually all the current from In/Out HI will flow through the DUT
resulting in an accurate measurement.
If the guard resistance path (R
G
) is <1k
Ω
, IR drop in the V,
Ω
Guard test lead could be high
enough such that a significant voltage drop appears across R. The resultant leakage current
through R will corrupt the measurement of the DUT.
Guard Sense is used to cancel the effect of IR drop in the V,
Ω
Guard test lead as shown in
Figure 6B. Guard Sense regulates the guard voltage to ensure that the same potential appears
on either side of R.
For DUT <1k
Ω
, 4-wire sensing should be used as shown in Figure 6C.
NOTE
Guard current (I
G
) must never exceed 50mA. If it does, guard voltage will become
less than the output voltage and corrupt the measurement.
DUT
V, Ω Guard
Sense HI
In/Out HI
In/Out LO
Sense LO
Guard Sense
Sense Mode: 4-wire
C. 6-wire connections
DUT
V, Ω Guard
In/Out HI
In/Out LO
Sense Mode: 2-wire
A. Basic connections
DUT
V, Ω Guard
In/Out HI
In/Out LO
Guard Sense
Sense Mode: 2-wire
B. Connections using guard sense
<1kΩ
RG
IG
≥1kΩ
RG
IG
R
0V
R
0V
Figure 6
Guarded ohms measurements

 Loading...
Loading...











