Flash Player security features 191
An XML policy file contains a single <cross-domain-policy> tag, which in turn contains zero
or more
<allow-access-from> tags. Each <allow-access-from> tag contains one attribute,
domain, which specifies either an exact IP address, an exact domain, or a wildcard domain (any
domain). Wildcard domains are indicated by either a single asterisk (
*), which matches all
domains and all IP addresses, or an asterisk followed by a suffix, which matches only those
domains that end with the specified suffix. Suffixes must begin with a dot. However, wildcard
domains with suffixes can match domains that consist of only the suffix without the leading dot.
For example, foo.com is considered to be part of *.foo.com. Wildcards are not allowed in IP
domain specifications.
If you specify an IP address, access will be granted only to SWF files loaded from that IP address
using IP syntax (for example, http://65.57.83.12/flashmovie.swf), not those loaded using
domain-name syntax. Flash Player does not perform DNS resolution.
Here is an example policy file that permits access to Flash documents that originate from
foo.com, friendOfFoo.com, *.foo.com, and 105.216.0.40, from a Flash document on foo.com:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- http://www.foo.com/crossdomain.xml -->
<cross-domain-policy>
<allow-access-from domain="www.friendOfFoo.com" />
<allow-access-from domain="*.foo.com" />
<allow-access-from domain="105.216.0.40" />
</cross-domain-policy>
A policy file that contains no <allow-access-from> tags has the same effect as not having a
policy on a server.
About compatibility with previous Flash Player security models
As a result of the security feature changes in Flash Player (see “Flash Player security features”
on page 188), content that runs properly in Flash Player 6 or earlier may not run properly in
Flash Player 7 or later.
For example, in Flash Player 6, a SWF file that resides in www.macromedia.com could access data
on a server located at data.macromedia.com. That is, Flash Player 6 allowed a SWF file from one
domain to load data from a “similar” domain.
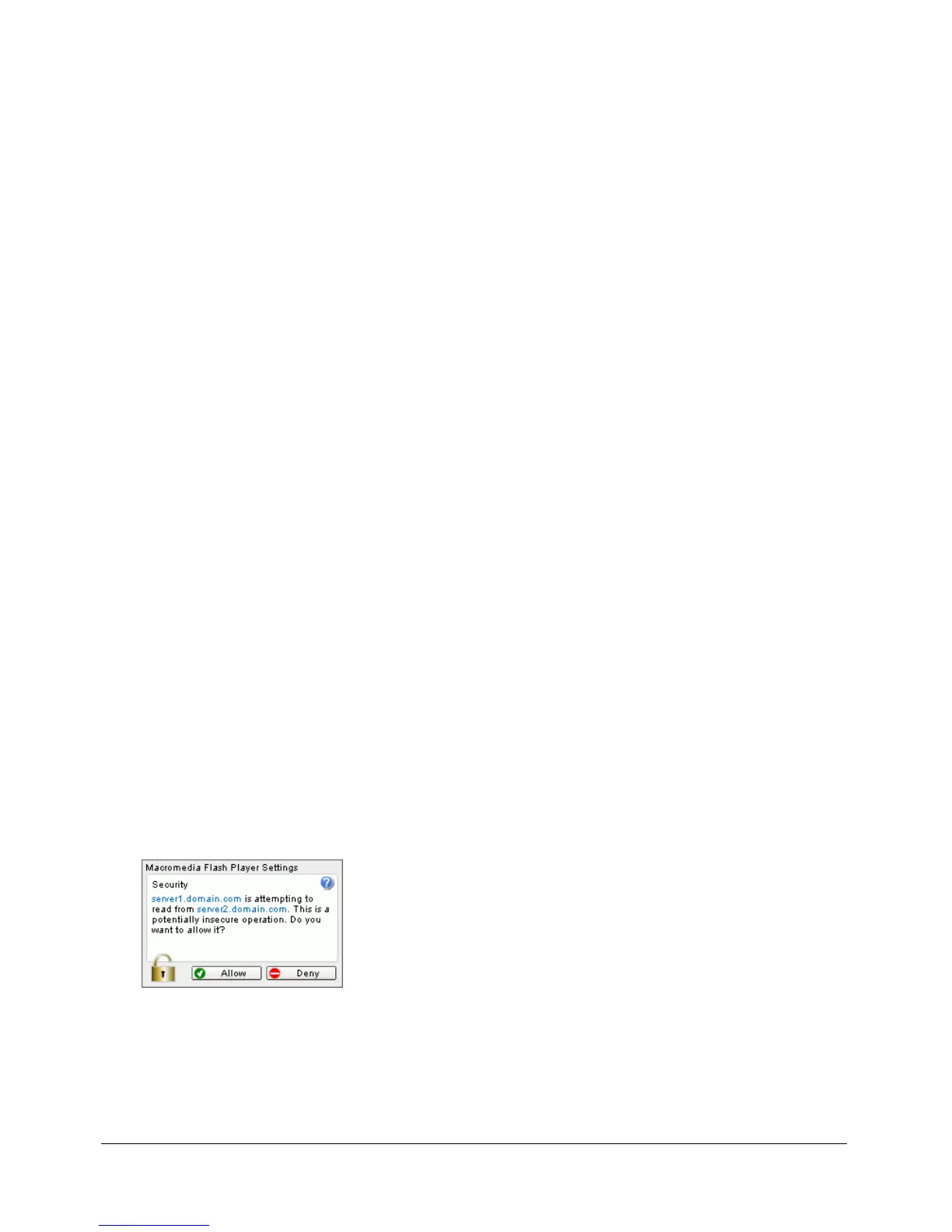
In Flash Player 7 and later, if a version 6 (or earlier) SWF file attempts to load data from a server
that resides in another domain, and that server doesn’t provide a policy file that allows access from
that SWF file’s domain, then the Macromedia Flash Player Settings dialog box appears. The
dialog box asks the user to allow or deny the cross-domain data access.
If the user clicks Allow, the SWF file is permitted to access the requested data; if the user clicks
Deny, the SWF file is not allowed to access the requested data.
To prevent this dialog box from appearing, create a security policy file on the server providing the
data. For more information, see “About allowing cross-domain data loading” on page 190.
 Loading...
Loading...











