65
Detectors Used in EMI Measurements
Quasi-peak Detector
Quasi-peak Detector
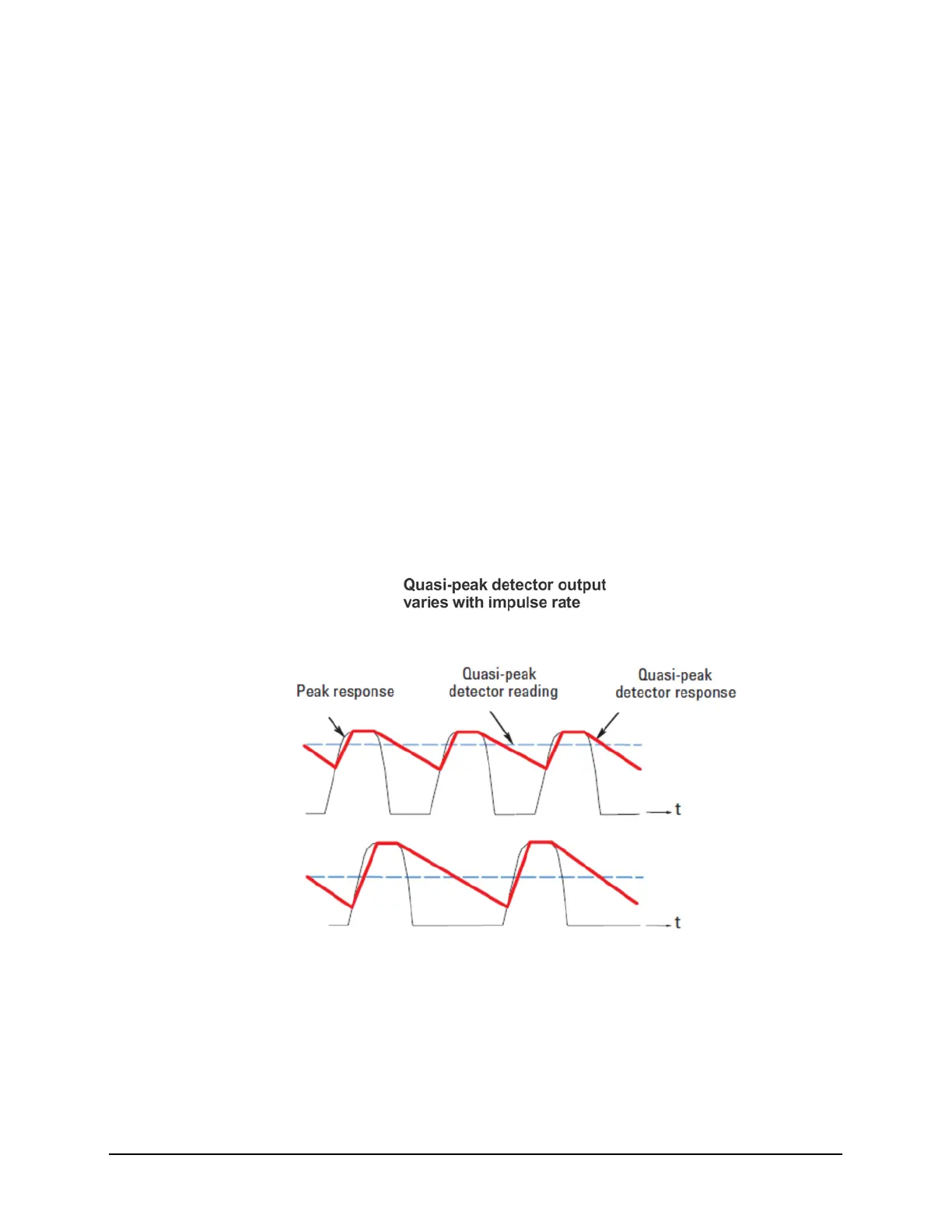
Most radiated and conducted limits are based on quasi-peak detection mode.
Quasi-peak detectors weigh signals according to their repetition rate, which is a way
of measuring their annoyance factor. As the repetition rate increases, the quasi-peak
detector does not have time to discharge as much, resulting in a higher voltage
output. (See the following graphic.) For continuous wave (CW) signals, the peak and
the quasi-peak are the same.
Quasi-peak detectors always give a reading less than or equal to peak detectors, but
quasi-peak measurements are much slower by two or three orders of magnitude
compared to a peak detector.
Quasi-peak detector operation
The quasi-peak detector has a charge rate much faster than the discharge rate. The
higher the repetition rate of the signal, the higher the output of the quasi-peak
detector. The quasi-peak detector also responds to different amplitude signals in a
linear fashion. High-amplitude, low-repetition-rate signals could produce the same
output as low-amplitude, high-repetition-rate signals.
Quasi-peak detector response diagram

 Loading...
Loading...