Appendix - 83
MELSEC-Q
APPENDICES
MOVEMENT AMOUNT PER PULSE
When using mm, inch, or degree units, the
movement amount is calculated and output
from the machine side showing how much the
motor shaft moves per pulse. Equivalent to the
positioning detection units. Positioning
accuracy in smaller units is not possible.
On the motor side, the movement amount per
axis rotation is normally designed as a
reference, so it is calculated as follows.
Movement amount per pulse =
P rate
No. of pulses per
encoder rotation
Movement amount
per rotation
Amount the motor moves (travel) per pulse.
MULTI-PHASE PULSE
A combination of pulses in which 2 or more
phases differ.
2-phase pulses, etc.
phase
Phase difference
B phase
phase
(ZERO signal)
MULTIPLYING RATE SETTING
The P rate. Refer to the term "P RATE".
NC LANGUAGE (Numerical Control
Language)
This is the language punched into the paper
tape that instructs the machining to the NC
module.
The NC language consists of EIA codes (EIA
language), ISO codes (ISO standards), and
JIS codes (JIS standards).
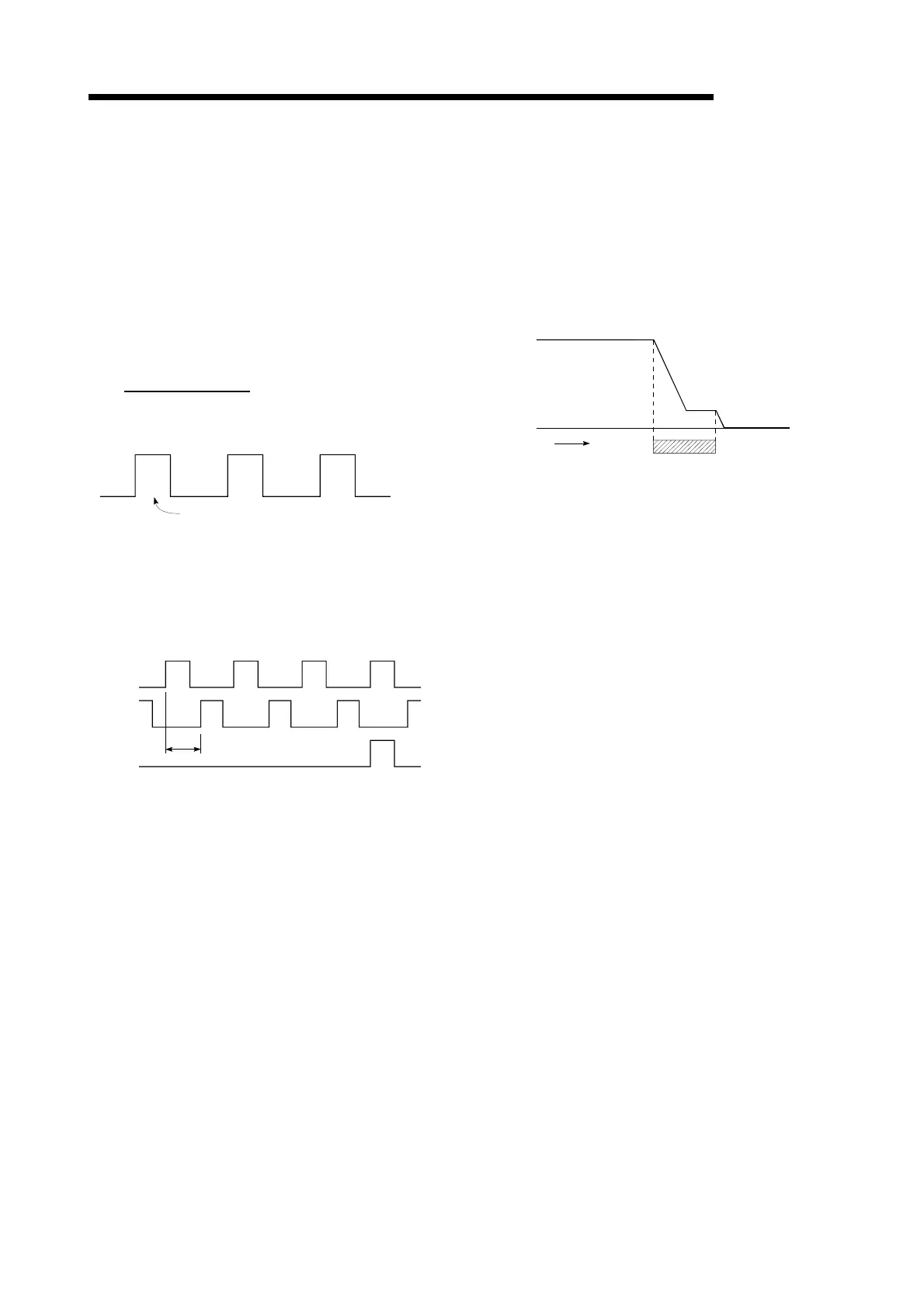
NEAR-POINT DOG
This is a limit switch placed before the OP.
When this switch turns ON, the feedrate is
changed to the creep speed. Because of that,
the time that this switch is ON must be long
enough to allow for the time required for
deceleration from the feedrate to the creep
speed.
ON OFF
Feedrate
Creep speed
Time
Near-point dog
NEW CURRENT VALUE (CURRENT VALUE
CHANGING)
The QD75 has no way of knowing the current
value when the machine is assembled and the
positioning module is connected, so this
function is used to teach it a temporary
approximate value as the current value. This
function can also be used to write a temporary
current value when the current value has been
lost due to accidents, etc. If an OPR is carried
out after that, the positioning module will
recognize the zero point.
In fixed-feed, etc., rewriting the current value
to 0 after the fixed-feed will keep the
accumulated value from being affected by the
upper stroke limit. The current value can be
changed during a positioning stop.

 Loading...
Loading...











