Overview (Pulse Oximeter)
Pulse oximetry is a continuous and non-invasive method of measuring the level of
arterial oxygen saturation in blood. The measurement is taken by placing a sensor on the
patient, usually on the hand or foot for neonates. The sensor connects to the pulse oximetry
instrument directly or with a patient cable. The sensor collects signal data from the patient
and sends it to the instrument. The instrument displays the calculated data in two ways:
1. As a percent value for arterial oxygen saturation (SpO
2
) and
2. As a pulse rate (bpm).
Pulse oximetry is governed by the following principles:
1. Oxyhemoglobin (oxygenated blood) and deoxyhemoglobin (non-oxygenated blood)
differ in their absorption of red and infrared light (spectrophotometry).
2. The amount of arterial blood in tissue changes with your pulse
(photoplethysmography). Therefore, the amount of light absorbed by varying
quantities of arterial blood changes as well.
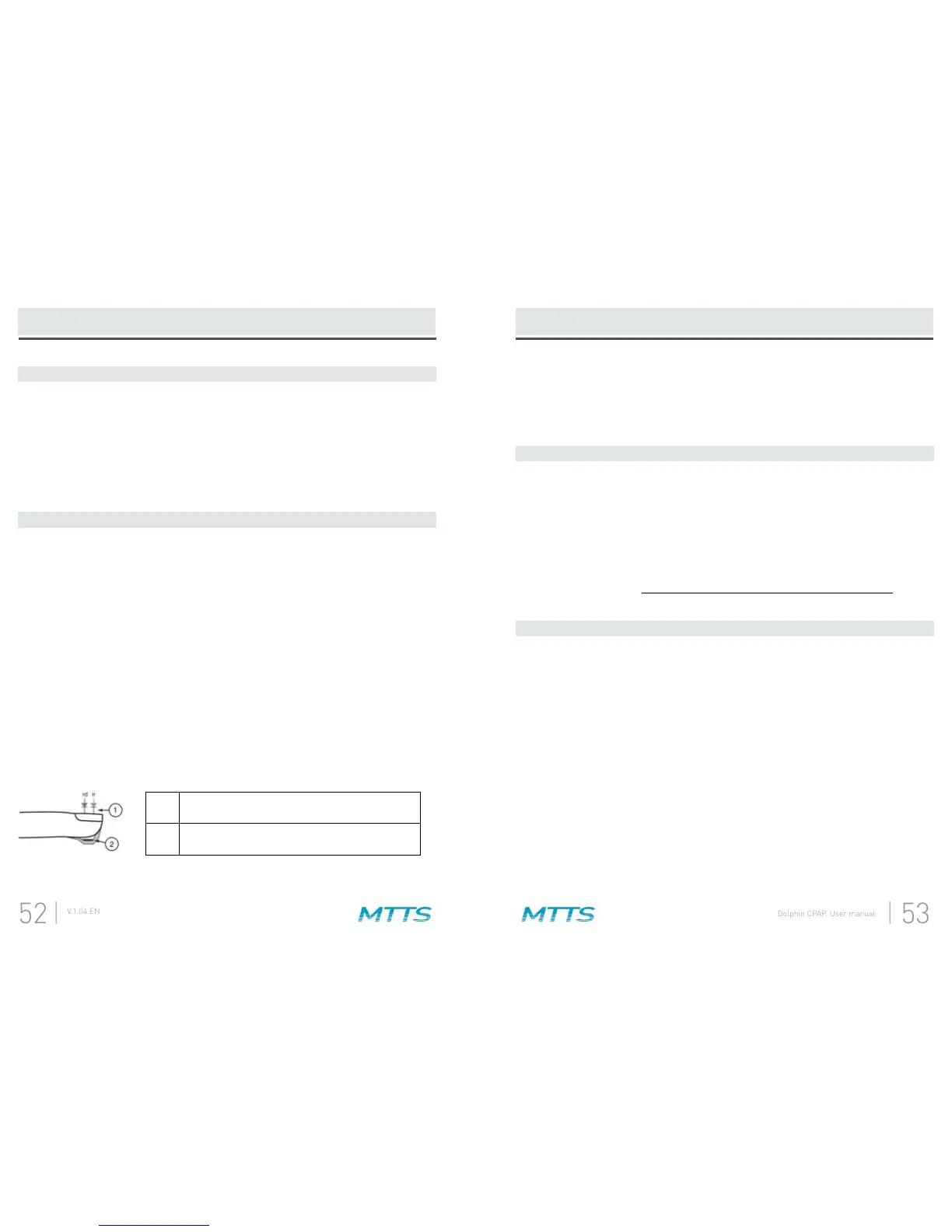
The Dolphin CPAP incorporates Masimo SET technology which uses a two-wavelength
pulsatile system to distinguish between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Signal
data is obtained by passing red (rd) (660 nm wavelength) and infrared (ir) (905 nm
measuring changes in light absorption during the pulsatile cycle. This information may
be useful to clinicians. The Dolphin CPAP utilizes a sensor with red and infrared light-
emitting diodes (LEDs) that pass light through the site to a photodiode (photodetector).
The radiant power of the light is rated at 0.79mW (max.). The photodetector receives
the light, converts it into an electronic signal and sends it to the Dolphin CPAP for
calculation.
1 Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
2 Recessed Photo Detector
General Description
Principle of Operation
Overview (Pulse Oximeter)
Once the Dolphin CPAP receives the signal from the sensor, it utilizes Masimo SET
signal extraction technology for calculation of the patient’s functional oxygen
saturation and pulse rate. The maximum of the skin surface temperature is measured
skin temperature test procedures.
The Dolphin CPAP is calibrated to measure and display functional saturation which is
the amount of oxygenated hemoglobin expressed as a percentage of the hemoglobin
that can transport oxygen. The Dolphin CPAP does not measure fractional saturation
which is oxygenated hemoglobin expressed as a percentage of all measured
hemoglobin. This includes measured dysfunctional hemoglobin such as
carboxyhemoglobin or methemoglobin. To convert fractional saturation to functional
saturation, the fractional saturation measurements must be converted according to:
Oxygen saturation measurements obtained from a pulse oximeter are commonly
compared to saturations calculated from the partial pressure of oxygen (PO
2
) obtained
from an arterial blood gas sample. When comparing the two measurements and
interpreting values, caution should be used, as the calculated value obtained from the
blood gas sample may differ from the SpO
2
measurement of the pulse oximeter.
Different results are usually obtained from the blood gas sample if the calculated
saturation is not appropriately corrected for the effects of variables that shift the
relationship between PO
2
and saturation, such as: pH, temperature, the partial
pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO
2
), 2,3-DPG, and fetal hemoglobin. Also, as blood gas
samples are usually taken over a period of 20 seconds (the time it takes to draw blood)
a meaningful comparison can only be achieved if the core oxygen saturation of the
patient is stable and not changing over the period of time that the blood gas sample is
taken.
Functional saturation =
Fractional saturation
x 100
Functional vs. Fractional Saturation
Measured vs. Calculated Saturation
 Loading...
Loading...