NPort 5000 Series User Manual
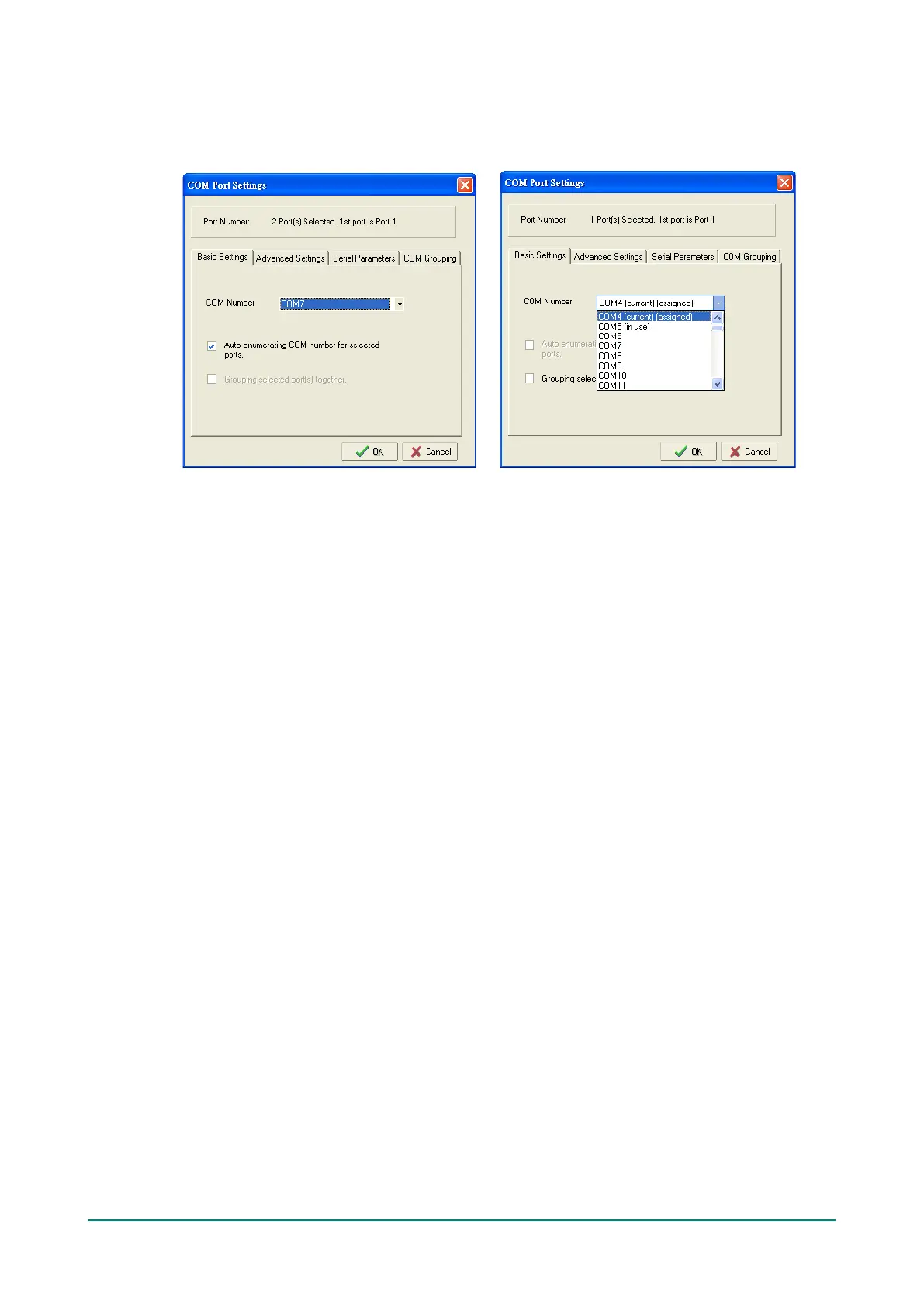
6. Select the COM Number.
COM ports that are “In use” or “Assigned” will also be indicated in this drop-down list. If you select
multiple serial ports or multiple NPort units, remember to check the “Auto Enumerating” function to use
the COM No. you select as the first COM No.
Hi-performance mode is the default for Tx mode. If the driver completes sending data out to the
NPort 5200A, the driver will respond “Tx Empty” to the program.
Under classical mode, the driver will not notify the user’s program that Tx is completed until all Tx
data has been sent out from the NPort 5200A; this mode will cause lower throughput. If you want to
ensure that all data is sent out before further processing, classical mode is recommended.
Enable/Disable Tx/Rx FIFO. If disabled, the NPort 5200A will send one byte each time the Tx FIFO
becomes empty; and an Rx interrupt will be generated for each incoming byte. This will result in a
faster response and lower throughput. If you want to use XON/XOFF flow control, we recommend
setting FIFO to Disable.
Fast Flush (only flush local buffer)
We have added one optional Fast Flush function to Moxa’s new NPort Real COM driver. NPort
Administrator Suite for NPort adds it after version 1.2.
For some applications, the user’s program will use the Win32 “PurgeComm()” function before it
reads or writes data. With our design, after the program uses this Purge Comm() function, the NPort
driver will keep querying the NPort’s firmware several times to make sure there is really no data
queued in the NPort firmware buffer, rather than just flushing the local buffer. This kind of design is
used because of some special considerations. However, it might take more time (on the order of
several hundred milliseconds) than a native COM1, because it needs to work via Ethernet. That’s
why the native COM ports on the motherboard can work fast with this function call, but the NPort
requires much more time. In order to accommodate other applications that require a faster response
time, the new NPort driver implements a new “Fast Flush” option. Note that by default, this function
is disabled.
To begin with, make sure there are some “PurgeComm()” functions being used in your application
program. In this kind of situation, you might find that your NPort exhibits a much poorer operation
performance than when using the native COM1 port. Once you have enabled the “Fast Flush”
function, you can check to see if there has been an improvement in performance.
By default, the optional “Fast Flush” function is disabled. If you would like to enable this function,
from the “NPort Administrator,” double click the COM ports that are mapped to the NPort, and then
select the “Fast Flush” checkbox. You should find that when “Fast Flush” is enabled, the NPort driver
will work faster with “PurgeComm().”

 Loading...
Loading...