AES: Use Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) keys for encryption. WPA2 uses AES Counter-Mode
encryption with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code (CBC-MAC) for message
integrity. The AES Counter-Mode/CBCMAC Protocol (AES-CCMP) provides extremely robust data
confidentiality using a 128-bit key. Use of AES-CCMP encryption is specified as a standard
requirement for WPA2. Before implementing WPA2 in the network, be sure client devices are
upgraded to WPA2-compliant hardware.
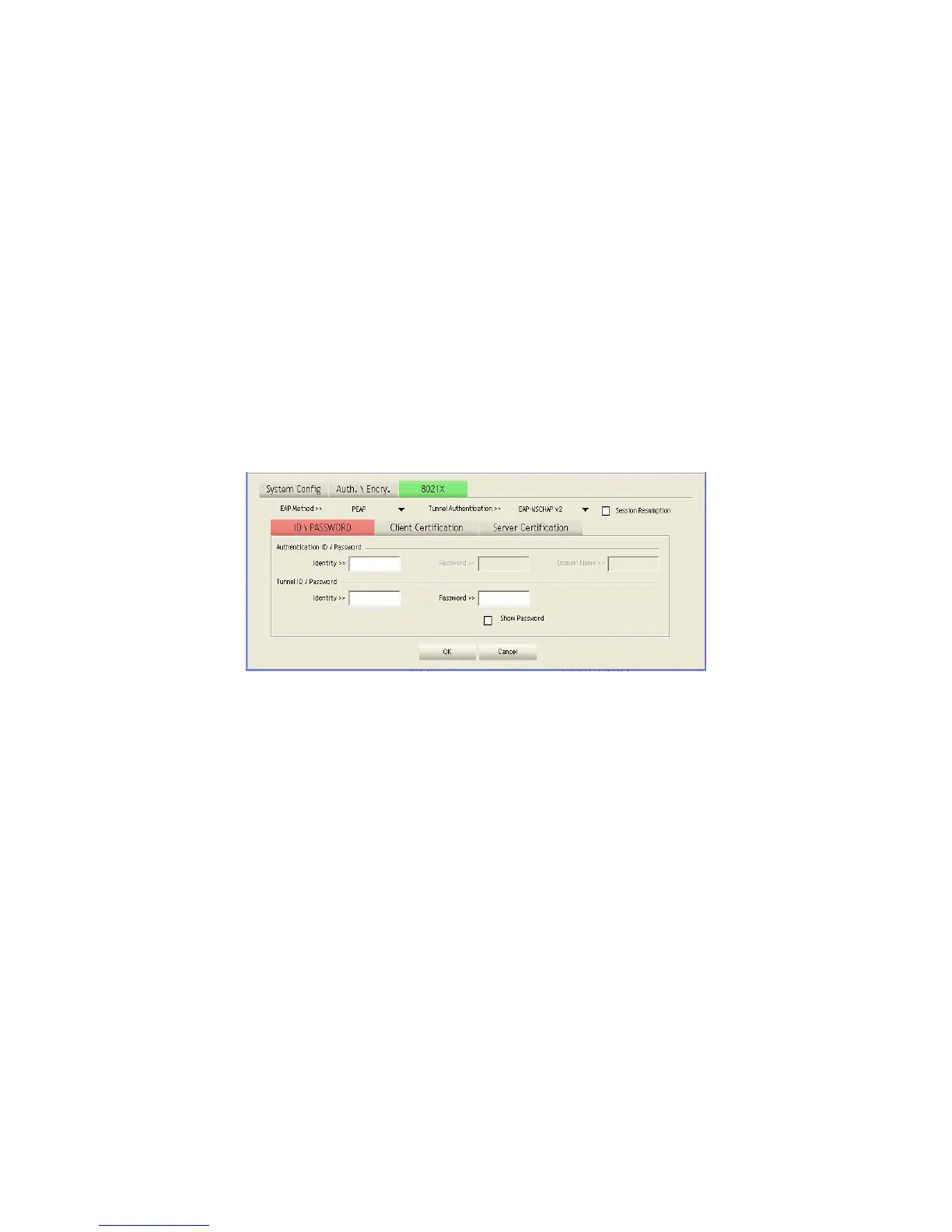
Click OK to confirm the configuration or click Cancel to cancel the settings.
802.1X: Use IEEE 802.1X (802.1X) for user authentication and distributing dynamically generated
encryption keys. IEEE 802.1X is a standard framework for Wireless Utility Configuration network
access control that uses a RADIUS server on the local network for user authentication. The 802.1X
standard uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to pass user credentials (either digital
certificates, usernames and passwords, or other) from the client to the RADIUS server.
EAP Method: Select an 802.1X authentication method.
PEAP: Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol. PEAP transport securely sends
authentication data by using tunneling between PEAP clients and an authentication server.
PEAP can authenticate wireless LAN clients using only server-side certificates, thus
simplifying the implementation and administration of a secure wireless LAN.
TLS / Smart Card: Transport Layer Security. Provides for certificate-based and mutual
authentication of the client and the network. It relies on client-side and server-side certificates
to perform authentication and can be used to dynamically generate user-based and session-
based WEP keys to secure subsequent communications between the WLAN client and the
access point.
15
 Loading...
Loading...











