What to do if drive motor becomes inoperative in Miller Welding System?
- PPatrick CrossAug 8, 2025
If the drive motor becomes inoperative in your Miller Welding System, cycle the unit power off and back on again.
What to do if drive motor becomes inoperative in Miller Welding System?
If the drive motor becomes inoperative in your Miller Welding System, cycle the unit power off and back on again.
What to do if CB1 opens and Miller Millermatic 141 shuts down?
If CB1 opens and the Miller Welding System shuts down, reset the supplementary protector.
What to do if contact tip has stuck to the workpiece in Miller Millermatic 141?
If the contact tip has stuck to the workpiece, release the gun trigger, turn off the unit, and remove the contact tip from the workpiece. Also, check the contact tip and replace it if it is damaged. Then, turn on the unit to continue operation.
What to do if contact tip is shorted to workpiece and Miller Welding System shuts down?
If the contact tip is shorted to the workpiece and the Miller Welding System shuts down the welding output, release the gun trigger to reset the unit.
Explains the meaning of warning symbols used in the manual.
Details hazards associated with arc welding and safety precautions.
Covers hazards from fumes, gases, and noise.
Details hazards from arc rays and flying sparks.
Covers fire and explosion risks during welding.
Addresses electric shock, EMF, and HF radiation hazards.
Details hazards related to gas cylinders and battery explosions.
Explains hazards using specific symbols for installation and operation.
Warning about chemicals in the product and their health effects.
Lists key safety standards and where to obtain them.
Explains safety symbols found on CE products.
Explains various symbols used for technical specifications.
Location of serial number and rating label for product identification.
Technical specifications of the welding unit including output and dimensions.
Details IP rating and temperature specifications for operation and storage.
Explains duty cycle limitations and overheating prevention.
Shows voltage and amperage output capabilities of the power source.
Guidelines for choosing a suitable location for the unit, considering airflow and stability.
Instructions for connecting the unit to a 120-volt power supply.
Recommendations for electrical service, including circuit protection and conductor sizing.
Guidance on selecting appropriate extension cords based on length and wire size.
Step-by-step instructions for installing the work clamp.
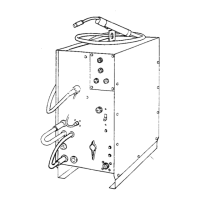
Instructions for routing the work cable within the unit.
Table detailing process, polarity, and cable connection settings.
Instructions on how to change the welding polarity.
Instructions for installing the welding gun or spool gun.
Steps for changing the drive roll or wire inlet guide.
Instructions for installing wire spools and adjusting hub tension.
Detailed steps for threading welding wire through the machine.
Instructions for connecting the shielding gas supply.
Procedure for removing the MIG gun to install a spool gun.
Guide to manual setup of voltage and wire speed controls.
Instructions for using the Auto-Set feature for simplified setup.
Explanation of Jog mode for feeding wire and its usage.
Chart providing recommended weld parameters for various materials and settings.
Detailed table of weld parameters for different materials and wire sizes.
Schedule and tasks for routine maintenance of the equipment.
Information on overload protection and how to reset it.
Explains drive motor protection and tip saver/short circuit protection.
A table listing common problems, probable causes, and remedies.
Provides the main circuit diagram for the welding unit.
Diagram showing typical connections for GMAW welding.
Guide to process control settings for GMAW welding.
Techniques for holding and positioning the welding gun correctly.
Factors influencing weld bead shape, including gun angles and speed.
Describes different gun movements for various weld types.
Illustrates common issues resulting in poor weld bead quality.
Illustrates characteristics of good weld beads.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for excessive spatter.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for porosity in welds.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for excessive weld penetration.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for lack of weld penetration.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for incomplete weld fusion.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for burn-through.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for wavy weld beads.
Identifies causes and corrective actions for weld distortion.
Chart of common shielding gases and their applications in GMAW.
Comprehensive troubleshooting guide for semiautomatic welding equipment.
List of recommended spare parts with part numbers and descriptions.
List of optional drive rolls available for the equipment.
List of available options for the equipment.
| Brand | Miller |
|---|---|
| Model | Millermatic 141 |
| Category | Welding System |
| Language | English |