Attention
The differences between the units
operating with the fluid R407C and
those operating with the fluid R22 are
described below.
Hiflex
20 All Versions
English
6 - Technical remarks
6.1 - Fluid, R407C
Recent international agreements (Montreal, London,
Copenhagen, Vienna and San Josè) have abolished
- with precise expiry dates - the production of the
HCFC fluids (e.g.: R22) considered as harmful for the
ozone layer. The new HFC fluids (hydrofluorocar
bons) which have to replace them contain no chlo
rine, a dangerous substance for the ozone layer. The
refrigerant R407C replace the fluid R22.
Its main features are:
Non-azeotropic mixture made of
R32/R125/R134a in which the percentage weight composition is, in ratio, 23/25/52.
Thermophysical features similar to R22.
ODP (Ozone Depletion Potential) equal to 0.
Not flammable in the air.
Low toxicity degree.
The new HFC fluids are essentially incompatible with the mineral oils which are usually used with the fluids
R12 and R22.
Therefore, new synthetic lubricants based on polyester molecules have been developed for their use.
Note: considering the peculiar thermophysical features of the fluid we give the description of the refrigera
ting cycle shown in the phase diagram of the R407C.
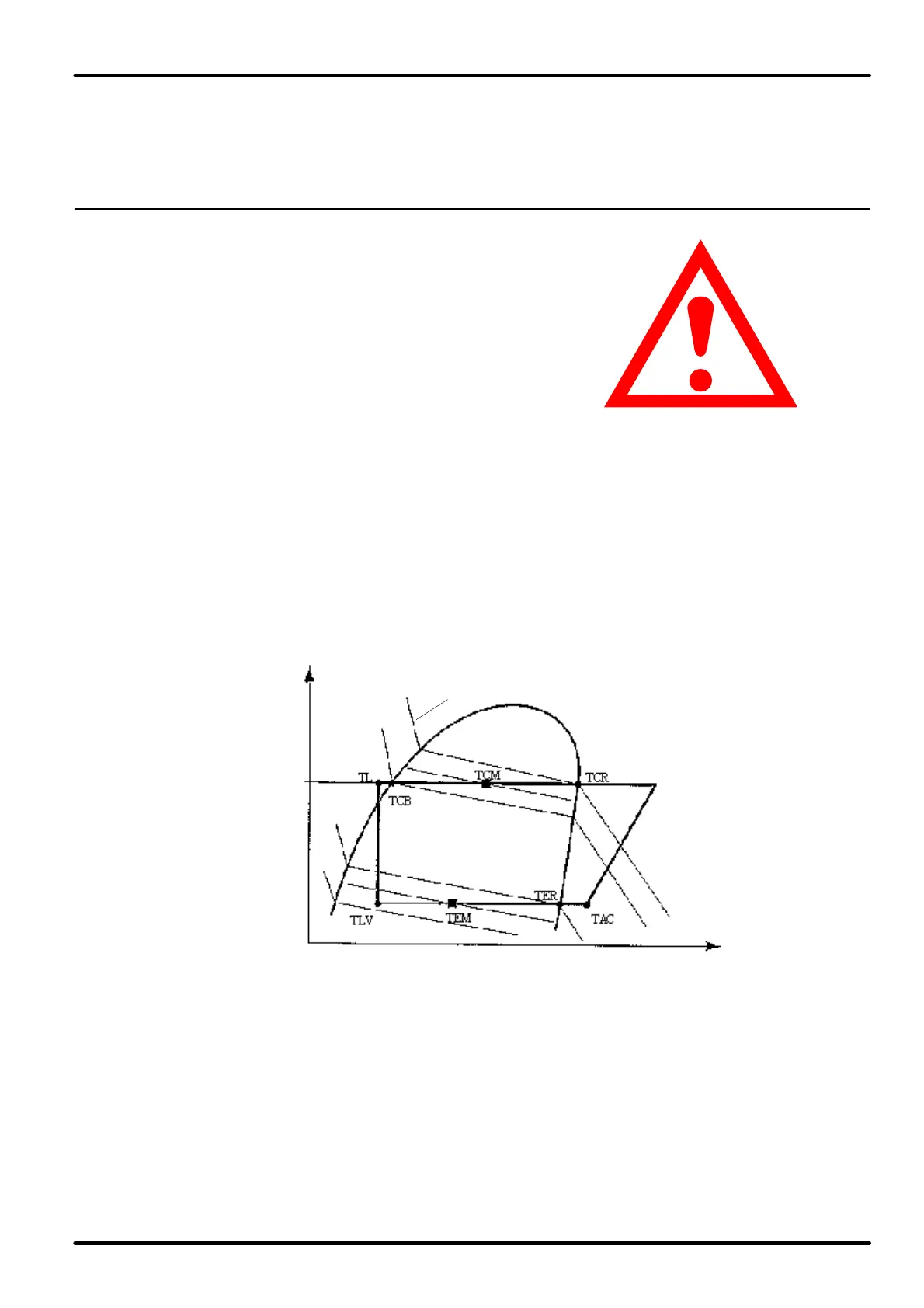
Isoterms
P (bar)
h (kJ/kg)
PC
PE
High pressure side Low pressure side
TCB: condensation temperature
bubble point (Liquid)
TCR: condensation temperature
dew point (Vapor)
TCM: average condensation temperature
(TCB+TCM)/2
TL: temperature of the refrigerant at
the expansion valve inlet
Overheating = TAC - TER
TLV: liquid-steam temperature
TER: evaporation temperature
dew point (Vapor)
TEM: average evaporation temperature
(TLV+TER)/2
TAC: temperature of the refrigerant at
the compressor inlet
Sub-cooling = TCB -TL
 Loading...
Loading...











