Operators Manual
23
Travel speed is the rate at which the torch is being pushed or pulled along the weld joint.
For a xed heat seng, the faster the travel speed, the lower the penetraon and the
lower and narrower the nished weld bead. Likewise, the slower the travel speed, the
deeper the penetraon and the higher and wider the nished weld bead.
6.2 Types of welding beads
As you become more familiar with your new welder and beer at laying some simple
weld beads, you can begin to try some dierent weld bead types.
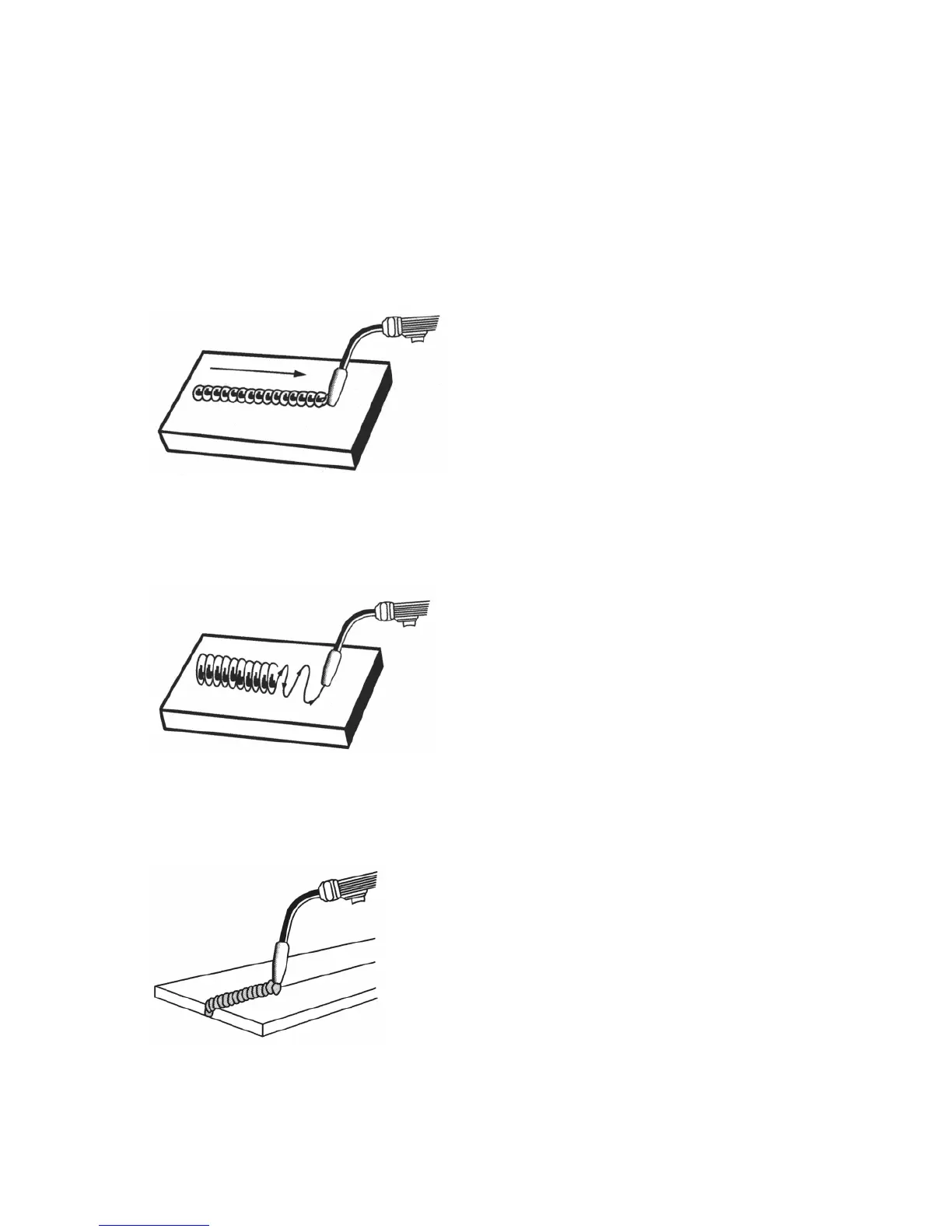
The STRINGER BEAD Is formed by traveling with the torch in a straight line while keeping
the wire and nozzle centered over the weld joint (See following gure).
The WEAVE BEAD Is used when you want to deposit metal over a wider space than would
be possible with a stringer bead. It is made by weaving from side to side while moving
with the torch. It is best to hesitate momentarily at each side before weaving back the
other way.
6.3 Welding posion
FLAT POSITION Is easiest of the welding posions and is most commonly used. It is best if
you can weld in the at posion if at all possible as good results are easier to achieve.
HORIZONTAL POSITION Is performed very much the same as the at weld except that
angle B (see HOLDING THE TORCH) is such that the wire, Directed more toward the metal
above the weld joint is to help prevent the weld puddle from running downward while
sll allowing slow enough travel speed.
 Loading...
Loading...