Processes
OM-263920B 2018-05
DIVERSIONt180 w/Auto-Linet
Processes
TIG (GTAW) Welding
Description
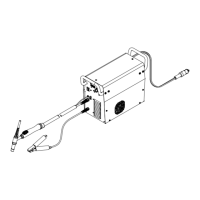
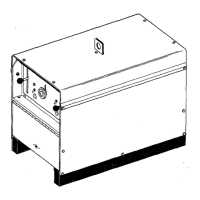
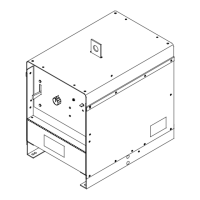
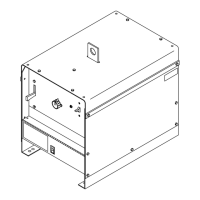
Diversion 180: 115-230 VAC Arc Weld-
ing Power Source w/Auto-Linet
File: TIG (GTAW)
Diversion 165: 230 Volt Arc Welding
Power Source
DIVERSIONt165 And
Scan this tag with your mobile device
to learn more about this product.
Individual carrier rates may apply.
Start by downloading the free mobile
app at http://gettag.mobi
(WP−17 Torch)
For product information,
Owner’s Manual translations,
and more, visit
www.MillerWelds.com