8. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
8. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
8.1 Protective Functions
When a fault occurs, the cause must be corrected before the fault can be cleared.
If protective function keeps active, it could lead to reduction in product life and
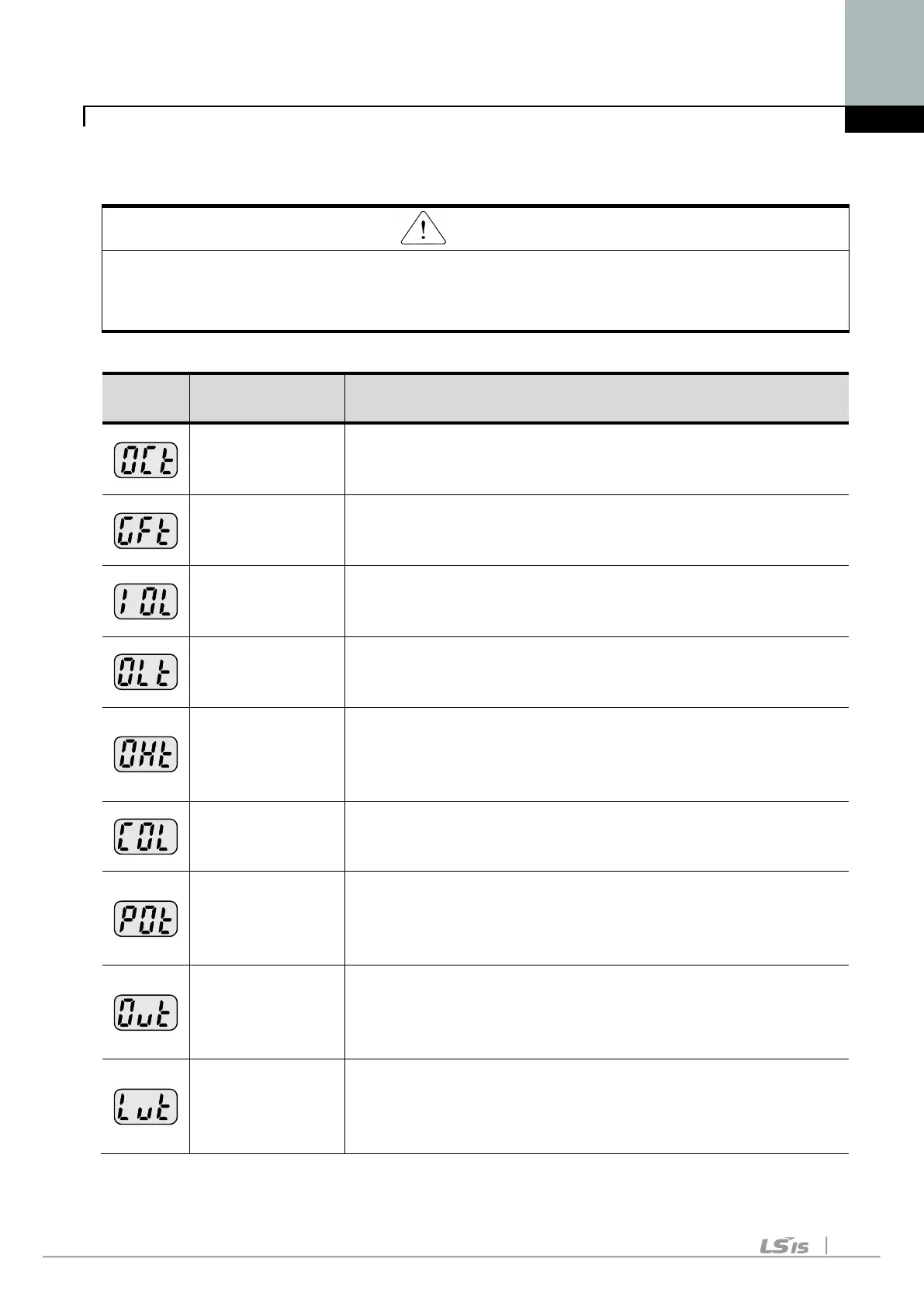
Fault Display and information
Descriptions
Overcurrent
The inverter turns off its output when the output current of
the inverter flows more than 200% of the inverter rated
Ground fault
current
The inverter turns off its output when a ground fault
occurs and the ground fault current is more than the
internal setting value of the inverter.
Inverter
Overload
The inverter turns off its output when the output current of
the inverter flows more than the rated level (150% for 1
Overload trip
The inverter turns off its output if the output current of
the inverter flows at 150% of the inverter rated current
for more than the current limit time (1 min).
Heat sink
overheat
The inverter turns off its output if the heat sink
overheats due to a damaged cooling fan or an alien
substance in the coo
ling fan by detecting the
temperature of the heat sink.
capacitor
The inverter turns off its output when it is time to
replace the old DC link capacitor to a new one.
Output Phase
loss
The inverter turns off its output when the one or more
of the output (U, V, W) phase is open. The inverter
detects the output current to check the phase loss of
Over voltage
The inverter turns off its output if the DC voltage of the
main circuit increases higher than 400 V when the
motor decelerates. This fault can also occur due to a
surge voltage generated at the power supply system.
Low voltage
The inverter turns off its output if the DC voltage is below
180V because insufficient torque or overheating of the
motor can occur when the input voltage of the inverter

 Loading...
Loading...