26
5 LD series main safety functions
5.1 Performance levels
The LD series robots’ main safety functions are implemented in hardware or electronic circuitry with certain
diagnostic functions implemented in firmware. The European Standard EN 1525 (Driverless Industrial Trucks
and Their Systems) provides normative requirements for this type of machinery.
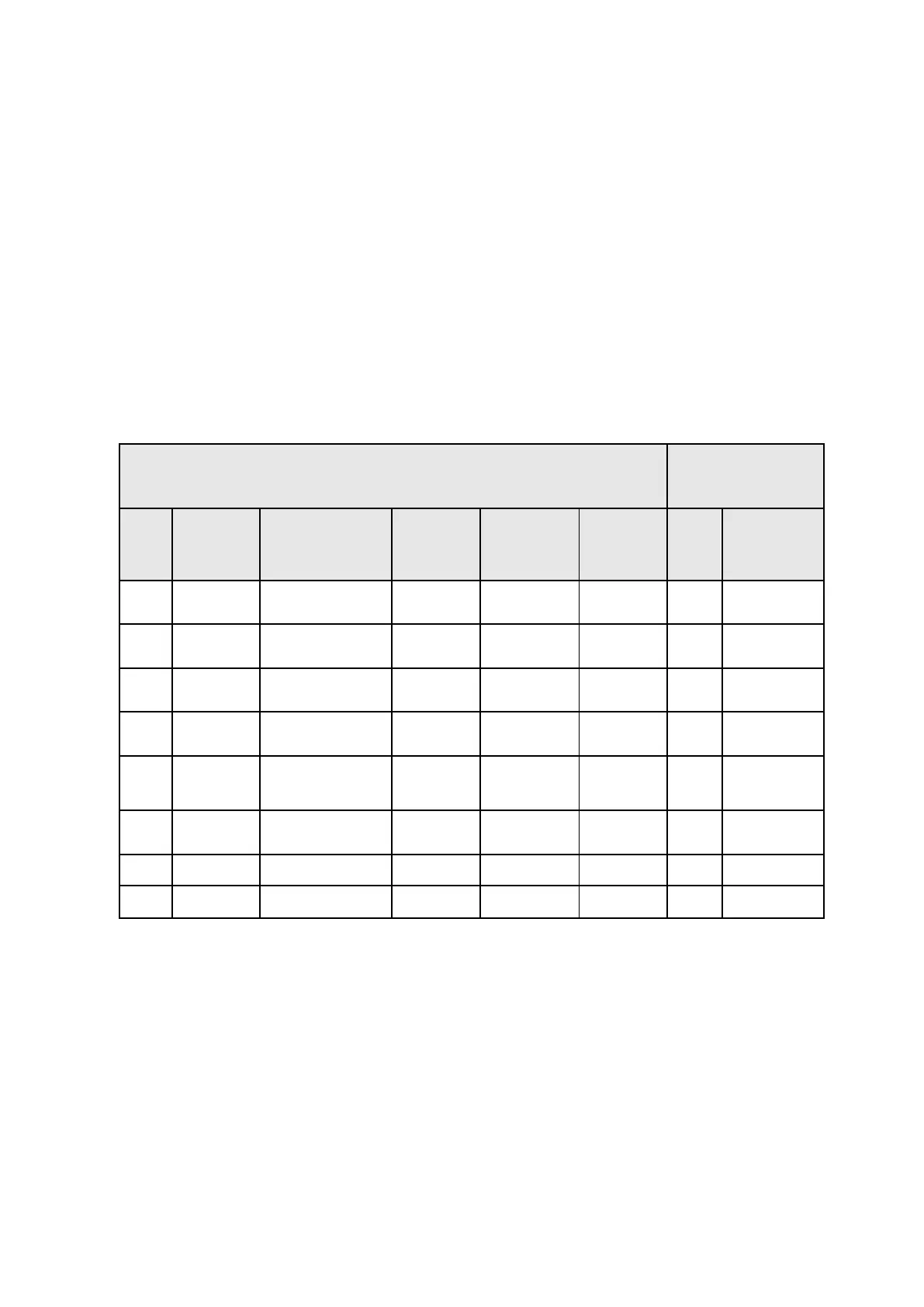
Table 3 enlists the essential safety function requirements set forth in EN 1525.
The sequence of the EN 1525 clauses in this table are modified for ease of explanation of the functional
blocks. This modification in sequence doesn’t impact the performance level calculations in any way.
Table 3: essential safety function requirements and achieved PL
Normative Requirements for AMR Mobile Robots
Achieved Performance
Levels PL
a
EN 1525
designated
architecture
(Cat EN 954-1)
Equivalent
required PL: PL
r
(EN ISO 13849-1)
Actual achieved
PL: PL
a
(EN ISO 13849-1)
LiDAR Personnel
Detection
Forward & Reverse
Speed Limits
Bypass of
Protective
Devices
Manual (Joystick)
Bypass
of Personnel Detection
5.2 Emergency Stop Circuit
Theory of operation
The emergency stop (E-STOP) is the most basic safety function of the LD Series robot and is a good starting
point to overview the safety systems.
The vehicle has six basic E-STOP sources. Sources 1, 2, and 3 are visible from outside the vehicle. Sources 4
and 5 are either internal function or user connected inputs. The Safety scanning lasers issues a protective
stop. This differs from an E-STOP only in that E-STOPs require that a human deliberately presses the ON
button on the AMR before motor power is restored, whereas motor power will be restored automatically 2 s
 Loading...
Loading...