13 Appendix C: Avoiding Passive
Intermodulation during RF Module and RRH
operation
Inwidebandfrequencieswhenseveraltransmittingandreceivingsignalsaresharing
samehardwaretherecouldbenotedeffectcalledPassiveIntermodulation(PIM)
Interference.UsingRFModulesmightcauseapotentialriskofgeneratingthird-order
intermodulationthatresultsindistortionsinownreceiver(RX)channel.AntennaLine
Devices(ALD)haveimportantroleinpreventingPassiveIntermodulationgeneration,
evenifusedRFModuleandRRHperformanceattheantennaconnectorcomplieswith
3GPPrequirements.PoorPIMperformanceofALDmightdegradesignificantlythe
referencesensitivity.ALDs,likeMHAs,providedbyNSNhavehighPIMrequirements.
Theriskmightbehighinthefollowingcases:
•
maximumbandwidth(BW)usedforthecarriersismorethan0.5xduplexseparation
oftheband
•
carriersinconfigurationarewidebandinnature(forexampleWCDMAorLTE),or
combinationofwidebandandnarrowbandcarriers(forexampleRFsharingGSM-
WCDMAorGSM-LTE).
•
antennalinePIMperformanceispoor,ornotontherequiredlevelforthe
configuration.
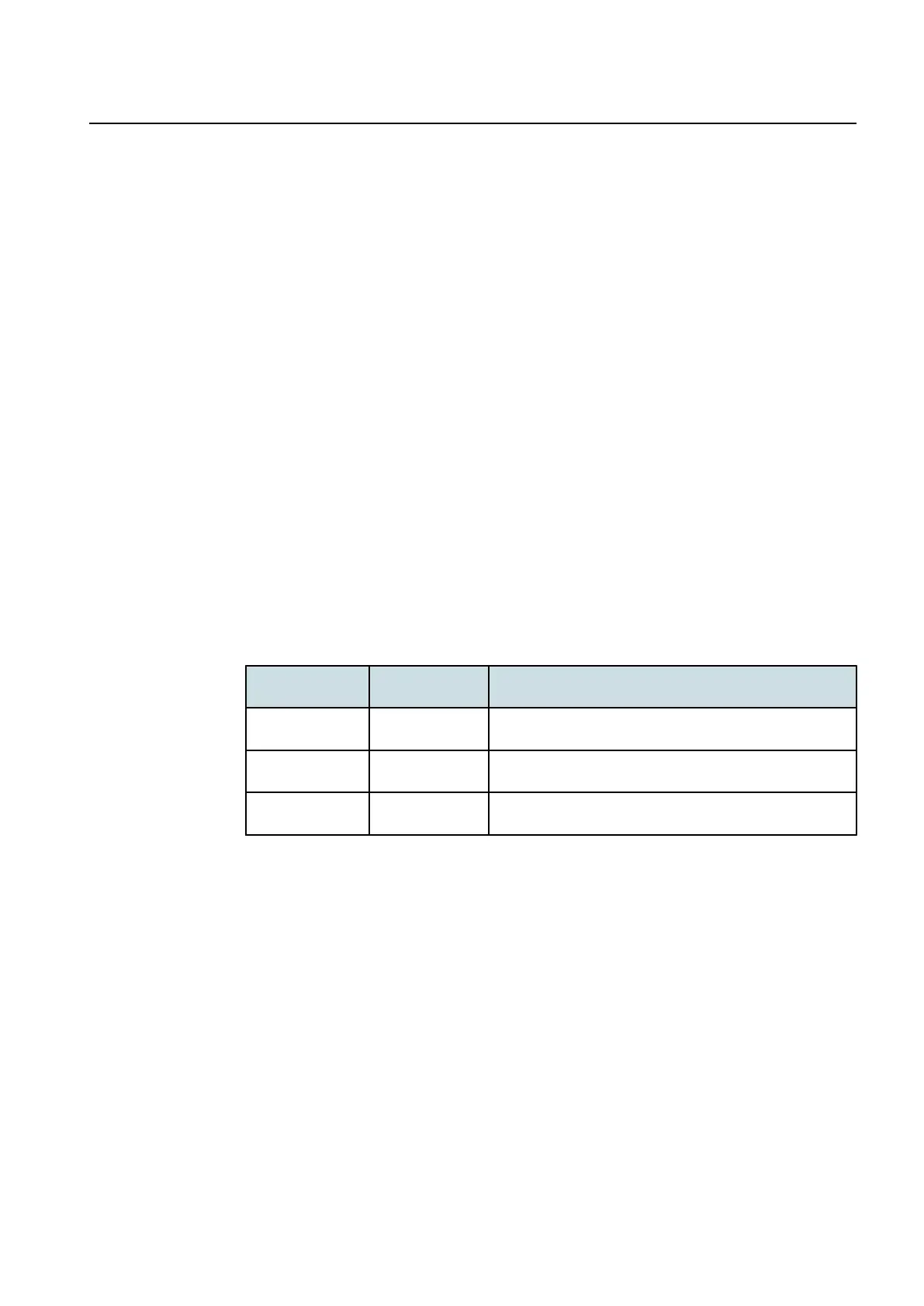
Table24
TypicalreferencesensitivitydegradationwithdifferentAntennalinePIM
performance.
PIM
performance
Typical
degradation
Note
-140dBc@2x43
dBm
~10dB Highdegradation,carrierconfigurationunusableinmany
cases
-153dBc@2x43
dBm
~2dB Modestdegradation,tolerableinmanycases
-161dBc@2x43
dBm
~0.2dB Minimaldegradation,however,difficulttoreachonthe
typicalsiteenvironment.
WhenusingwidebandcarrierconfigurationswherePIMproductsfallintoownreceiver
band,itisrecommendedthatantennalinePIMperformanceisatleast-153dBc
measuredwith2x43dBtestsignals.
However,thiskindofperformancemightbeverydifficulttoachieveandmaintainover
timeinoutdoorenvironmentduetomechanismsbehindthePIMincludingcorrosion,
oxidation,materialimperfections,anddefectsinworkmanship.Someofthese
parametersmightchange,andcandegradeperformanceduringoperation.Takingthat
intoconsideration,itishighlyrecommendednottousecarrierconfigurationswhichare
generatingintermodulationresultsinlandinginownreceiverchannels.
FlexiMultiradioBTSRadioModuleandRemoteRadio
HeadDescription
AppendixC:AvoidingPassiveIntermodulationduring
RFModuleandRRHoperation
Issue:05 DN0951745 61

 Loading...
Loading...